
Draw a labelled diagram of a thermos flask. Explain how the transfer of heat by conduction, convection and radiation is reduced to minimum in it.
Answer
524.7k+ views
Hint: In order to solve this question first we will draw a labelled diagram of thermos flask and know what the terms conduction, convection and radiation means. Then we will know what factors of thermos flask prevent transfer of heat by conduction, convection or radiation.
Complete answer:
The labelled diagram of thermos flask is as shown below:
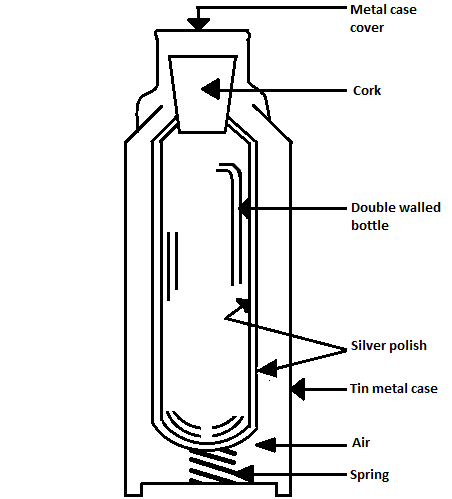
Now let us see the definitions of conduction, convection and radiation.
The process by which heat is directly transferred through the medium of a substance when there’s a difference of temperature between neighboring regions, without the movement of the substance is known as conduction. The movement caused within a fluid by the tendency of hotter and less dense material to rise, and colder, denser material to sink under the influence of gravity, which consequently results in transfer of heat is known as convection. Heat transfer in metal is taken place by conduction method whereas heat transfer in liquid is taken place by convection method. Conduction, convection and radiation all three methods require medium to transfer (in vacuum transfer of heat is not possible). Radiation is the energy that comes from a source (generally Sun) and travels through space at the speed of light.
Now, we shall see the factors which prevent the transfer of heat by conduction, convection or radiation in a thermos flask.
1) The loss of heat by conduction does not take place in between two walls, rubber glass, cork and air as there is vacuum preventing it.
Cork in the neck of the flask and the cup over it prevent loss of heat by convection method.
2) As there is vacuum between the walls, heat cannot be lost or gained by conduction or convection.
3) As the outer surface of the inner wall and inner surface of the outer wall are silvered, heat loss will be minimized by radiation. The inner wall of the flask is a poor radiator and the outer wall is a good reflector of radiation.
Note:
One must know the difference between conduction, convection and radiation. Conduction is the transfer of heat in metals, convection is transfer of heat in liquid and radiation is the energy emitted by the Sun.
Complete answer:
The labelled diagram of thermos flask is as shown below:

Now let us see the definitions of conduction, convection and radiation.
The process by which heat is directly transferred through the medium of a substance when there’s a difference of temperature between neighboring regions, without the movement of the substance is known as conduction. The movement caused within a fluid by the tendency of hotter and less dense material to rise, and colder, denser material to sink under the influence of gravity, which consequently results in transfer of heat is known as convection. Heat transfer in metal is taken place by conduction method whereas heat transfer in liquid is taken place by convection method. Conduction, convection and radiation all three methods require medium to transfer (in vacuum transfer of heat is not possible). Radiation is the energy that comes from a source (generally Sun) and travels through space at the speed of light.
Now, we shall see the factors which prevent the transfer of heat by conduction, convection or radiation in a thermos flask.
1) The loss of heat by conduction does not take place in between two walls, rubber glass, cork and air as there is vacuum preventing it.
Cork in the neck of the flask and the cup over it prevent loss of heat by convection method.
2) As there is vacuum between the walls, heat cannot be lost or gained by conduction or convection.
3) As the outer surface of the inner wall and inner surface of the outer wall are silvered, heat loss will be minimized by radiation. The inner wall of the flask is a poor radiator and the outer wall is a good reflector of radiation.
Note:
One must know the difference between conduction, convection and radiation. Conduction is the transfer of heat in metals, convection is transfer of heat in liquid and radiation is the energy emitted by the Sun.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




