
Draw a labelled diagram of the human digestive system and explain it.
Answer
524.2k+ views
Hint: The energy required for all the processes and activities that happen in our bodies comes from the foods we ingest. The digestive system allows us to utilize food from such diverse sources as meat from an animal and therefore the roots of a plant, and utilize them as an energy source.
Complete answer:
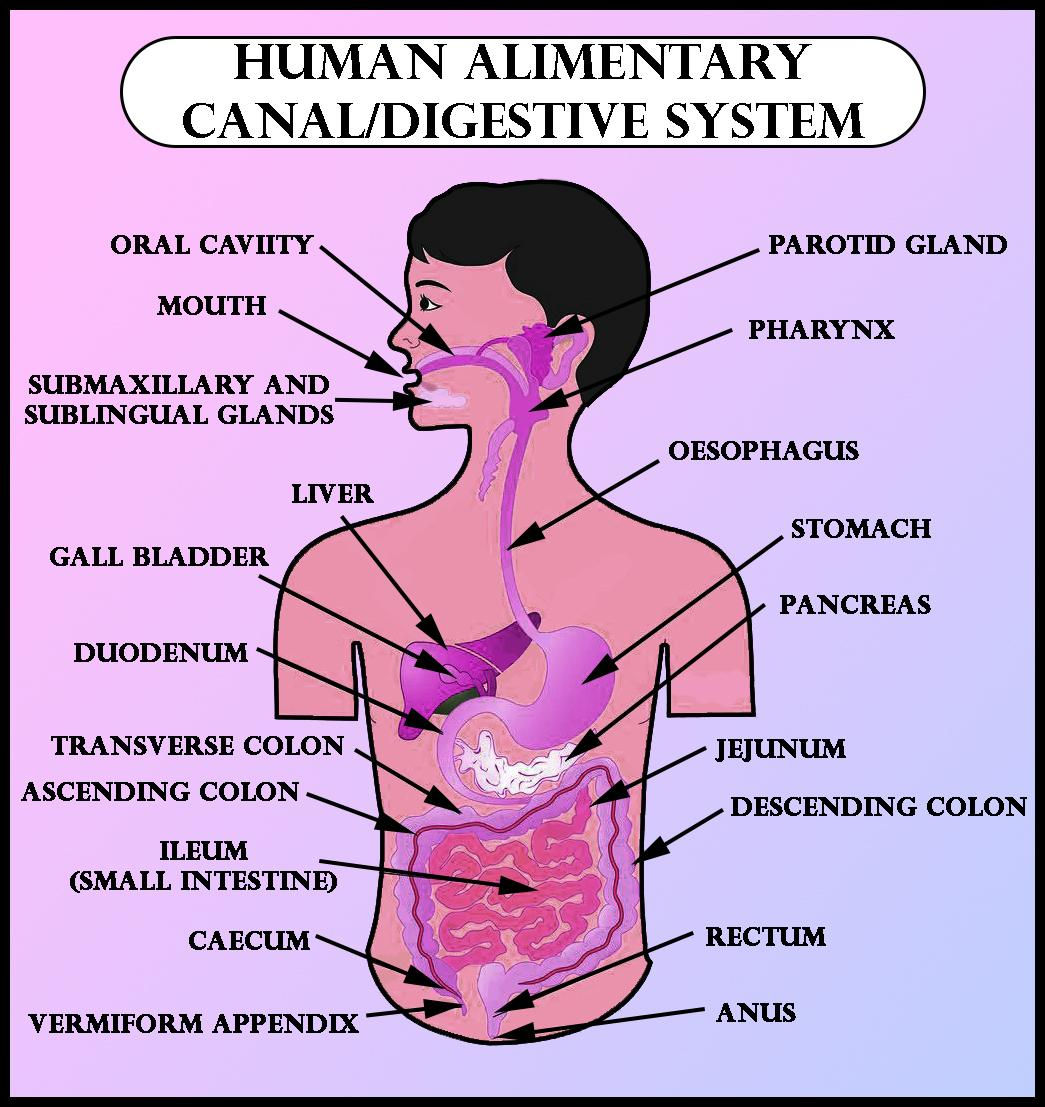
Anatomically, the digestive system is formed from the alimentary canal which includes the mouth, stomach, esophagus, small intestine, and large intestine that contains the rectum and anus alongside accessory organs like the liver, pancreas, and gallbladder.
