
Draw MOT diagram for ${{\text{B}}_{\text{2}}}$ molecule and calculate its bond order.
Answer
566.4k+ views
Hint: We know that molecular orbital diagrams are used to determine the bonding in a diatomic molecule. The molecular orbital diagrams are used to predict the magnetic properties of a molecule. Molecular orbital diagrams help in determining the bond order of the molecule.
Formula used: ${\text{Bond order}} = \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {{\text{Number of electrons in BMO}}} \right) - \left( {{\text{Number of electrons in ABMO}}} \right)$
Complete Solution :
We know that molecular orbital theory (MOT) explains the formation of molecules.
According to molecular orbital theory, the atomic orbitals having comparable energy overlap and result in the formation of the same number of molecular orbitals. The molecular orbitals having the same sign combine and give bonding molecular orbitals.
We have to draw the molecular orbital diagram for ${{\text{B}}_{\text{2}}}$ molecule.
The ${{\text{B}}_{\text{2}}}$ molecule is formed by the combination of two boron atoms. The two boron atoms are linked by a covalent bond.
The atomic number of boron is 5. The electronic configuration of boron is as follows:
$1{s^2}2{s^2}2{p^1}$
The molecular orbital diagram for ${{\text{B}}_{\text{2}}}$ molecule is as follows:
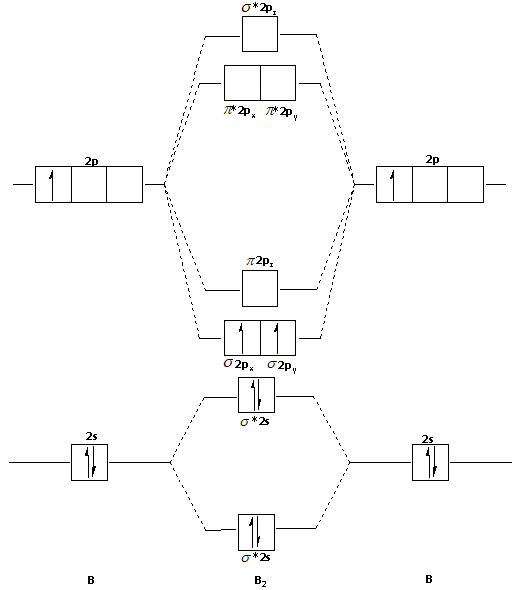
We know that bond order is the difference between the number of bonds and the antibonds.
Now, we have to calculate the bond order of ${{\text{B}}_{\text{2}}}$ molecule using the formula as follows:
${\text{Bond order}} = \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {{\text{Number of electrons in BMO}}} \right) - \left( {{\text{Number of electrons in ABMO}}} \right)$
From the diagram, we can see that the number of electrons in bonding molecular orbitals are 4 and the number of electrons in antibonding molecular orbitals are 2.
Thus,
${\text{Bond order}} = \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {4 - 2} \right)$
${\text{Bond order}} = 1$
Thus, the bond order for ${{\text{B}}_{\text{2}}}$ molecule is 1.
Note: In the molecular orbital diagram, we can see that there are unpaired electrons in the ${{\text{B}}_{\text{2}}}$ molecule. Thus, the ${{\text{B}}_{\text{2}}}$ molecule is paramagnetic in nature. If there are no unpaired electrons then the molecules are diamagnetic in nature.
Formula used: ${\text{Bond order}} = \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {{\text{Number of electrons in BMO}}} \right) - \left( {{\text{Number of electrons in ABMO}}} \right)$
Complete Solution :
We know that molecular orbital theory (MOT) explains the formation of molecules.
According to molecular orbital theory, the atomic orbitals having comparable energy overlap and result in the formation of the same number of molecular orbitals. The molecular orbitals having the same sign combine and give bonding molecular orbitals.
We have to draw the molecular orbital diagram for ${{\text{B}}_{\text{2}}}$ molecule.
The ${{\text{B}}_{\text{2}}}$ molecule is formed by the combination of two boron atoms. The two boron atoms are linked by a covalent bond.
The atomic number of boron is 5. The electronic configuration of boron is as follows:
$1{s^2}2{s^2}2{p^1}$
The molecular orbital diagram for ${{\text{B}}_{\text{2}}}$ molecule is as follows:

We know that bond order is the difference between the number of bonds and the antibonds.
Now, we have to calculate the bond order of ${{\text{B}}_{\text{2}}}$ molecule using the formula as follows:
${\text{Bond order}} = \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {{\text{Number of electrons in BMO}}} \right) - \left( {{\text{Number of electrons in ABMO}}} \right)$
From the diagram, we can see that the number of electrons in bonding molecular orbitals are 4 and the number of electrons in antibonding molecular orbitals are 2.
Thus,
${\text{Bond order}} = \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {4 - 2} \right)$
${\text{Bond order}} = 1$
Thus, the bond order for ${{\text{B}}_{\text{2}}}$ molecule is 1.
Note: In the molecular orbital diagram, we can see that there are unpaired electrons in the ${{\text{B}}_{\text{2}}}$ molecule. Thus, the ${{\text{B}}_{\text{2}}}$ molecule is paramagnetic in nature. If there are no unpaired electrons then the molecules are diamagnetic in nature.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




