
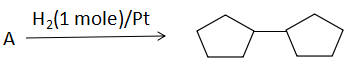
Double bond equivalent (degree of unsaturation) of (A) is:
A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D .4

Answer
586.8k+ views
Hint: Degree of unsaturation can be simply calculated as sum of no. of double bond and no. of ring present in the structure. In this question we have H2/Pt as a catalyst and this catalyst adds two hydrogen atoms to the alkene.
Complete step by step answer:
In this question we have been given a chemical equation in which hydrogenation (addition of hydrogen) occurs by using the catalyst $H_2/Pt$ and a product is formed, which has two cyclopentane rings in it and we have been asked what is the unknown reactant. As we know H2 with Pt act on alkyne to give alkene and alkane by adding two H atoms at the double and triple bond centre. One mole of \[{H_2}/Pt\] requires for hydrogenation of one bond. In this equation it is given that we have used only 1 mole of \[{H_2}/Pt\] . So, the reactant contained only one extra bond as compare to the product. Now we have asked the degree of unsaturation of the reactant.
So, as we know, the degree of unsaturation = no. of double bond + no. of ring present in the structure.
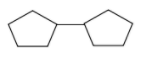
As we can see there are two rings in the product with no double bond. So, the reactant will have 2 ring and one double bond. So, as per our formula no. of ring + no. of double bond, the degree of unsaturation of the reactant will be \[2 + 1 = 3\] .
Therefore, the correct option is option C.
Note:
We can also solve this question by Double bond equivalent =\[C + 1 - \dfrac{{H}}{2} - \dfrac{{X}}{2} + \dfrac{N}{2}\]
Here X and N is 0 and \[C = 10\] and \[H = 2\;\] less than the product\[ = 18 - 2 = 16\]
Hence, \[DBE = 10 + 1 - \dfrac{{16}}{2} = 10 + 1 - 8 = 3\] S
Complete step by step answer:
In this question we have been given a chemical equation in which hydrogenation (addition of hydrogen) occurs by using the catalyst $H_2/Pt$ and a product is formed, which has two cyclopentane rings in it and we have been asked what is the unknown reactant. As we know H2 with Pt act on alkyne to give alkene and alkane by adding two H atoms at the double and triple bond centre. One mole of \[{H_2}/Pt\] requires for hydrogenation of one bond. In this equation it is given that we have used only 1 mole of \[{H_2}/Pt\] . So, the reactant contained only one extra bond as compare to the product. Now we have asked the degree of unsaturation of the reactant.
So, as we know, the degree of unsaturation = no. of double bond + no. of ring present in the structure.

As we can see there are two rings in the product with no double bond. So, the reactant will have 2 ring and one double bond. So, as per our formula no. of ring + no. of double bond, the degree of unsaturation of the reactant will be \[2 + 1 = 3\] .
Therefore, the correct option is option C.
Note:
We can also solve this question by Double bond equivalent =\[C + 1 - \dfrac{{H}}{2} - \dfrac{{X}}{2} + \dfrac{N}{2}\]
Here X and N is 0 and \[C = 10\] and \[H = 2\;\] less than the product\[ = 18 - 2 = 16\]
Hence, \[DBE = 10 + 1 - \dfrac{{16}}{2} = 10 + 1 - 8 = 3\] S
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




