
Draw a neat labelled diagram of ‘cyclotron’.
Answer
586.5k+ views
Hint: Let us see in brief how a cyclotron works-
A machine used to accelerate charged particles to high energies is Cyclotron. Cyclotron operates on the assumption that magnetic Lorentz force is encountered by a charged particle travelling perpendicular to a magnetic field because of which the particle travels along a circular direction.
Stepwise solution:
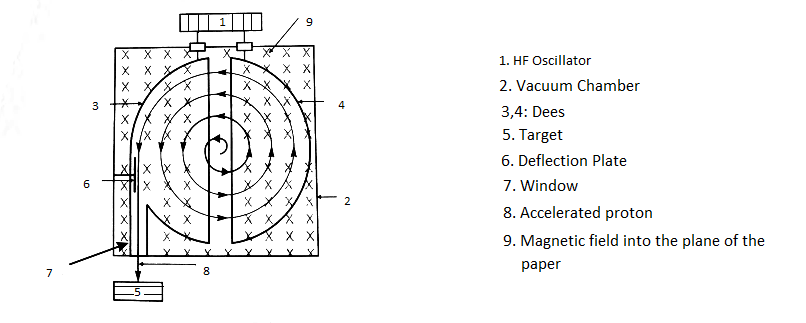
HF OSCILLATOR: It is named as a high frequency oscillator, whose function in the cyclotron is to change the potential difference. It is connected across both the Dees.
VACUUM CHAMBER: A cyclotron accelerates charged particles into a radial direction from the middle of a flat cylindrical vacuum chamber. The particles are kept by a rigid magnetic field on a radial trajectory and propelled by a continuously changing electric field (radio frequency).
DEES: In a cyclotron, in an evacuated chamber between the poles of a magnet, two hollow semi-circular electrodes, or Dees, shaped as ‘D’ s, are placed back to back, separated by a short distance.The polarity of the RF voltage reverses every time after the particles pass to the other Dee electrode.
DEFLECTION PLATE: The deflector plate is used in such a way that the direction of the spiralling charged particle inside a cyclotron shifts to the point where it needs to be. It is present before the target to adjust the direction of motion of the accelerated protons.
ACCELERATED PROTON: These are highly energetic charged particles,driven by an alternating electrical field, in a steady magnetic field.
Note: Cyclotron is an electrically driven mechanism that generates a beam of charged particles which find uses in medical, industrial and research applications. It is also used to produce radioactive isotopes.
A machine used to accelerate charged particles to high energies is Cyclotron. Cyclotron operates on the assumption that magnetic Lorentz force is encountered by a charged particle travelling perpendicular to a magnetic field because of which the particle travels along a circular direction.
Stepwise solution:

HF OSCILLATOR: It is named as a high frequency oscillator, whose function in the cyclotron is to change the potential difference. It is connected across both the Dees.
VACUUM CHAMBER: A cyclotron accelerates charged particles into a radial direction from the middle of a flat cylindrical vacuum chamber. The particles are kept by a rigid magnetic field on a radial trajectory and propelled by a continuously changing electric field (radio frequency).
DEES: In a cyclotron, in an evacuated chamber between the poles of a magnet, two hollow semi-circular electrodes, or Dees, shaped as ‘D’ s, are placed back to back, separated by a short distance.The polarity of the RF voltage reverses every time after the particles pass to the other Dee electrode.
DEFLECTION PLATE: The deflector plate is used in such a way that the direction of the spiralling charged particle inside a cyclotron shifts to the point where it needs to be. It is present before the target to adjust the direction of motion of the accelerated protons.
ACCELERATED PROTON: These are highly energetic charged particles,driven by an alternating electrical field, in a steady magnetic field.
Note: Cyclotron is an electrically driven mechanism that generates a beam of charged particles which find uses in medical, industrial and research applications. It is also used to produce radioactive isotopes.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




