
Draw a neat diagram of the human brain and label any four parts.
Answer
595.2k+ views
Hint: The brain is the coordinating centre of the body and it is made up of many specialised areas that work together. It has 4 lobes frontal, parietal, temporal and occipital lobe and it is majorly divided into cerebrum, cerebellum and brainstem.
Complete answer:
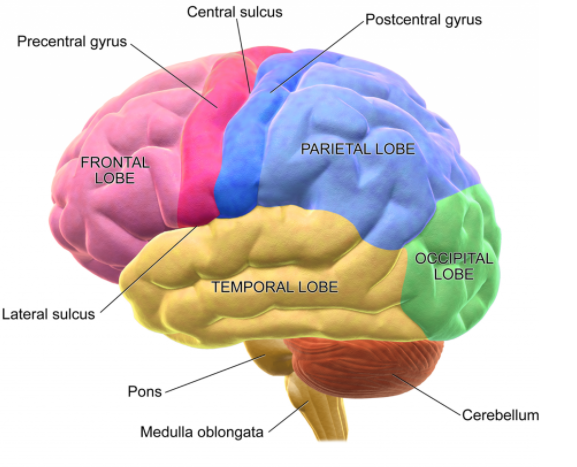
The brain is one of the largest and most complex organs in the human body. It is made up of billions of nerves that communicate in a connection called synapses. Brain is made up of soft tissue, which includes white matter, gray matter, nerve, non- neuronal cells and blood vessels. The brain is made up of many specialised areas that work together, first is the cortex, which is the outermost layer of the brain cell and is responsible for thinking and voluntary movement. The brainstem is present between the spinal cord and the rest of the brain. Basic functions like breathing and sleep are controlled here. The basal ganglia present in the centre of the brain coordinates messages between multiple other brain areas. The cerebellum is present at the base and the back of the brain. The cerebellum is responsible for coordination and balance. Brain is also divided into several lobes-frontal lobe, parietal lobe, temporal lobe and occipital lobe. The brain is surrounded by three layers called meninges. Outside the meninges, the skull or cranium is present that protects the brain from injury. Hypothalamus, thalamus, pituitary gland, pineal gland, amygdala, hippocampus and the midbrain are also the part of the brain.
Note: The main 3 parts of the brain are cerebrum, cerebellum and brainstem. The brainstem is made up of the midbrain, pons and medulla oblongata. Medulla oblongata continues posteriorly with spinal cord.
Complete answer:

The brain is one of the largest and most complex organs in the human body. It is made up of billions of nerves that communicate in a connection called synapses. Brain is made up of soft tissue, which includes white matter, gray matter, nerve, non- neuronal cells and blood vessels. The brain is made up of many specialised areas that work together, first is the cortex, which is the outermost layer of the brain cell and is responsible for thinking and voluntary movement. The brainstem is present between the spinal cord and the rest of the brain. Basic functions like breathing and sleep are controlled here. The basal ganglia present in the centre of the brain coordinates messages between multiple other brain areas. The cerebellum is present at the base and the back of the brain. The cerebellum is responsible for coordination and balance. Brain is also divided into several lobes-frontal lobe, parietal lobe, temporal lobe and occipital lobe. The brain is surrounded by three layers called meninges. Outside the meninges, the skull or cranium is present that protects the brain from injury. Hypothalamus, thalamus, pituitary gland, pineal gland, amygdala, hippocampus and the midbrain are also the part of the brain.
Note: The main 3 parts of the brain are cerebrum, cerebellum and brainstem. The brainstem is made up of the midbrain, pons and medulla oblongata. Medulla oblongata continues posteriorly with spinal cord.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




