
How would you draw a Lewis structure of \[N_3^ - \]?
Answer
564.9k+ views
Hint: In order to draw a Lewis structure for \[N_3^ - \], we must first know what a Lewis structure is. Lewis structure can also be called the Electron dot structure. This will describe the chemical bonding present between the atoms in a molecule.
Complete step by step answer:
- Let us understand deeply about the Lewis structure. Lewis structure is also called the electron structure. This will describe the nature of the bond present and the position of the atoms present in the molecule which are connected in the molecule. It will be easier to draw the electron dot structure, if we know the molecular or chemical formula of the compound. The Lewis structure will give the chemical bonding between the atoms. Each dot in the Lewis structure will represent an electron. When electron dots are present in the pairs it will represent the chemical bond.
- In order to write the Lewis structure for \[N_3^ - \], we have to first calculate total valence electrons present in the \[N_3^ - \]molecule. Nitrogen is a chemical element with atomic number 7 and the electronic configuration of nitrogen is given as \[1{s^2}2{s^2}2{p^3}\]. It will be having 5 valence electrons in the outermost orbitals. In \[N_3^ - \] molecules, there are five valence electrons and total three nitrogen atoms and as there is a negative charge, one electron will be added. Therefore, the total valence electron in \[N_3^ - \]molecules is 16.
i.e., \[5 \times 3 + 1 = 16\]
- The central atom is the nitrogen atom, now we have to place these valence electrons around the central metal atom in such a way that all the three nitrogen atoms will acquire an octet configuration.
The Lewis structure for \[N_3^ - \] molecule is given below:
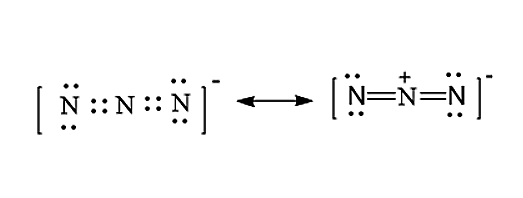
Note: We have to remember that the Lewis structure is very important because
- It will help to predict the geometry of the compound.
- polarity
- reactivity of organic and inorganic compounds.
Complete step by step answer:
- Let us understand deeply about the Lewis structure. Lewis structure is also called the electron structure. This will describe the nature of the bond present and the position of the atoms present in the molecule which are connected in the molecule. It will be easier to draw the electron dot structure, if we know the molecular or chemical formula of the compound. The Lewis structure will give the chemical bonding between the atoms. Each dot in the Lewis structure will represent an electron. When electron dots are present in the pairs it will represent the chemical bond.
- In order to write the Lewis structure for \[N_3^ - \], we have to first calculate total valence electrons present in the \[N_3^ - \]molecule. Nitrogen is a chemical element with atomic number 7 and the electronic configuration of nitrogen is given as \[1{s^2}2{s^2}2{p^3}\]. It will be having 5 valence electrons in the outermost orbitals. In \[N_3^ - \] molecules, there are five valence electrons and total three nitrogen atoms and as there is a negative charge, one electron will be added. Therefore, the total valence electron in \[N_3^ - \]molecules is 16.
i.e., \[5 \times 3 + 1 = 16\]
- The central atom is the nitrogen atom, now we have to place these valence electrons around the central metal atom in such a way that all the three nitrogen atoms will acquire an octet configuration.
The Lewis structure for \[N_3^ - \] molecule is given below:
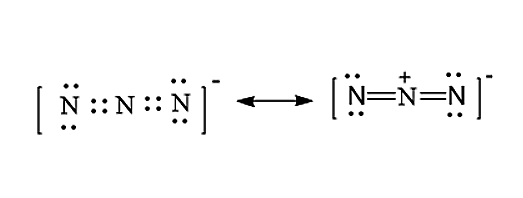
Note: We have to remember that the Lewis structure is very important because
- It will help to predict the geometry of the compound.
- polarity
- reactivity of organic and inorganic compounds.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




