
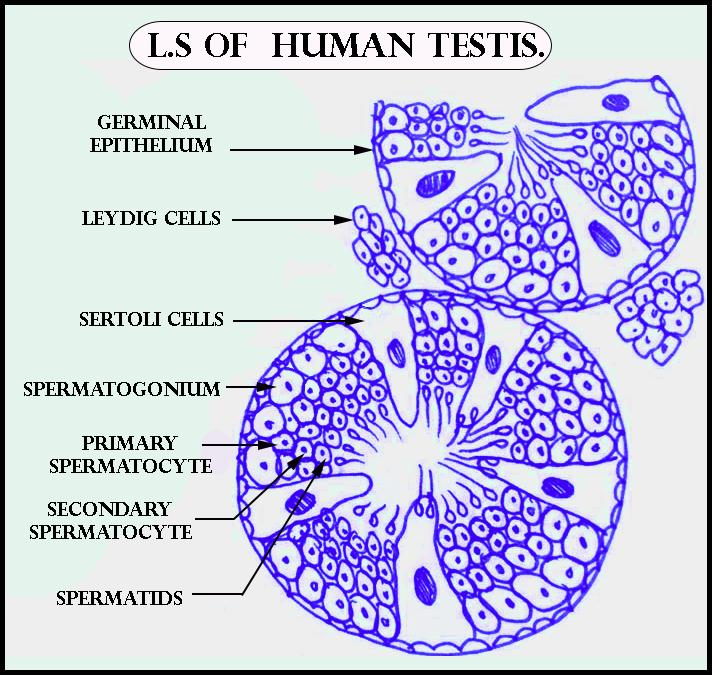
Draw a labelled diagram of L.S of Human Testis.
Answer
591.9k+ views
Hint: There are male and female reproductive organs. The male reproductive organ is the testis and that for females is the ovaries. Male gonads produce sperms while that for females is ovum or eggs.
Complete answer:
Testicle or testis (plural testes) is the male reproductive gland or gonad in altogether animals, including humans. It's homologous to the feminine ovary. The functions of the testes are to supply both sperm and androgens, primarily testosterone.
Additional Information: -Males have two testicles of comparable size contained within the scrotum, which is an extension of the wall. Scrotal asymmetry isn't unusual: one testicle extends farther down into the scrotum than the opposite than to differences within the anatomy of the vasculature.
-The testes are covered by a tough membrane shell called the tunica albuginea. In the testes, there are very fine coiled tubes called seminiferous tubules. The tubules are lined by germ cells that develop from puberty through adulthood into sperm cells (also referred to as spermatozoa or male gametes). The developing sperm moves through the seminiferous tubules then to the rete testis, which is located within the mediastinum testis, to the efferent ducts, then it moves towards the epididymis where newly created sperm cells mature. The sperm enter the vas deferens and are eventually expelled through the urethra and out of the urethral orifice through muscular contractions.
-Spermatogenesis is enhanced at temperatures slightly but which is almost near to our temperature. The spermatogenesis is a process that is efficient at lower and accurate at the temperature than 33 °C. Because the testes are located outside the body, the graceful tissue of the scrotum can move them closer or further far away from the body. The temperature of the testes is usually maintained at 35 degrees Celsius (95 degrees Fahrenheit), i.e. two degrees below the temperature of our body which is 37 degrees Celsius (98.6 degrees Fahrenheit). Higher temperatures affect spermatogenesis. There are a variety of mechanisms to maintain the testes at the optimum temperature.
Note: Don't get confused by this 2 terms:
Spermatogenesis: the process by which haploid(n) spermatozoa develops from germ cells in the seminiferous tubules of the male reproductive organ.
Spermiogenesis: Spermiogenesis is the last stage of spermatogenesis, in which the maturation of spermatids into mature spermatozoa occurs.
Complete answer:
Testicle or testis (plural testes) is the male reproductive gland or gonad in altogether animals, including humans. It's homologous to the feminine ovary. The functions of the testes are to supply both sperm and androgens, primarily testosterone.

Additional Information: -Males have two testicles of comparable size contained within the scrotum, which is an extension of the wall. Scrotal asymmetry isn't unusual: one testicle extends farther down into the scrotum than the opposite than to differences within the anatomy of the vasculature.
-The testes are covered by a tough membrane shell called the tunica albuginea. In the testes, there are very fine coiled tubes called seminiferous tubules. The tubules are lined by germ cells that develop from puberty through adulthood into sperm cells (also referred to as spermatozoa or male gametes). The developing sperm moves through the seminiferous tubules then to the rete testis, which is located within the mediastinum testis, to the efferent ducts, then it moves towards the epididymis where newly created sperm cells mature. The sperm enter the vas deferens and are eventually expelled through the urethra and out of the urethral orifice through muscular contractions.
-Spermatogenesis is enhanced at temperatures slightly but which is almost near to our temperature. The spermatogenesis is a process that is efficient at lower and accurate at the temperature than 33 °C. Because the testes are located outside the body, the graceful tissue of the scrotum can move them closer or further far away from the body. The temperature of the testes is usually maintained at 35 degrees Celsius (95 degrees Fahrenheit), i.e. two degrees below the temperature of our body which is 37 degrees Celsius (98.6 degrees Fahrenheit). Higher temperatures affect spermatogenesis. There are a variety of mechanisms to maintain the testes at the optimum temperature.
Note: Don't get confused by this 2 terms:
Spermatogenesis: the process by which haploid(n) spermatozoa develops from germ cells in the seminiferous tubules of the male reproductive organ.
Spermiogenesis: Spermiogenesis is the last stage of spermatogenesis, in which the maturation of spermatids into mature spermatozoa occurs.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




