
Draw a neat diagram of Spirogyra and label the Outermost layer of the cell.
Answer
578.4k+ views
Hint: The outer layer of the Spirogyra is the structural layer which is present in only some types of the cell. It helps in providing structural and mechanical support to the cell along with protection.
Complete answer:
The outermost layer of the Spirogyra is the cell wall. Spirogyra which is commonly known as water silk is a filamentous green alga that comes in the order Zygnematales. Each cell of the filaments Spirogyra has an outsized central vacuole, within which the nucleus is suspended by fine strands of cytoplasm. The chloroplasts make a spiral around the vacuole and also have specialized bodies referred to as pyrenoids that store starch. The cell wall mainly consists of an inner layer made up of cellulose and an outer layer made up of pectin, which is liable for the slippery texture of the algae.
Additional Information: The Spirogyra is named so for the helical or spiral arrangement of the chloroplasts that is characteristic of the genus. It is usually found in freshwater habitats, and there are more than 400 species of Spirogyra known in the world. Spirogyra measures something approx 11 to 110 μm in width and may grow to several centimeters in length. Spirogyra is very commonly seen in relatively clear water bodies, developing slimy filamentous green masses. In the spring season, it was noticed that the Spirogyra grows underwater, but when there is enough sunlight and heat they produce large amounts of oxygen, adhering as bubbles between the tangled filaments. The filaments of the Spirogyra come to the surface and appear as slimy green mats. Spirogyra features a cell wall, nucleus, pyrenoid, and spiral chloroplasts.
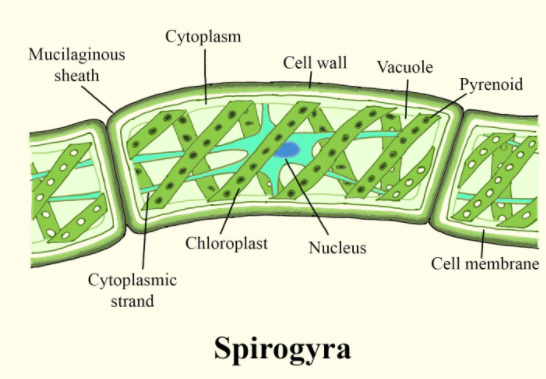
Note: The Spirogyra can reproduce both sexually and asexually. In the vegetative reproduction of the Spirogyra, the fragmentation takes place, and due to this Spirogyra simply undergoes intercalary cellular division which helps to increase the length of the new filaments.
Complete answer:
The outermost layer of the Spirogyra is the cell wall. Spirogyra which is commonly known as water silk is a filamentous green alga that comes in the order Zygnematales. Each cell of the filaments Spirogyra has an outsized central vacuole, within which the nucleus is suspended by fine strands of cytoplasm. The chloroplasts make a spiral around the vacuole and also have specialized bodies referred to as pyrenoids that store starch. The cell wall mainly consists of an inner layer made up of cellulose and an outer layer made up of pectin, which is liable for the slippery texture of the algae.
Additional Information: The Spirogyra is named so for the helical or spiral arrangement of the chloroplasts that is characteristic of the genus. It is usually found in freshwater habitats, and there are more than 400 species of Spirogyra known in the world. Spirogyra measures something approx 11 to 110 μm in width and may grow to several centimeters in length. Spirogyra is very commonly seen in relatively clear water bodies, developing slimy filamentous green masses. In the spring season, it was noticed that the Spirogyra grows underwater, but when there is enough sunlight and heat they produce large amounts of oxygen, adhering as bubbles between the tangled filaments. The filaments of the Spirogyra come to the surface and appear as slimy green mats. Spirogyra features a cell wall, nucleus, pyrenoid, and spiral chloroplasts.

Note: The Spirogyra can reproduce both sexually and asexually. In the vegetative reproduction of the Spirogyra, the fragmentation takes place, and due to this Spirogyra simply undergoes intercalary cellular division which helps to increase the length of the new filaments.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




