
Draw nitrogen cycle? Explain the different steps.
Answer
591.3k+ views
Hint: The nitrogen cycle is a multifaceted bio, geo, and chemical cycle in which the element nitrogen is renewed from its inactive distinctive molecular form $(N_{2})$ into an arrangement that is useful in organic processes.
Complete answer:
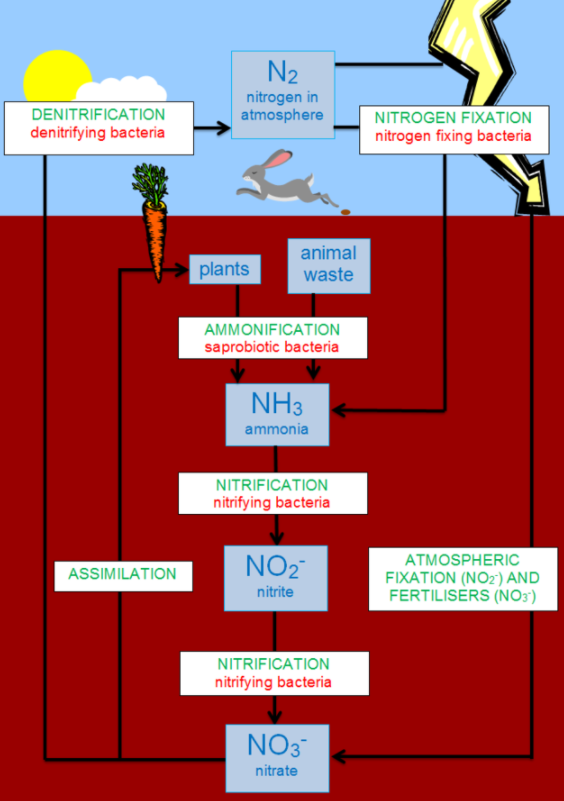
The steps in the nitrogen cycle consist of:
> Nitrogen Fixation: It is defined as a process by which the molecular nitrogen in the atmosphere is transformed into the compound ammonia or associated nitrogenous complexes in soil. The atmospheric nitrogen is in the form of molecular dinitrogen, a moderately non-reactive molecule that is metabolic which is useless to all but helpful to a few microorganisms.
> Ammonification: The process of Ammonification normally refers to any chemical reaction wherein the groups of $NH_{2}$ are transformed into the compound ammonia or its ionic form, which is ammonium $(NH_{4}^{+})$, as an end product. Thus, we can see that it is a process in which organic nitrogen present in plants and animals after their demise is changed to ammonium ions.
> Nitrification: It is a process in which ammonium ions are transformed into nitrates.
The element nitrogen up taking by plants:
The nitrate which is formed in the process of Nitrification is used by most florae as inorganic metabolites and can be changed by them into amino collections and other nitrogen-comprising mixtures.
> The fixation of Nitrogen: The process of reduction of distinctive nitrogen to the ammonium ion
> The Denitrification: The process of reduction of remaining nitrates to nitrogen gas or nitrous oxide by certain microorganisms.
Note: It is significant to note that the various types of microorganisms play an imperative role in each of the following steps. Nitrous oxide $(N_{2} O)$ which has increased in the atmosphere as an effect of agronomic fertilization, sweltering of biomass, livestock, and feedlots, and manufacturing sources. Nitrous oxide has poisonous effects in the stratosphere.
Complete answer:

The steps in the nitrogen cycle consist of:
> Nitrogen Fixation: It is defined as a process by which the molecular nitrogen in the atmosphere is transformed into the compound ammonia or associated nitrogenous complexes in soil. The atmospheric nitrogen is in the form of molecular dinitrogen, a moderately non-reactive molecule that is metabolic which is useless to all but helpful to a few microorganisms.
> Ammonification: The process of Ammonification normally refers to any chemical reaction wherein the groups of $NH_{2}$ are transformed into the compound ammonia or its ionic form, which is ammonium $(NH_{4}^{+})$, as an end product. Thus, we can see that it is a process in which organic nitrogen present in plants and animals after their demise is changed to ammonium ions.
> Nitrification: It is a process in which ammonium ions are transformed into nitrates.
The element nitrogen up taking by plants:
The nitrate which is formed in the process of Nitrification is used by most florae as inorganic metabolites and can be changed by them into amino collections and other nitrogen-comprising mixtures.
> The fixation of Nitrogen: The process of reduction of distinctive nitrogen to the ammonium ion
> The Denitrification: The process of reduction of remaining nitrates to nitrogen gas or nitrous oxide by certain microorganisms.
Note: It is significant to note that the various types of microorganisms play an imperative role in each of the following steps. Nitrous oxide $(N_{2} O)$ which has increased in the atmosphere as an effect of agronomic fertilization, sweltering of biomass, livestock, and feedlots, and manufacturing sources. Nitrous oxide has poisonous effects in the stratosphere.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




