
Draw Lewis structure, tell shape (VSEPR) and formal charge of \[C{{O}_{3}}^{2-}\].
Answer
537.9k+ views
Hint: Lewis dot structure is defined as the position of atoms and the bonds nature which have been connected in the molecule. They help us to determine the bond pair and the lone pair of each atom present in the molecule. The formal charge is not the real charge but a theoretical charge which helps to determine the lowest energy structure.
Complete step by step answer:
To make the lewis structure, we need to count the total number of the valence electrons in a molecule. If the molecule is added then more electrons will be added as the number of electrons added is equal to the magnitude of negative charge. If the molecule is cationic then the electrons will be subtracted. The atom which is least electronegative will be the central atom. Now lone pairs will be assigned to the atoms of molecules. If the octet configuration is not attained even after assigning the lone pairs then double bond or triple bond will be made. If required we can convert a lone pair to bond pair.
The formula for formal charge is
$\text{Formal charge} = \text{Valence electrons } –\text{ Non bonding valence electrons} - \dfrac{ \text{bonding electrons}}{2}$
So for \[C{{O}_{3}}^{2-}\] the lewis structure is:
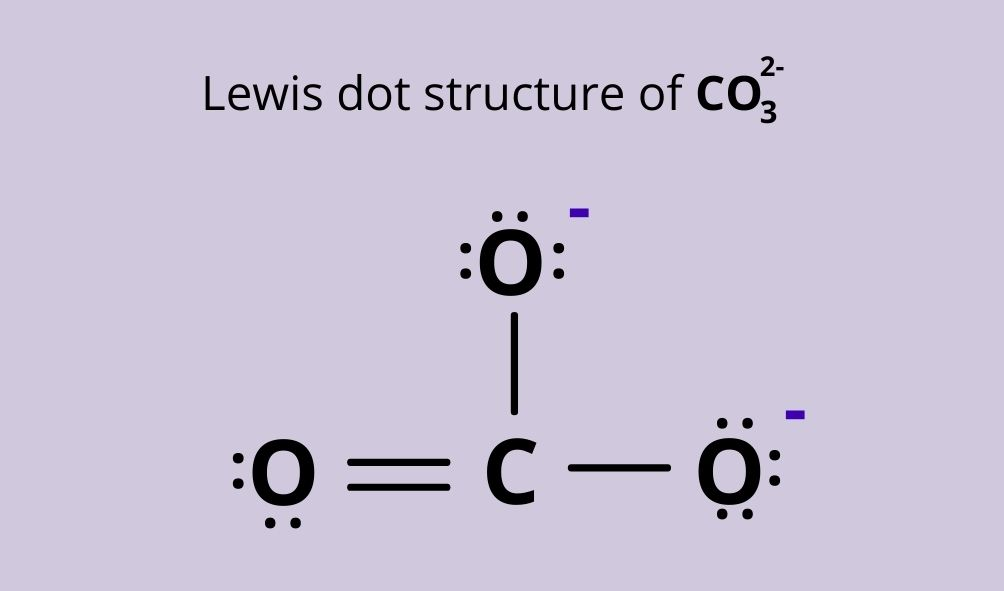
So now to calculate the formal charge on the double bonded oxygen atom we will find its valence electrons which is equal to 6 and the non bonding valence electrons is 4 and bonding electrons are equal to 4 so on substituting the values we get
Formal charge for double bonded oxygen atom = \[6-4-\dfrac{1}{2}\times 4=0\]
So now to calculate the other two oxygen atom formal charges, the valence electrons is equal to 6 and non bonding valence electrons is equal to 6 and the bonding electrons is equal to 2. Now substitute the value
formal charge for the oxygen atom with a negative charge \[=6-6-\dfrac{1}{2}\times 2=-1\]
the average formal charge on each oxygen atom will be \[=\dfrac{-1+(-1)+0}{3}=-0.67\]
and the formal charge on carbon will be equal to zero. The valence electron on carbon is 4 and non bonding valence electron is 0 and bonding electron is 8. On substituting the value we get
formal charge on carbon \[=4-0-\dfrac{8}{2}=0\].
So now to determine the shape by VSEPR the formula is \[=\dfrac{1}{2}\]$(\text{bond pair + lone pair})$
So, In a carbon atom, the bond pair $= 4$ and the lone pair $= 2$.
So now substituting the value we get the hybridization \[= \dfrac{1}{2}(4+2)=3\].
So the hybridization will be \[s{{p}^{2}}\] and the geometry will be trigonal planar as it has three electron pairs with the bond angle of \[{{120}^{\circ}}\].
Note: The carbonates are used to soft the water and as the raw material for the manufacturing of paper. On heating carbonate they decompose to oxide and carbon dioxide. They are sparingly soluble in water. The carbonates are solid and colourless but the carbonates of transition metals are coloured.
Complete step by step answer:
To make the lewis structure, we need to count the total number of the valence electrons in a molecule. If the molecule is added then more electrons will be added as the number of electrons added is equal to the magnitude of negative charge. If the molecule is cationic then the electrons will be subtracted. The atom which is least electronegative will be the central atom. Now lone pairs will be assigned to the atoms of molecules. If the octet configuration is not attained even after assigning the lone pairs then double bond or triple bond will be made. If required we can convert a lone pair to bond pair.
The formula for formal charge is
$\text{Formal charge} = \text{Valence electrons } –\text{ Non bonding valence electrons} - \dfrac{ \text{bonding electrons}}{2}$
So for \[C{{O}_{3}}^{2-}\] the lewis structure is:

So now to calculate the formal charge on the double bonded oxygen atom we will find its valence electrons which is equal to 6 and the non bonding valence electrons is 4 and bonding electrons are equal to 4 so on substituting the values we get
Formal charge for double bonded oxygen atom = \[6-4-\dfrac{1}{2}\times 4=0\]
So now to calculate the other two oxygen atom formal charges, the valence electrons is equal to 6 and non bonding valence electrons is equal to 6 and the bonding electrons is equal to 2. Now substitute the value
formal charge for the oxygen atom with a negative charge \[=6-6-\dfrac{1}{2}\times 2=-1\]
the average formal charge on each oxygen atom will be \[=\dfrac{-1+(-1)+0}{3}=-0.67\]
and the formal charge on carbon will be equal to zero. The valence electron on carbon is 4 and non bonding valence electron is 0 and bonding electron is 8. On substituting the value we get
formal charge on carbon \[=4-0-\dfrac{8}{2}=0\].
So now to determine the shape by VSEPR the formula is \[=\dfrac{1}{2}\]$(\text{bond pair + lone pair})$
So, In a carbon atom, the bond pair $= 4$ and the lone pair $= 2$.
So now substituting the value we get the hybridization \[= \dfrac{1}{2}(4+2)=3\].
So the hybridization will be \[s{{p}^{2}}\] and the geometry will be trigonal planar as it has three electron pairs with the bond angle of \[{{120}^{\circ}}\].
Note: The carbonates are used to soft the water and as the raw material for the manufacturing of paper. On heating carbonate they decompose to oxide and carbon dioxide. They are sparingly soluble in water. The carbonates are solid and colourless but the carbonates of transition metals are coloured.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

How do I convert ms to kmh Give an example class 11 physics CBSE




