
What does the Ringing/Girdling experiments demonstrate ?
A. Phloem is responsible for translocation of food.
B. Xylem is responsible for the ascent of sap.
C. Transpiration pull
D. Both (a) and (b)
Answer
606k+ views
Hint: This experiment is used to identify the tissue through which the food is transported.
Complete answer:
Phloem is the living tissue in vascular plants that transports the soluble organic compounds made during photosynthesis (photosynthates) to different parts of the plant where needed.This transportation process is called translocation. Phloem cells are usually located outside the xylem. They consist of companion cells and sieve tubes. Sieve tubes do not have ribosomes or nucleus, so they need companion cells to help them function as transport molecules. These companion cells provide them with proteins necessary for signalling and ATP in order to help in transportation. The basic function of xylem is to transport water from roots to stems and leaves.
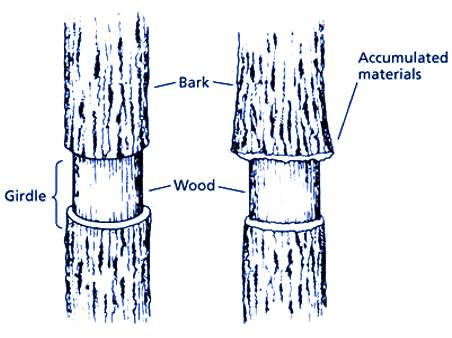
Ringing/Girdling experiments demonstrate that the phloem is responsible for translocation of food because the phloem is present outside the xylem. So, when a ring of bark is removed from a woody plant, the woody xylem part remains intact, which causes the water and the nutrients to reach the leaves. This process of removal of a ring of bark(phloem) from the wood is done by a technique known as girdling. After girdling, photosynthates get accumulated just above the girdle region and are not transported to other parts below the girdle. This experiment shows that phloem is responsible for food transport and it doesn't affect water transport done by xylem present in the inner side of the vascular plant.
Transpiration is the process through which water molecules move upwards from the roots and eventually escape from the stomata of the leaves in the form of vapor. When a water molecule escapes out into the atmosphere through the stomata, it pulls the water molecule below to take its place.
So, the correct answer is option (A)
Note:
1. Photosynthates is another word for food of plants.They are mainly sucrose produced in the mesophyll cells of photosynthesizing leaves.
2. Stomata are pores in the leaf that allow gas exchange where water vapor leaves the plant and carbon dioxide enters. Special cells called guard cells control each pore's opening or closing. When stomata are open, transpiration rates increase; when th
Complete answer:
Phloem is the living tissue in vascular plants that transports the soluble organic compounds made during photosynthesis (photosynthates) to different parts of the plant where needed.This transportation process is called translocation. Phloem cells are usually located outside the xylem. They consist of companion cells and sieve tubes. Sieve tubes do not have ribosomes or nucleus, so they need companion cells to help them function as transport molecules. These companion cells provide them with proteins necessary for signalling and ATP in order to help in transportation. The basic function of xylem is to transport water from roots to stems and leaves.
Ringing/Girdling experiments demonstrate that the phloem is responsible for translocation of food because the phloem is present outside the xylem. So, when a ring of bark is removed from a woody plant, the woody xylem part remains intact, which causes the water and the nutrients to reach the leaves. This process of removal of a ring of bark(phloem) from the wood is done by a technique known as girdling. After girdling, photosynthates get accumulated just above the girdle region and are not transported to other parts below the girdle. This experiment shows that phloem is responsible for food transport and it doesn't affect water transport done by xylem present in the inner side of the vascular plant.
Transpiration is the process through which water molecules move upwards from the roots and eventually escape from the stomata of the leaves in the form of vapor. When a water molecule escapes out into the atmosphere through the stomata, it pulls the water molecule below to take its place.

So, the correct answer is option (A)
Note:
1. Photosynthates is another word for food of plants.They are mainly sucrose produced in the mesophyll cells of photosynthesizing leaves.
2. Stomata are pores in the leaf that allow gas exchange where water vapor leaves the plant and carbon dioxide enters. Special cells called guard cells control each pore's opening or closing. When stomata are open, transpiration rates increase; when th
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




