
Draw a neat diagram of the blast furnace used in the extraction of iron and label the parts.
Answer
595.2k+ views
Hint: Iron is extracted from iron ores such as haematite contain iron(III) oxide, ${ Fe }_{ 2 }{ O }_{ 3 }$ in a huge container called a blast furnace. Now you should try to answer this question.
Complete step by step solution:
We should know that Carbon is more reactive than iron, so it can displace iron from iron(III) oxide. Here we can see the equations for the reaction:
${ 2Fe }_{ 2 }{ O }_{ 3 }(s)+3C(s)\rightarrow 4Fe(l)+3CO_{ 2 }(g)$
The blast furnace is so hot that carbon monoxide can be used, in place of carbon, to reduce the iron(III) oxide:
${ Fe }_{ 2 }{ O }_{ 3 }(s)+3CO(s)\rightarrow 2Fe(l)+3CO_{ 2 }(g)$
Now, we will discuss the reaction involved in removing the impurities.
The calcium carbonate or we can say the limestone thermally decomposes to form calcium oxide.
$CaCO_{ 3 }(s)\rightarrow CaO(s)+CO_{ 2 }(g)$
The calcium oxide formed will then react with silica impurities in the haematite, to produce slag (calcium silicate). This reaction is a neutralization reaction because calcium oxide is basic and silica is acidic.
$CaO(s)+SiO_{ 2 }(g)\rightarrow CaSiO_{ 3 }(l)$
This diagram below represents the temperatures required for each reaction to proceed successfully -
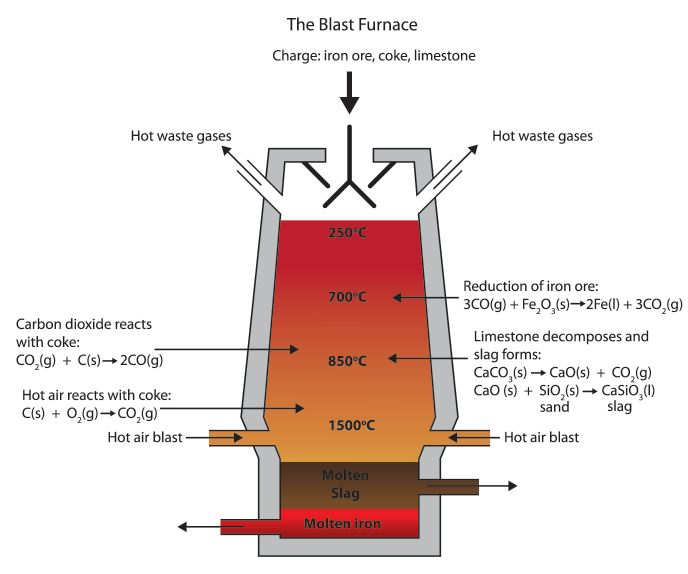
Note: We should know that the molten iron from the bottom of the furnace can be used as cast iron. It is very runny when it is molten and doesn't shrink much when it solidifies. It is therefore ideal for making castings as the name suggests.
Complete step by step solution:
We should know that Carbon is more reactive than iron, so it can displace iron from iron(III) oxide. Here we can see the equations for the reaction:
${ 2Fe }_{ 2 }{ O }_{ 3 }(s)+3C(s)\rightarrow 4Fe(l)+3CO_{ 2 }(g)$
The blast furnace is so hot that carbon monoxide can be used, in place of carbon, to reduce the iron(III) oxide:
${ Fe }_{ 2 }{ O }_{ 3 }(s)+3CO(s)\rightarrow 2Fe(l)+3CO_{ 2 }(g)$
Now, we will discuss the reaction involved in removing the impurities.
The calcium carbonate or we can say the limestone thermally decomposes to form calcium oxide.
$CaCO_{ 3 }(s)\rightarrow CaO(s)+CO_{ 2 }(g)$
The calcium oxide formed will then react with silica impurities in the haematite, to produce slag (calcium silicate). This reaction is a neutralization reaction because calcium oxide is basic and silica is acidic.
$CaO(s)+SiO_{ 2 }(g)\rightarrow CaSiO_{ 3 }(l)$
This diagram below represents the temperatures required for each reaction to proceed successfully -

Note: We should know that the molten iron from the bottom of the furnace can be used as cast iron. It is very runny when it is molten and doesn't shrink much when it solidifies. It is therefore ideal for making castings as the name suggests.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




