
Draw a labelled diagram of mature dicot embryos.
Answer
582.6k+ views
Hint: Plant embryos have structures called cotyledons in plants. The central portion of the seed embryo to which the epicotyl in-the immature shoot and the radicle-the immature roots are attached is cotyledon.
Complete Answer:
- Plants are categorised according to the number of cotyledons in the embryo present. It is a monocotyledon plant if the embryo has one cotyledon (monocotyledon), and if there are two cotyledons (dicotyledon), it is a dicotyledon plant.
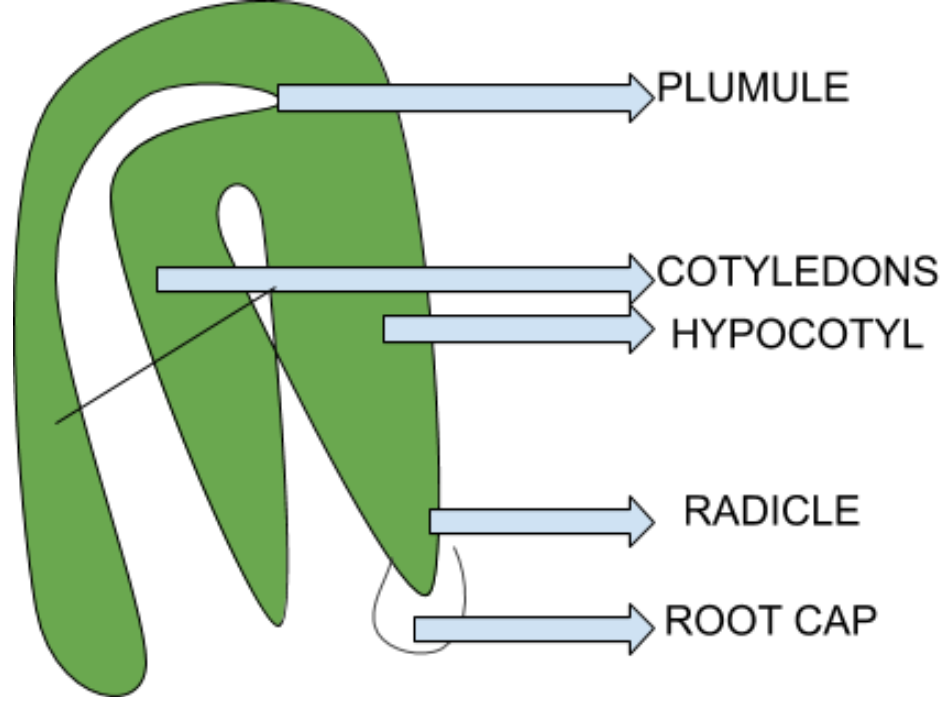
- Sections of the standard embryo dicot include: Plumule, cotyledon, hypocotyl, radical and root cap.
- A standard cotyledon embryo, consisting of an embryonic axis and two cotyledons.
- The portion of the embryonic axis above the cotyledon stage is epicotyl, which ends with the tip of the plumule or stem.
- The cylindrical part below the cotyledon stage is hypocotyl, which ends at its lower end in the radical or root tip. With a root cap, the tip of the root is sealed.
- Subdivision of Seed: Seeds can be subdivided into endosperm and non-endosperm, depending on the form and position of storage materials.
- Endospermic: Endospermic seeds are those which in the mature seed have an endosperm. It is fleshy, oily, surrounds the embryo, and acts as the sole organ of food storage. A thin and papery cotyledon is present within the seed cover. The plants of Monocot have endospermic seeds.
- Non-endospermic seeds: Non-endospermic seeds do not have an endosperm in the mature crop. Cotyledons are thick and fleshy, and are the only food storage organs. Dicot plants have non-endospermic seeds.
Note: Plant embryogenesis is a mechanism that occurs to produce a fully developed plant embryo following the fertilization of an ovule. This is a relevant step in the plant life cycle, followed by dormancy and germination. In order to become a mature embryo, the zygote formed after fertilization must undergo various cell divisions and differentiations.
Complete Answer:
- Plants are categorised according to the number of cotyledons in the embryo present. It is a monocotyledon plant if the embryo has one cotyledon (monocotyledon), and if there are two cotyledons (dicotyledon), it is a dicotyledon plant.
- Sections of the standard embryo dicot include: Plumule, cotyledon, hypocotyl, radical and root cap.
- A standard cotyledon embryo, consisting of an embryonic axis and two cotyledons.
- The portion of the embryonic axis above the cotyledon stage is epicotyl, which ends with the tip of the plumule or stem.
- The cylindrical part below the cotyledon stage is hypocotyl, which ends at its lower end in the radical or root tip. With a root cap, the tip of the root is sealed.
- Subdivision of Seed: Seeds can be subdivided into endosperm and non-endosperm, depending on the form and position of storage materials.
- Endospermic: Endospermic seeds are those which in the mature seed have an endosperm. It is fleshy, oily, surrounds the embryo, and acts as the sole organ of food storage. A thin and papery cotyledon is present within the seed cover. The plants of Monocot have endospermic seeds.
- Non-endospermic seeds: Non-endospermic seeds do not have an endosperm in the mature crop. Cotyledons are thick and fleshy, and are the only food storage organs. Dicot plants have non-endospermic seeds.

Note: Plant embryogenesis is a mechanism that occurs to produce a fully developed plant embryo following the fertilization of an ovule. This is a relevant step in the plant life cycle, followed by dormancy and germination. In order to become a mature embryo, the zygote formed after fertilization must undergo various cell divisions and differentiations.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




