
What is double respiration? Which group of animals does exhibit the phenomenon of double respiration?
Answer
510k+ views
Hint: Double respiration is similar to the process of respiration in mammals with some differences that is air passes through the lungs twice to absorb the oxygen in double the amount.
Complete answer:
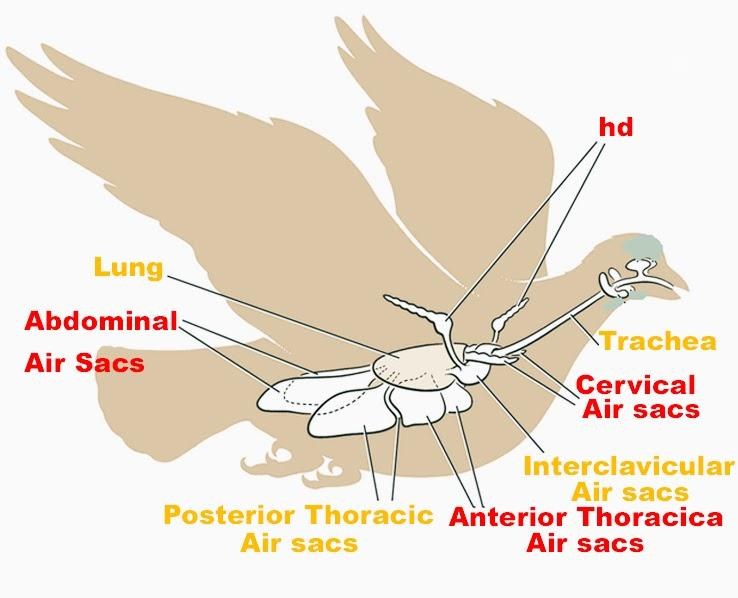
The process by which inhaled oxygen is employed twice for the method of respiration is understood as double respiration. This phenomenon of double respiration exhibits in birds.
Respiratory Cycle of a Bird:
During the first inspiration, through the nostrils of a bird the air travels into the nasal cavity. From the nasal cavity, the air passes via the larynx into the trachea. Air moves through the trachea to the syrinx, then to the caudal (posterior) air sacs. Through these caudal air sacs, a small amount of air passes to the lungs.
During the method of first expiration, the air is moved from the posterior air sacs into the lungs. The bronchi now divides into capillaries. Through these air capillaries, these blood capillaries flow and that is the place where the oxygen and carbon dioxide are exchanged.
During the method of second inspiration the air moves to the cranial air sacs. At the second expiration, the air moves out of the cranial air sacs, into the trachea via the syrinx, then through the larynx, the air finally reaches the nasal cavity and then out of the nostrils.
Note:
The intercostal muscles, abdominal muscles, and sternum are the muscles involved in this process of double respiration. In birds air sacs are unidirectional and it allows the flow of oxygen only during either inspiration or expiration while in other animals like mammals both take place simultaneously.
Complete answer:
The process by which inhaled oxygen is employed twice for the method of respiration is understood as double respiration. This phenomenon of double respiration exhibits in birds.
Respiratory Cycle of a Bird:
During the first inspiration, through the nostrils of a bird the air travels into the nasal cavity. From the nasal cavity, the air passes via the larynx into the trachea. Air moves through the trachea to the syrinx, then to the caudal (posterior) air sacs. Through these caudal air sacs, a small amount of air passes to the lungs.
During the method of first expiration, the air is moved from the posterior air sacs into the lungs. The bronchi now divides into capillaries. Through these air capillaries, these blood capillaries flow and that is the place where the oxygen and carbon dioxide are exchanged.
During the method of second inspiration the air moves to the cranial air sacs. At the second expiration, the air moves out of the cranial air sacs, into the trachea via the syrinx, then through the larynx, the air finally reaches the nasal cavity and then out of the nostrils.

Note:
The intercostal muscles, abdominal muscles, and sternum are the muscles involved in this process of double respiration. In birds air sacs are unidirectional and it allows the flow of oxygen only during either inspiration or expiration while in other animals like mammals both take place simultaneously.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Accountancy: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




