
Draw a labeled diagram of an anatropous ovule and label six parts other than the gametophyte.
Answer
602.4k+ views
Hint: In this condition, the micropyle is close to the funicular attachment. This is the stage of development where the egg is ready for fertilization by the sperm from a pollen grain.
In anatropous ovule, the plant ovule is oriented in an inverted condition so that the micropyle is bent down to the funiculus to which the ovule is attached. The chalazal end is located towards the top position. The ovule is a female reproductive part of the plant that eventually develops into the seed after fertilization.
Complete answer:
Structure of ovule:
Funicle: It is a small structure that connects the ovule to the placenta.
Hilum: It is the point of attachment where the body of the ovule fuses with the funicle.
Nucellus: This is the body of ovule that consists of a mass of parenchymatous cells known as nucellus. The nucellus can be massive or thin. The cells of nucellus have abundant food material.
Integuments: Nucellus is enclosed by the one or two or multicellular protective envelopes called integuments. In higher dicots, there is only one integument in ovule while in monocots or primitive dicots, two integuments are found in the ovule.
Chalaza: It is the place of the origin of integuments that typically lies at the opposite end of the micropyle. It represents the basal part of the ovule.
Micropyle: Micropyle is a pore that presents in the integuments at the end. It is located opposite to the chalazal end.
Note:
In amphitropous condition, the anatropous arrangement of the ovule is tilted 90 degrees.
In ovule, the megaspores persist inside the ovule and are divided by mitosis to produce the haploid female gametophyte.
The nucellus is structurally and functionally equivalent to the megasporangium.
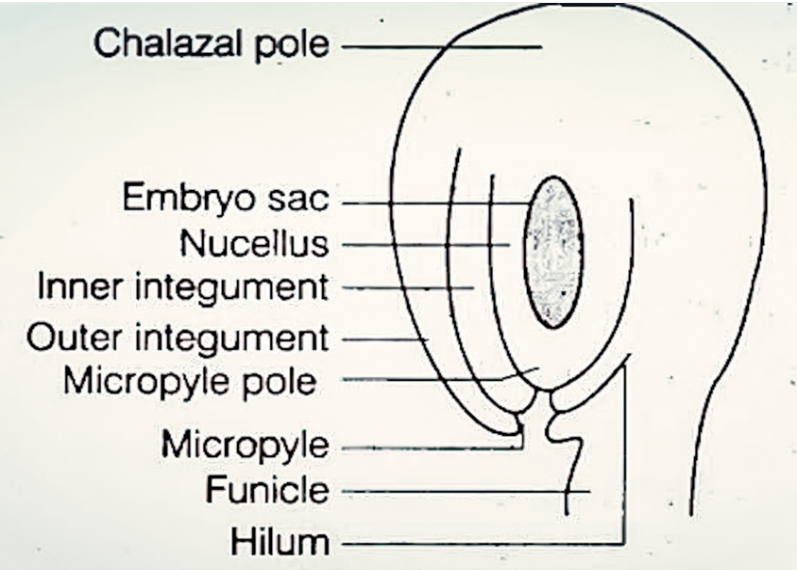
Figure: Structure of a typical anatropous ovule
In anatropous ovule, the plant ovule is oriented in an inverted condition so that the micropyle is bent down to the funiculus to which the ovule is attached. The chalazal end is located towards the top position. The ovule is a female reproductive part of the plant that eventually develops into the seed after fertilization.
Complete answer:
Structure of ovule:
Funicle: It is a small structure that connects the ovule to the placenta.
Hilum: It is the point of attachment where the body of the ovule fuses with the funicle.
Nucellus: This is the body of ovule that consists of a mass of parenchymatous cells known as nucellus. The nucellus can be massive or thin. The cells of nucellus have abundant food material.
Integuments: Nucellus is enclosed by the one or two or multicellular protective envelopes called integuments. In higher dicots, there is only one integument in ovule while in monocots or primitive dicots, two integuments are found in the ovule.
Chalaza: It is the place of the origin of integuments that typically lies at the opposite end of the micropyle. It represents the basal part of the ovule.
Micropyle: Micropyle is a pore that presents in the integuments at the end. It is located opposite to the chalazal end.
Note:
In amphitropous condition, the anatropous arrangement of the ovule is tilted 90 degrees.
In ovule, the megaspores persist inside the ovule and are divided by mitosis to produce the haploid female gametophyte.
The nucellus is structurally and functionally equivalent to the megasporangium.

Figure: Structure of a typical anatropous ovule
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




