
Draw a flowchart to show the breakdown of glucose by various pathways.
Answer
528.2k+ views
Hint: Glucose can be broken down by various pathways depending on the availability and unavailability of oxygen.
Complete Answer:
Hear the term glucose with reference to cellular metabolism and what strikes our mind is energy! Glucose is the most preferred respiratory substrate and therefore, there are many pathways that a cell can use to make sure glucose is broken down in order to obtain the ATP (adenosine triphosphate).
Generally, we use the term respiration in order to explain the metabolic process through which cells use a food source and perform its breakdown to extract out the energy.
Now these pathways are primarily defined by the absence and presence of oxygen. So we say that a cell performs aerobic respiration when oxygen is available, because then oxygen acts as the electron acceptor at the end of the electron transport chain. When there is an unavailability of oxygen, then anaerobic respiration occurs.
So, whether a cell performs anaerobic respiration or aerobic respiration, there is a common pathway that has to happen in order to initiate the breakdown of glucose. It is called the glycolysis and it occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell. The end product of the glycolysis is pyruvic acid.
The glycolysis pathway is shown below:
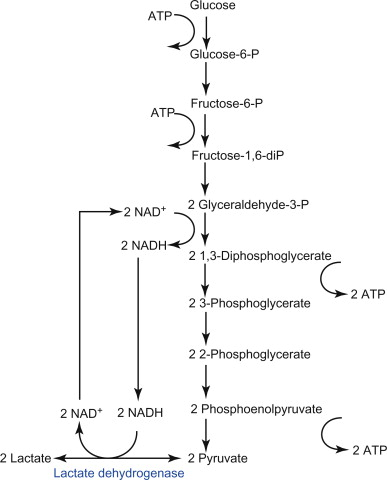
Now this pyruvate so obtained can follow any one of the three pathways:
a) Krebs cycle and electron transport cell when oxygen is available
b) Fermentation in the absence of oxygen
c) Lactic acid pathway in the lack or inadequate supply of oxygen
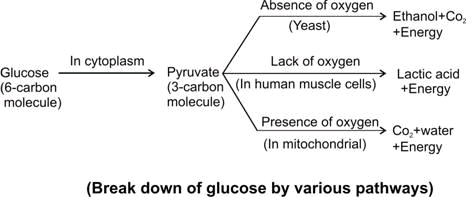
Note: Fermentation is commercially used to prepare products like bread and alcoholic beverages due to its end products. The carbon dioxide gives rise in the bread dough and ethanol is used in alcoholic beverages.
Complete Answer:
Hear the term glucose with reference to cellular metabolism and what strikes our mind is energy! Glucose is the most preferred respiratory substrate and therefore, there are many pathways that a cell can use to make sure glucose is broken down in order to obtain the ATP (adenosine triphosphate).
Generally, we use the term respiration in order to explain the metabolic process through which cells use a food source and perform its breakdown to extract out the energy.
Now these pathways are primarily defined by the absence and presence of oxygen. So we say that a cell performs aerobic respiration when oxygen is available, because then oxygen acts as the electron acceptor at the end of the electron transport chain. When there is an unavailability of oxygen, then anaerobic respiration occurs.
So, whether a cell performs anaerobic respiration or aerobic respiration, there is a common pathway that has to happen in order to initiate the breakdown of glucose. It is called the glycolysis and it occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell. The end product of the glycolysis is pyruvic acid.
The glycolysis pathway is shown below:

Now this pyruvate so obtained can follow any one of the three pathways:
a) Krebs cycle and electron transport cell when oxygen is available
b) Fermentation in the absence of oxygen
c) Lactic acid pathway in the lack or inadequate supply of oxygen

Note: Fermentation is commercially used to prepare products like bread and alcoholic beverages due to its end products. The carbon dioxide gives rise in the bread dough and ethanol is used in alcoholic beverages.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