Explanation of the human digestive system are-
(i) Food is crushed and cut in the mouth with the help of teeth and is mixed with saliva that is secreted by three salivary glands (one below the tongue and two at the side of the jaw) to make it wet and slippery, this process is known as mastication.
(ii) Saliva contains amylase that breaks down complex carbohydrates and the tongue helps in pushing the food to the next part of the alimentary canal.
(iii) The soft food then passes through the oesophagus in a wave-like movement known as a peristaltic movement.
(iv) In the stomach, food mixes with gastric juices and dil. HCl. The food is broken down into simple substances with the help of digestive enzymes like pepsinogen, while mucus protects the walls of the stomach.
(v) From the stomach, the food moves into the small intestines with the help of ring-like muscles called pyloric sphincters which allow only a little food to pass through at a time.
(vi) In the small intestine, the carbohydrates, proteins, and fats are broken down with the help of juices secreted by the pancreas, liver, and the small intestine itself.
(vii) Fat is converted into small globule-like forms with the help of bile juices from the liver. This process is known as emulsification.
(viii) Pancreatic juices contain trypsin enzymes that break down proteins and lipase that breaks down fats.
(ix) The later part of the small intestines is alkaline in nature and helps in the digestion of carbohydrates.
(x) The broken-down food is then absorbed by small projections present on the inside walls of the intestine called villi. Villi are surrounded by blood and lymph vessels that absorb the food and transport it to the rest of the body.
(xi) Finally, the food moves into the large intestine where most of the water is removed from the food and is then passed out of the body through the anus.
Note: The method of digestion begins from the mouth and ends within the small intestine – the large intestines’ main function is to soak up the remaining water from the undigested food and enable bacterial fermentation of materials which will not be digested.
Complete answer:

Anatomically, the digestive system is formed from the alimentary canal which includes the mouth, stomach, esophagus, small intestine, and large intestine that contains the rectum and anus alongside accessory organs like the liver, pancreas, and gallbladder.
Explanation of the human digestive system are-
(i) Food is crushed and cut in the mouth with the help of teeth and is mixed with saliva that is secreted by three salivary glands (one below the tongue and two at the side of the jaw) to make it wet and slippery, this process is known as mastication.
(ii) Saliva contains amylase that breaks down complex carbohydrates and the tongue helps in pushing the food to the next part of the alimentary canal.
(iii) The soft food then passes through the oesophagus in a wave-like movement known as a peristaltic movement.
(iv) In the stomach, food mixes with gastric juices and dil. HCl. The food is broken down into simple substances with the help of digestive enzymes like pepsinogen, while mucus protects the walls of the stomach.
(v) From the stomach, the food moves into the small intestines with the help of ring-like muscles called pyloric sphincters which allow only a little food to pass through at a time.
(vi) In the small intestine, the carbohydrates, proteins, and fats are broken down with the help of juices secreted by the pancreas, liver, and the small intestine itself.
(vii) Fat is converted into small globule-like forms with the help of bile juices from the liver. This process is known as emulsification.
(viii) Pancreatic juices contain trypsin enzymes that break down proteins and lipase that breaks down fats.
(ix) The later part of the small intestines is alkaline in nature and helps in the digestion of carbohydrates.
(x) The broken-down food is then absorbed by small projections present on the inside walls of the intestine called villi. Villi are surrounded by blood and lymph vessels that absorb the food and transport it to the rest of the body.
(xi) Finally, the food moves into the large intestine where most of the water is removed from the food and is then passed out of the body through the anus.
Note: The method of digestion begins from the mouth and ends within the small intestine – the large intestines’ main function is to soak up the remaining water from the undigested food and enable bacterial fermentation of materials which will not be digested.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




