
Draw the circuit symbols for p-n-p and n-p-n transistors.
Answer
524.8k+ views
Hint: In n-p-n transistors 2 segments of n-type semiconductor are separated by a segment of p-type semiconductor. While in the p-n-p transistor 2 segments of p-type semiconductor are separated by a segment of n-type semiconductor.
Complete step by step solution:
The schematic representations of an n-p-n and p-n-p configuration are given as
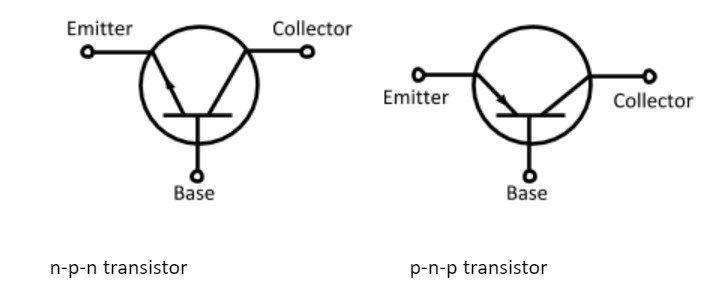
The sign of arrow in the circuit represents
1. Direction of current in circuit
2. Type of transistor
3. Emitter segment of transistor
Here 3 segments are present in transistor
(A) Emitter – It is of moderate size and heavily doped. It supplies a large number of majority carriers for the current flow through the transistor.
(B) Base – This is the central segment.
It is very thin and lightly doped.
(C) Collector – This segment collects a major portion of the majority carries supplies by the emitter. This collector side is moderately doped and larger in size as compared to the emitter.
Note: In order to draw the circuit diagram we must know about the direction of current and doping & thickness of emitter, collector and base.
Complete step by step solution:
The schematic representations of an n-p-n and p-n-p configuration are given as

The sign of arrow in the circuit represents
1. Direction of current in circuit
2. Type of transistor
3. Emitter segment of transistor
Here 3 segments are present in transistor
(A) Emitter – It is of moderate size and heavily doped. It supplies a large number of majority carriers for the current flow through the transistor.
(B) Base – This is the central segment.
It is very thin and lightly doped.
(C) Collector – This segment collects a major portion of the majority carries supplies by the emitter. This collector side is moderately doped and larger in size as compared to the emitter.
Note: In order to draw the circuit diagram we must know about the direction of current and doping & thickness of emitter, collector and base.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




