
Draw a labeled diagram of a replicating fork.
Answer
581.7k+ views
Hint: Replicating fork is the structure of the DNA double helix after the unzipping by ligase enzyme. This leads to two strands called leading and lagging strands.
Complete answer:
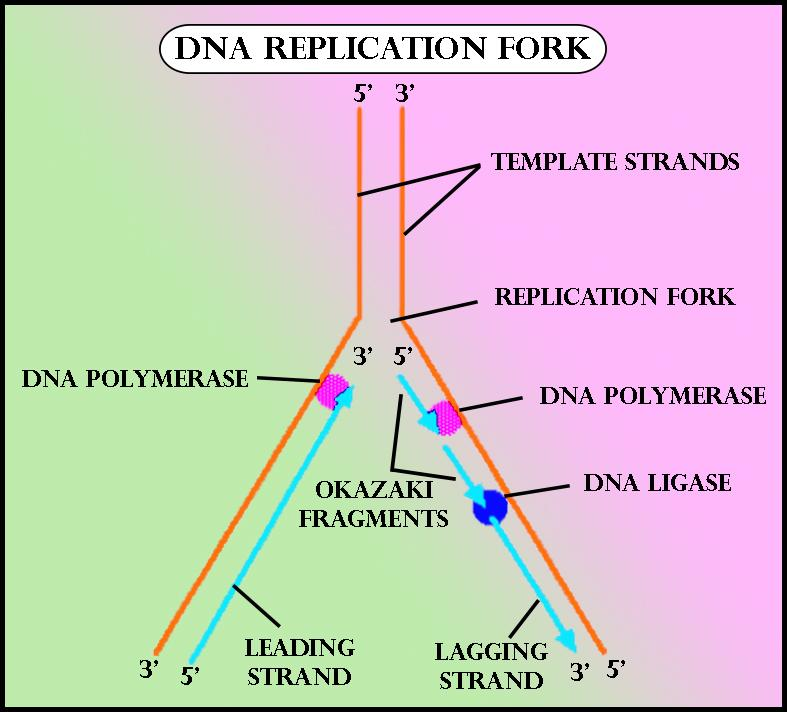
DNA replication is the process of duplication of DNA during cell division. DNA is a self-replicating structure and the semi-conservative process of DNA replication occurs in the sequence of initiation, elongation, and termination. The "unzipping" of the DNA double helix occurs by helicase enzyme which breaks the hydrogen bonds holding the complementary bases.
The structure after the unzipping resembles a Y shape and is called a replicating fork. One of the strands orients in the 3' to 5' direction and called as leading strand whereas the other, called the lagging strand, is oriented in 5' to 3' direction.
Additional Information: -Leading strand: Primer, a piece of RNA, comes and binds to the end of the leading strand. This acts as the starting point for DNA synthesis. DNA polymerase adds new complementary DNA in the 5' to 3' direction. This type of replication is continuous.
-Lagging strand: At various points along the lagging strand, the primase enzyme makes numerous RNA primers. Ozaki fragments, which are chunks of DNA, are added to the lagging strand in the 5' to 3' direction. This is discontinuous replication as the fragments need to be joined up later.
After all, bases are matched up, the enzyme exonuclease strips away the primers. An enzyme called DNA ligase seals the sequence of DNA and makes it into two continuous double strands.
Note: The replicating fork is asymmetrical because of the semi-conservative nature. By semi-conservative, we mean that after the replication of the double helix of DNA, new and old strands are formed. In replicating a fork, one half is a part of the original DNA whereas the other is brand new.
Complete answer:

DNA replication is the process of duplication of DNA during cell division. DNA is a self-replicating structure and the semi-conservative process of DNA replication occurs in the sequence of initiation, elongation, and termination. The "unzipping" of the DNA double helix occurs by helicase enzyme which breaks the hydrogen bonds holding the complementary bases.
The structure after the unzipping resembles a Y shape and is called a replicating fork. One of the strands orients in the 3' to 5' direction and called as leading strand whereas the other, called the lagging strand, is oriented in 5' to 3' direction.
Additional Information: -Leading strand: Primer, a piece of RNA, comes and binds to the end of the leading strand. This acts as the starting point for DNA synthesis. DNA polymerase adds new complementary DNA in the 5' to 3' direction. This type of replication is continuous.
-Lagging strand: At various points along the lagging strand, the primase enzyme makes numerous RNA primers. Ozaki fragments, which are chunks of DNA, are added to the lagging strand in the 5' to 3' direction. This is discontinuous replication as the fragments need to be joined up later.
After all, bases are matched up, the enzyme exonuclease strips away the primers. An enzyme called DNA ligase seals the sequence of DNA and makes it into two continuous double strands.
Note: The replicating fork is asymmetrical because of the semi-conservative nature. By semi-conservative, we mean that after the replication of the double helix of DNA, new and old strands are formed. In replicating a fork, one half is a part of the original DNA whereas the other is brand new.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




