
Draw a well labelled diagram of a dry cell and explain its construction.
Answer
515.4k+ views
Hint: Electric cells are used to power devices such as clocks, calculators, and phones. It is a minor source of power. It's also known as a dry cell or a pencil cell. Chemical energy is converted into electrical energy by this device. A dry cell is a non-rechargeable main cell that cannot be used again. These cells are used in a variety of household items such as radios, transistors, tape recorders, calculators, and so on.
Complete answer:
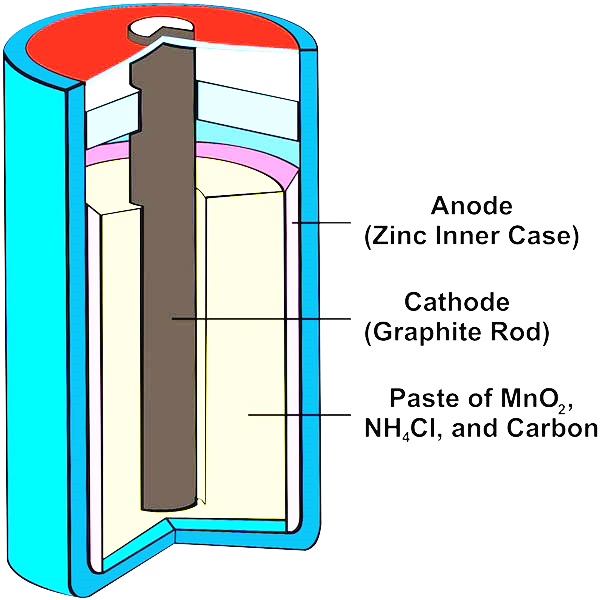
The dry cell is one of many electrochemical cell types. The electrolyte is immobilised as a paste in a dry cell, with just enough moisture to allow current to flow. Since it has no free liquid, unlike a wet cell, a dry cell can run in any direction without spilling.
It consists of a zinc jar on one side of the cell with a narrow brass cap labelled positive (+) and a metal base on the other side of the cell labelled negative (-).
A carbon rod is inserted in the cell's middle, surrounded by a muslin bag containing a mixture of manganese dioxide (\[Mn{O_2}\]) and charcoal (C).
The electrolyte is a moist paste of ammonium chloride (\[N{H_4}Cl\]), plaster of Paris, starch, and other materials, and the zinc container's outer body (except the base) is insulated with thick cardboard or plastic.
Working:
As a cell is attached to a light bulb, the chemical reaction within the cell speeds up, and current begins to circulate through the bulb. As a result, the lamp illuminates.
These dry cells have a limited amount of power.
Note:
A typical dry cell has a zinc anode, which is typically in the shape of a cylindrical tub, and a carbon cathode, which is usually in the shape of a central rod. The electrolyte is ammonium chloride, which is applied to the zinc anode as a paste. A second paste made of ammonium chloride and manganese dioxide fills the vacuum between the electrolyte and the carbon cathode, with the latter serving as a depolariser. Ammonium chloride is substituted with zinc chloride in some projects, which are mostly sold as "heavy duty."
Complete answer:

The dry cell is one of many electrochemical cell types. The electrolyte is immobilised as a paste in a dry cell, with just enough moisture to allow current to flow. Since it has no free liquid, unlike a wet cell, a dry cell can run in any direction without spilling.
It consists of a zinc jar on one side of the cell with a narrow brass cap labelled positive (+) and a metal base on the other side of the cell labelled negative (-).
A carbon rod is inserted in the cell's middle, surrounded by a muslin bag containing a mixture of manganese dioxide (\[Mn{O_2}\]) and charcoal (C).
The electrolyte is a moist paste of ammonium chloride (\[N{H_4}Cl\]), plaster of Paris, starch, and other materials, and the zinc container's outer body (except the base) is insulated with thick cardboard or plastic.
Working:
As a cell is attached to a light bulb, the chemical reaction within the cell speeds up, and current begins to circulate through the bulb. As a result, the lamp illuminates.
These dry cells have a limited amount of power.
Note:
A typical dry cell has a zinc anode, which is typically in the shape of a cylindrical tub, and a carbon cathode, which is usually in the shape of a central rod. The electrolyte is ammonium chloride, which is applied to the zinc anode as a paste. A second paste made of ammonium chloride and manganese dioxide fills the vacuum between the electrolyte and the carbon cathode, with the latter serving as a depolariser. Ammonium chloride is substituted with zinc chloride in some projects, which are mostly sold as "heavy duty."
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




