
Draw a neat labelled diagram of cell cycle.
Answer
524.5k+ views
Hint: Cell cycle is a sequence of events that take place in four stages (G1, S, G2and M phase) for the successful division of a cell. It is broadly divided into two parts- interphase (prepares the cell for the next mitosis) and mitotic phase (cell division).
Complete answer:
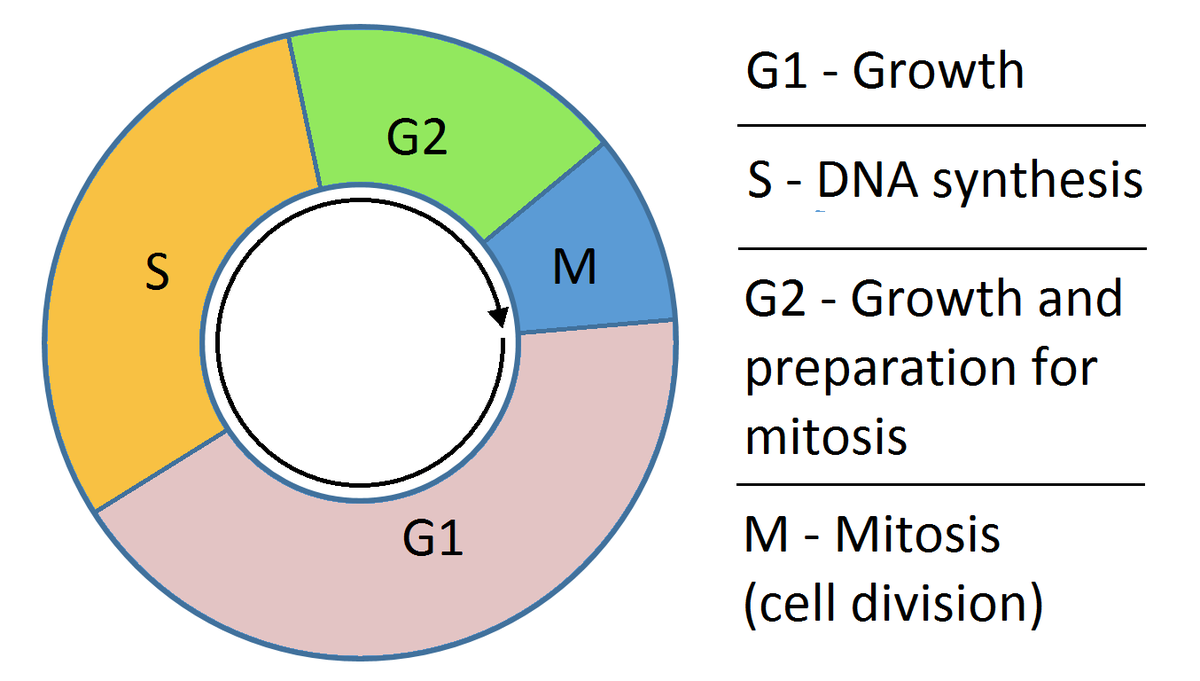
Cell cycle is the ordered sequence of events that takes place in a cell while it is preparing for cell division. The cell cycle is a four-stage process- G1 (gap 1) stage, S (synthesis) phase, G2 (gap 2) phase and M (mitosis) phase.
Additional information:
A cell cycle is an ordered sequence of events by which a cell duplicates its genome, synthesizes the other constituents of the cell and eventually divides to form two daughter cells. It has four stages- G1, S, G2 and M phase. The interphase is the longest phase as it includes G1, S and G2 phases of the cell cycle. The cell then leaves interphase, undergoes mitosis and marks the completion of division with the formation of daughter cells. As the cell division is over and the daughter cells are formed, each daughter cell enters their own interphase and begins a new cell cycle.
Phases of cell cycle:
• A eukaryotic cell divides once in every 24hrs. The cell cycle is divided into two basic phases- interphase and mitosis phase.
• Mitosis phase (1-2hrs) 🡪 It begins with nuclear division followed by karyokinesis and cytokinesis.
• Interphase (22hrs approx.) 🡪 This is the resting phase of the cell during which it prepares for the next division.
- G1 phase: Cell is metabolically active and grows continuously but DNA replication doesn’t occur.
- S phase: DNA replication takes place. DNA per cell doubles up.
- G2 phase: Proteins are synthesized in preparation for mitosis while the cell continues to grow.
Note: Cells cease to divide further if they exit the G1 phase to enter the inactive stage called quiescent stage of the cell cycle. Cells primarily enter the G0 phase due to environmental factors like nutrient deprivation which leads to depletion of resources essential for proliferation.
Complete answer:

Cell cycle is the ordered sequence of events that takes place in a cell while it is preparing for cell division. The cell cycle is a four-stage process- G1 (gap 1) stage, S (synthesis) phase, G2 (gap 2) phase and M (mitosis) phase.
Additional information:
A cell cycle is an ordered sequence of events by which a cell duplicates its genome, synthesizes the other constituents of the cell and eventually divides to form two daughter cells. It has four stages- G1, S, G2 and M phase. The interphase is the longest phase as it includes G1, S and G2 phases of the cell cycle. The cell then leaves interphase, undergoes mitosis and marks the completion of division with the formation of daughter cells. As the cell division is over and the daughter cells are formed, each daughter cell enters their own interphase and begins a new cell cycle.
Phases of cell cycle:
• A eukaryotic cell divides once in every 24hrs. The cell cycle is divided into two basic phases- interphase and mitosis phase.
• Mitosis phase (1-2hrs) 🡪 It begins with nuclear division followed by karyokinesis and cytokinesis.
• Interphase (22hrs approx.) 🡪 This is the resting phase of the cell during which it prepares for the next division.
- G1 phase: Cell is metabolically active and grows continuously but DNA replication doesn’t occur.
- S phase: DNA replication takes place. DNA per cell doubles up.
- G2 phase: Proteins are synthesized in preparation for mitosis while the cell continues to grow.
Note: Cells cease to divide further if they exit the G1 phase to enter the inactive stage called quiescent stage of the cell cycle. Cells primarily enter the G0 phase due to environmental factors like nutrient deprivation which leads to depletion of resources essential for proliferation.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE




