
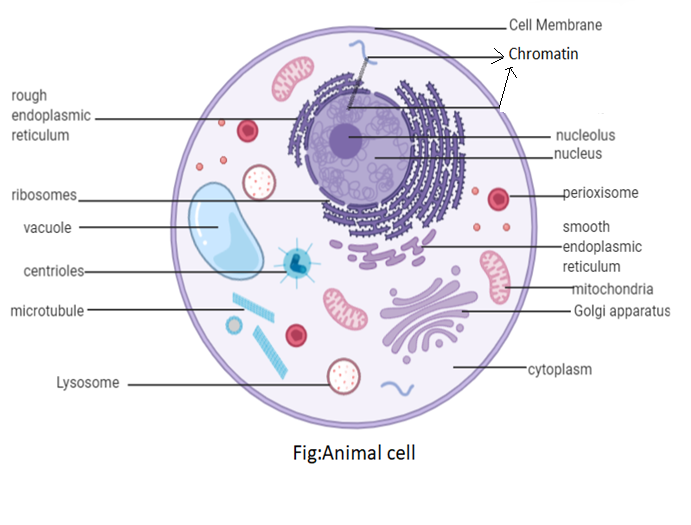
Draw a neat labeled diagram of animal cells.
Answer
555.3k+ views
Hint: Animals are complicated organisms. While animals exhibit locomotion, plants are sessile. Animals can't synthesize their food.
Complete step by step answer:
A cell is a living organism's fundamental structural and functional unit. A cell is the essential building block of life, that keeps anything alive and is self-sufficient to execute all of an organism's fundamental functions, as per the postulates of cell theory.
The cellular components are called cell organelles. In these cell organelles, both membrane and non-membrane bound organelles, present inside the cells, are included and are different in their structures and functions. Cell organelles are called cellular elements. Both membrane and non-membrane bound organelles, found within the cells, are included in these cell organelles and are distinct in their structures and functions.
A few of them operate by offering form and protection, while others are involved in a cell's locomotion and reproduction. Within the cell, there are different organelles and they are divided into three groups based on the presence or absence of the membrane.
The cell wall, ribosomes, and cytoskeleton are organelles of cells that are non-membrane-bound. Both prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells are present.
Vacuole, Lysosome, Endoplasmic Reticulum, Golgi Apparatus, are single membrane-bound organelles found only in eukaryotic cells. Double membrane-bound organelles found only in eukaryotic cells are the nucleus, mitochondria, and chloroplast.
Note: The ability to execute photosynthesis is typically seen in organisms belonging to the Plantae kingdom, but photosynthesis can also be done by some other organisms belonging to the Monera kingdom, the Protista kingdom, etc. Euglena is an organism that exhibits characters that are both plant and animal-like, and a mixotrophic nutrition mode is observed.
Complete step by step answer:
A cell is a living organism's fundamental structural and functional unit. A cell is the essential building block of life, that keeps anything alive and is self-sufficient to execute all of an organism's fundamental functions, as per the postulates of cell theory.
The cellular components are called cell organelles. In these cell organelles, both membrane and non-membrane bound organelles, present inside the cells, are included and are different in their structures and functions. Cell organelles are called cellular elements. Both membrane and non-membrane bound organelles, found within the cells, are included in these cell organelles and are distinct in their structures and functions.
A few of them operate by offering form and protection, while others are involved in a cell's locomotion and reproduction. Within the cell, there are different organelles and they are divided into three groups based on the presence or absence of the membrane.
The cell wall, ribosomes, and cytoskeleton are organelles of cells that are non-membrane-bound. Both prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells are present.
Vacuole, Lysosome, Endoplasmic Reticulum, Golgi Apparatus, are single membrane-bound organelles found only in eukaryotic cells. Double membrane-bound organelles found only in eukaryotic cells are the nucleus, mitochondria, and chloroplast.

Note: The ability to execute photosynthesis is typically seen in organisms belonging to the Plantae kingdom, but photosynthesis can also be done by some other organisms belonging to the Monera kingdom, the Protista kingdom, etc. Euglena is an organism that exhibits characters that are both plant and animal-like, and a mixotrophic nutrition mode is observed.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




