
How many double bond equivalents (degrees of unsaturation) are in 2,2,3,3-tetramethyl-4-octyne?
Answer
490.2k+ views
Hint: The degree of unsaturation is a computation that calculates the total number of rings and $\pi $ bonds in an organic molecule's chemical formula. In organic chemistry, a formula is used to aid in the drawing of chemical structures. It provides no information about the individual components, such as the number of rings, double bonds (one $\pi $ bond each), or triple bonds (two $\pi $ bonds each).
Complete answer:
An alkyne is an unsaturated hydrocarbon with at least one carbon—carbon triple bond in organic chemistry. With only one triple bond and no additional functional groups, the simplest acyclic alkynes form a homologous series with the generic chemical formula ${C_n}{H_{2n - 2}}$.
The standard formula for computing the double bond equivalent (DBE) is:
\[{\text{DBE = C - }}\dfrac{{\text{H}}}{{\text{2}}}{\text{ + }}\dfrac{{\text{N}}}{{\text{2}}}{\text{ + 1}}\]
where C denotes the number of carbon atoms, H denotes the amount of hydrogen and halogen atoms, and N denotes the number of nitrogen atoms in the molecule if any exist.
The molecular formula of 2,2,3,3-tetramethyl-4-octyne can be given as \[{C_{12}}{H_{22}}\]
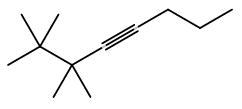
There dbe equals
\[{\text{DBE = 12 - }}\dfrac{{22}}{{\text{2}}}{\text{ + }}\dfrac{0}{{\text{2}}}{\text{ + 1 = 12 - 11 + 1 = 13 - 11 = 2 }}\]
NMR, mass spectrometry, and IR spectroscopy, as well as qualitative examination, are used to verify the final structure. It works by comparing the current molecular formula to what may be a potential formula if the structure was saturated (no rings and just bonds) and all atoms had their normal valence.
Note:
Because joining two elements to form a ring or adding one extra bond in a structure reduces the need for two H's, the DBE (or IHD) for hydrocarbons tells us the number of rings and/or extra bonds in a non-saturated structure, which equals the number of hydrogen pairs required to make the structure saturated. For non-hydrocarbons, the elements in a pair can be any elements from the periodic table's lithium and fluorine families, although not necessarily all H's.
Complete answer:
An alkyne is an unsaturated hydrocarbon with at least one carbon—carbon triple bond in organic chemistry. With only one triple bond and no additional functional groups, the simplest acyclic alkynes form a homologous series with the generic chemical formula ${C_n}{H_{2n - 2}}$.
The standard formula for computing the double bond equivalent (DBE) is:
\[{\text{DBE = C - }}\dfrac{{\text{H}}}{{\text{2}}}{\text{ + }}\dfrac{{\text{N}}}{{\text{2}}}{\text{ + 1}}\]
where C denotes the number of carbon atoms, H denotes the amount of hydrogen and halogen atoms, and N denotes the number of nitrogen atoms in the molecule if any exist.
The molecular formula of 2,2,3,3-tetramethyl-4-octyne can be given as \[{C_{12}}{H_{22}}\]

There dbe equals
\[{\text{DBE = 12 - }}\dfrac{{22}}{{\text{2}}}{\text{ + }}\dfrac{0}{{\text{2}}}{\text{ + 1 = 12 - 11 + 1 = 13 - 11 = 2 }}\]
NMR, mass spectrometry, and IR spectroscopy, as well as qualitative examination, are used to verify the final structure. It works by comparing the current molecular formula to what may be a potential formula if the structure was saturated (no rings and just bonds) and all atoms had their normal valence.
Note:
Because joining two elements to form a ring or adding one extra bond in a structure reduces the need for two H's, the DBE (or IHD) for hydrocarbons tells us the number of rings and/or extra bonds in a non-saturated structure, which equals the number of hydrogen pairs required to make the structure saturated. For non-hydrocarbons, the elements in a pair can be any elements from the periodic table's lithium and fluorine families, although not necessarily all H's.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




