
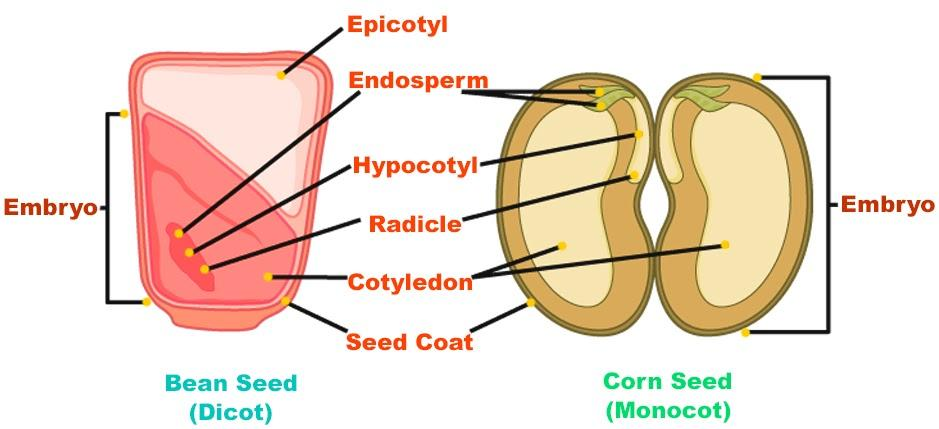
Draw a labeled diagram of the embryo of a dicot seed. Also, write the role of cotyledons.
Answer
510.6k+ views
Hint: They are the major food storing reservoir of seed. Plants are classified into dicots and monocots according to the number of cotyledons present in the embryo. The embryonic axis consists of three parts: the plumule, the radicle, and the hypocotyl. The embryonic axis terminates in a radicle and that is the region from which the root will develop.
Complete answer:
Plant embryos in seeds have structures called cotyledons. A cotyledon is the central portion of an embryo to which the epicotyls, the immature shoots, and the radicals that are the immature roots, are attached. If the embryo has only one cotyledon, it is a monocot plant or monocotyledons and if it has two cotyledons it is a dicot plant or dicotyledons.
Role of cotyledons:
In plants, the cotyledons are photosynthetic and function as leaves. The cotyledons are the first part of the plant that emerges from the soil.
The cotyledons last only some days after growing from the soil and give way for other plant growth, while some cotyledons can last for years.
It also helps the new plant when it begins to grow, because they contain the stored food reserves from the seed, to give the plant its initial burst of energy to grow.
When the seed germinates or begins to grow, then the cotyledon may become the first leaves of the seedling.
It contains protein, fats, and starches which provide energy for the developing seedling.
Note:
The embryo is an undeveloped plant inside a seed from which a new plant develops. The seed is along with the ovule and is protected by a seed coat. It is formed from the integuments of the ovule sac. In dicots, the seed coat contains an outer coat which is known as the testa and an inner coat which is known as the tegmen.
Complete answer:
Plant embryos in seeds have structures called cotyledons. A cotyledon is the central portion of an embryo to which the epicotyls, the immature shoots, and the radicals that are the immature roots, are attached. If the embryo has only one cotyledon, it is a monocot plant or monocotyledons and if it has two cotyledons it is a dicot plant or dicotyledons.
Role of cotyledons:
In plants, the cotyledons are photosynthetic and function as leaves. The cotyledons are the first part of the plant that emerges from the soil.
The cotyledons last only some days after growing from the soil and give way for other plant growth, while some cotyledons can last for years.
It also helps the new plant when it begins to grow, because they contain the stored food reserves from the seed, to give the plant its initial burst of energy to grow.
When the seed germinates or begins to grow, then the cotyledon may become the first leaves of the seedling.
It contains protein, fats, and starches which provide energy for the developing seedling.

Note:
The embryo is an undeveloped plant inside a seed from which a new plant develops. The seed is along with the ovule and is protected by a seed coat. It is formed from the integuments of the ovule sac. In dicots, the seed coat contains an outer coat which is known as the testa and an inner coat which is known as the tegmen.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




