
Draw a well labelled diagram of Euglena.
Answer
524.7k+ views
Hint: It is a eukaryotic organism that exhibits features of both animal and plant. That is why it is called a link between plants and animals.
Complete Answer:
- Euglena is a unicellular eukaryotic organism. The cell body is elongated and uninucleated i.e. having one nucleus. The cell wall is absent. Instead, a proteinaceous layer is present which is known as pellicle. The pellicle is composed of overlapping and interlocking strips that are wrapped around the cell in a spiral manner.
- This arrangement of pellicular strips contributes flexibility to the cell. Sliding of these strips along one another results in the movement of the cell. Due to these strips the cell becomes able to contract and change its shape.
- The plasma membrane is thin and encloses the cytoplasm and all cell organelles. The anterior end of the cell has a flask shaped reservoir with a small opening known as cytostome. One or more contractile vacuoles are present which functions to remove the extra water.
- Euglena has two flagella that arise from the blepharoplast located at the base of the reservoir. Typically, one flagellum is long and projects out from the cell whereas; other flagellum is very short and does not emerge from the reservoir.
- The flagellum helps the organism in swimming. A prominent red coloured eye spot or stigma is present. The red colour of stigma is due to the presence of reddish carotenoid pigment granules. It is a light perceiving organ. It helps the organism to find the light and move towards it.
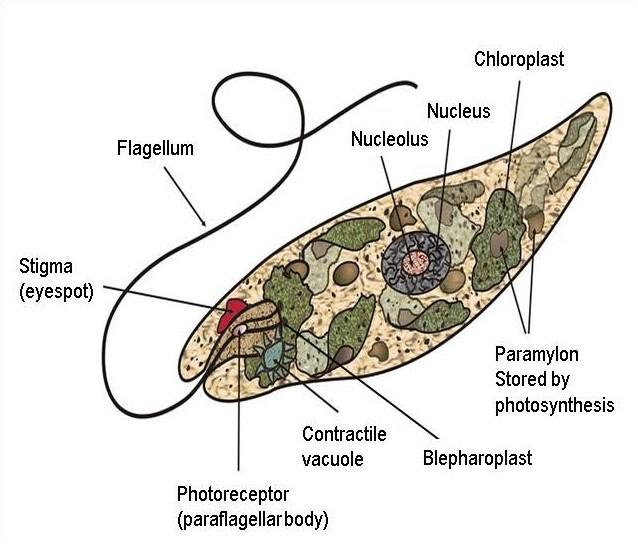
Fig: Cellular organisation of Euglena
- The chloroplasts are present along with other cell organelles such as golgi bodies, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum etc. Different photosynthetic pigments like chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b, xanthophylls and beta carotene are present in the chloroplast.
- Euglena chloroplasts also possess pyrenoids that are the centres for paramylon synthesis.
In the presence of sufficient sunlight, the organism uses chlorophyll pigments to produce sugars by photosynthesis. But they are not fully autotrophic.
- Rather these are photoautotrophs because they require some organic nutrients and vitamins to perform photosynthesis. When light is not available they become heterotrophic. The property of being a photosynthetic organism as well as a facultative heterotroph makes Euglena a unique organism.
Note: Euglena survives best in stagnant waters like ponds and lakes. In certain cases, Euglena gives red colouration to water due to increase in astaxanthin, a characteristic euglenoid xanthophyll pigment.
Complete Answer:
- Euglena is a unicellular eukaryotic organism. The cell body is elongated and uninucleated i.e. having one nucleus. The cell wall is absent. Instead, a proteinaceous layer is present which is known as pellicle. The pellicle is composed of overlapping and interlocking strips that are wrapped around the cell in a spiral manner.
- This arrangement of pellicular strips contributes flexibility to the cell. Sliding of these strips along one another results in the movement of the cell. Due to these strips the cell becomes able to contract and change its shape.
- The plasma membrane is thin and encloses the cytoplasm and all cell organelles. The anterior end of the cell has a flask shaped reservoir with a small opening known as cytostome. One or more contractile vacuoles are present which functions to remove the extra water.
- Euglena has two flagella that arise from the blepharoplast located at the base of the reservoir. Typically, one flagellum is long and projects out from the cell whereas; other flagellum is very short and does not emerge from the reservoir.
- The flagellum helps the organism in swimming. A prominent red coloured eye spot or stigma is present. The red colour of stigma is due to the presence of reddish carotenoid pigment granules. It is a light perceiving organ. It helps the organism to find the light and move towards it.

Fig: Cellular organisation of Euglena
- The chloroplasts are present along with other cell organelles such as golgi bodies, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum etc. Different photosynthetic pigments like chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b, xanthophylls and beta carotene are present in the chloroplast.
- Euglena chloroplasts also possess pyrenoids that are the centres for paramylon synthesis.
In the presence of sufficient sunlight, the organism uses chlorophyll pigments to produce sugars by photosynthesis. But they are not fully autotrophic.
- Rather these are photoautotrophs because they require some organic nutrients and vitamins to perform photosynthesis. When light is not available they become heterotrophic. The property of being a photosynthetic organism as well as a facultative heterotroph makes Euglena a unique organism.
Note: Euglena survives best in stagnant waters like ponds and lakes. In certain cases, Euglena gives red colouration to water due to increase in astaxanthin, a characteristic euglenoid xanthophyll pigment.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




