
Draw a molecular orbital diagram of ${N_2}$ or ${O_2}$ with magnetic behavior and bond order.
Answer
529.4k+ views
Hint: Generally the molecular orbital diagrams are used to understand the bonding of a diatomic molecule. You should know that molecular orbital diagrams are used to deduce magnetic properties of a molecule; they also help us to find out the bond order of the molecule.
Complete step by step answer:
First let us understand the concept of molecular orbital theory.
On a very general basis, electrons are not assigned to individual bonds between atoms, but they move under the influence of the nuclei in the whole molecule. Molecular orbital theory is a method for describing the electronic structure of the molecule.
Now, let us draw the molecular orbital diagram of ${N_2}$ .
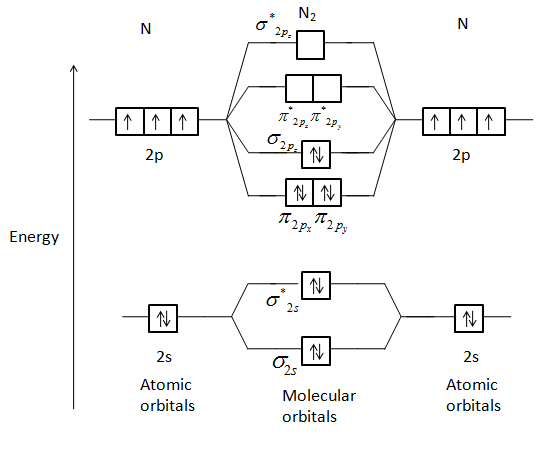
Now, first let us understand what magnetic behavior and bond order means.
- Magnetic behavior:
As we know the electron has an electron magnetic dipole moment, which is generally generated by the electron’s spin property, which induces an electric charge into motion. As we can see the term “magnetic” it refers to the magnetic dipole. There are many types of magnetic behavior which are paramagnetic, diamagnetic and ferromagnetic.
- Bond order:
In simple words, It can be stated that bond order is the difference between the number of bonds and antibonds. Bond number also gives an indication of the stability of a bond.
Lets calculate the bond order for ${N_2}$ :
The total number of electrons present in the ${N_2}$ molecule is 14.
Number of electrons in bonding orbitals : 8
Number of electrons in antibonding orbitals : 2
So, the formula to find bond order is
Bond order = $\dfrac{1}{2}$ (Number of electrons in BMO) – (Number of electrons in ABMO)
Bond order = $\dfrac{1}{2}$ (8) – (2)
Bond order = $\dfrac{1}{2}$ (6)
Bond order = 3
- ${N_2}$ molecules are diamagnetic, with no unpaired electrons. This means half of the electrons spin clockwise and half of the electrons spin anticlockwise. Because of their opposite spins they produce magnetic fields in the opposite direction thus resultant magnetism becomes zero. Which is also called diamagnetism.
Note: You should generally know that the electron probability distribution around a nucleus in an atom is given by an atomic orbital; likewise the electron probability distribution around a group of nuclei in a molecule is given by a molecular orbital diagram.
Complete step by step answer:
First let us understand the concept of molecular orbital theory.
On a very general basis, electrons are not assigned to individual bonds between atoms, but they move under the influence of the nuclei in the whole molecule. Molecular orbital theory is a method for describing the electronic structure of the molecule.
Now, let us draw the molecular orbital diagram of ${N_2}$ .

Now, first let us understand what magnetic behavior and bond order means.
- Magnetic behavior:
As we know the electron has an electron magnetic dipole moment, which is generally generated by the electron’s spin property, which induces an electric charge into motion. As we can see the term “magnetic” it refers to the magnetic dipole. There are many types of magnetic behavior which are paramagnetic, diamagnetic and ferromagnetic.
- Bond order:
In simple words, It can be stated that bond order is the difference between the number of bonds and antibonds. Bond number also gives an indication of the stability of a bond.
Lets calculate the bond order for ${N_2}$ :
The total number of electrons present in the ${N_2}$ molecule is 14.
Number of electrons in bonding orbitals : 8
Number of electrons in antibonding orbitals : 2
So, the formula to find bond order is
Bond order = $\dfrac{1}{2}$ (Number of electrons in BMO) – (Number of electrons in ABMO)
Bond order = $\dfrac{1}{2}$ (8) – (2)
Bond order = $\dfrac{1}{2}$ (6)
Bond order = 3
- ${N_2}$ molecules are diamagnetic, with no unpaired electrons. This means half of the electrons spin clockwise and half of the electrons spin anticlockwise. Because of their opposite spins they produce magnetic fields in the opposite direction thus resultant magnetism becomes zero. Which is also called diamagnetism.
Note: You should generally know that the electron probability distribution around a nucleus in an atom is given by an atomic orbital; likewise the electron probability distribution around a group of nuclei in a molecule is given by a molecular orbital diagram.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




