
Where does the Ultrafiltration process take place?
Answer
582.9k+ views
Hint: In general, Ultrafiltration is a purification process which is pressure driven that separates particulate matter from soluble compounds using an ultrafine membrane.
Complete Answer:
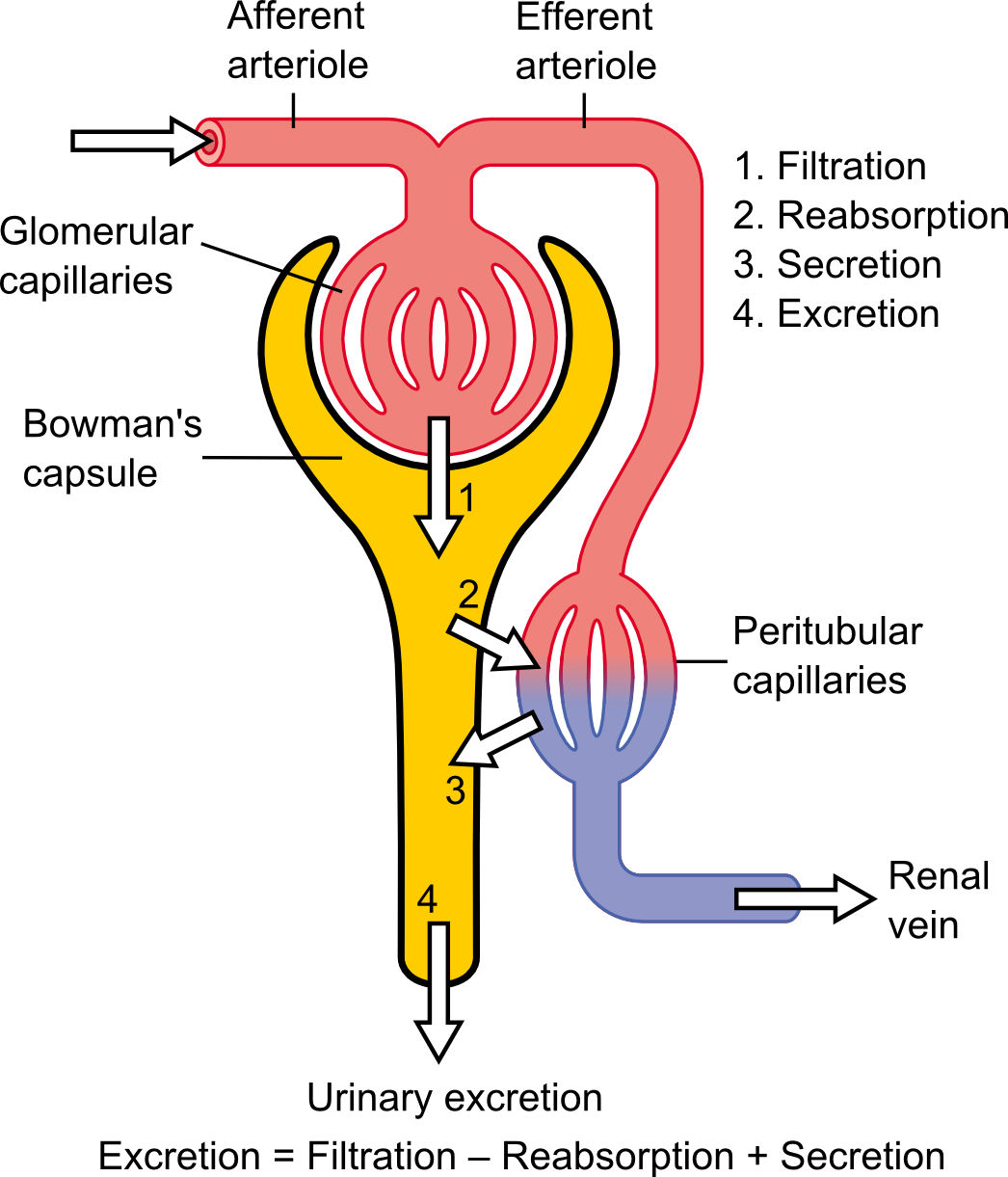
- Ultrafiltration occurs in the Bowman’s capsule of the kidney. Bowman’s capsule is also called the capsula glomeruli or glomerular capsule. It is a part of the nephron ( functional unit of kidneys ).
- Bowman’s capsule is a double walled cup like structure . It contains a dense capillaries network called glomerulus.
- Blood flows in these capillaries through the afferent arterioles and leaves through the efferent arterioles.
Ultrafiltration: It is a pressure driven process.
- In this process, the high hydrostatic pressure forces small molecules such as water, glucose , amino acids, NaCl and urea in a tubular fluid through the filter across the basement membrane of Bowman’s capsule. This process is called the Ultrafiltration.
- The resulting fluid will be virtually free of large proteins and blood cells and is called an ultrafiltrate of glomerular filtrate.
- Glomerular pressure is about 75mm of mercury.
- The components of filtrate such as sodium ions, potassium ions, etc. are then reabsorbed in the renal; tubule.
Selectivity of ions by glomerulus layers:
- The structure of layers of glomerulus are selectively permeable.
For example – small ions such as potassium ion, sodium ion pass freely while larger proteins such as hemoglobin and albumin cannot pass through it.
- Also negatively charged molecules will pass through in less number than that of positively charged ions.
Note: Ultrafiltration is a very specific process. It is a process by which metabolic wastes are separated from the blood and urine is formed.
Complete Answer:
- Ultrafiltration occurs in the Bowman’s capsule of the kidney. Bowman’s capsule is also called the capsula glomeruli or glomerular capsule. It is a part of the nephron ( functional unit of kidneys ).
- Bowman’s capsule is a double walled cup like structure . It contains a dense capillaries network called glomerulus.
- Blood flows in these capillaries through the afferent arterioles and leaves through the efferent arterioles.
Ultrafiltration: It is a pressure driven process.
- In this process, the high hydrostatic pressure forces small molecules such as water, glucose , amino acids, NaCl and urea in a tubular fluid through the filter across the basement membrane of Bowman’s capsule. This process is called the Ultrafiltration.
- The resulting fluid will be virtually free of large proteins and blood cells and is called an ultrafiltrate of glomerular filtrate.
- Glomerular pressure is about 75mm of mercury.
- The components of filtrate such as sodium ions, potassium ions, etc. are then reabsorbed in the renal; tubule.

Selectivity of ions by glomerulus layers:
- The structure of layers of glomerulus are selectively permeable.
For example – small ions such as potassium ion, sodium ion pass freely while larger proteins such as hemoglobin and albumin cannot pass through it.
- Also negatively charged molecules will pass through in less number than that of positively charged ions.
Note: Ultrafiltration is a very specific process. It is a process by which metabolic wastes are separated from the blood and urine is formed.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




