
Draw the detailed structure of the Nucleus.
Answer
568.5k+ views
Hint: The nucleus is the master organelle of a cell. It is usually found in the centre of a cell. The nucleus is a double membrane organelle that encloses the genetic material of the cell. It is the hereditary unit of organisms. The nucleus guides and regulates the cell function and division.
Complete answer: The nucleus is the largest cell organelle of the cell which is a double membrane protected organelle. The covering of the nucleus is called the nuclear membrane. The membrane consists of pores through which the nucleus and cytoplasm exchange specific materials. The space inside the nucleus is filled with nucleoplasm. The nucleoplasm contains chromosomes which are the condensed DNA molecules. The chromosomes are thread-like structures. Another important thing in the nucleosome is the nucleolus. The nucleolus is a spherical structure that forms ribosomes. The chromosomes consist of genes. The genes encode cellular proteins that further assists cell functioning. Also, genes are the units that get transferred from parent to offspring. All eukaryotic cells consist of a membrane-bound nucleus. On the other hand, prokaryotes do not contain a nucleus, the genetic material lies freely in the cytoplasm. The region in a prokaryotic cell where the chromosomes are present is called the nucleoid. Important cellular processes like replication and transcription occur inside the nucleus. Thus, the nucleus directly regulates cellular functions. Replication is a process of the formation of DNA from existing DNA molecules. This process occurs during cell division. The nucleus is the last to divide into the newly formed daughter cells.
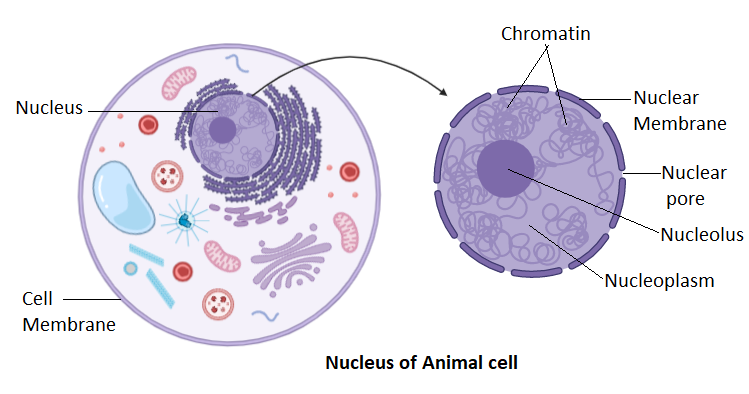
Note: Almost all cells of the body contain a nucleus. The nucleus assists in gene regulation. Gene regulation means switching on and off of the genes for their expressions. Cells specialized to perform beating of the heart have their genes off for thinking function as in brain cells. The RBCs are the cells that lack a nucleus and hence they die in a short period of life.
Complete answer: The nucleus is the largest cell organelle of the cell which is a double membrane protected organelle. The covering of the nucleus is called the nuclear membrane. The membrane consists of pores through which the nucleus and cytoplasm exchange specific materials. The space inside the nucleus is filled with nucleoplasm. The nucleoplasm contains chromosomes which are the condensed DNA molecules. The chromosomes are thread-like structures. Another important thing in the nucleosome is the nucleolus. The nucleolus is a spherical structure that forms ribosomes. The chromosomes consist of genes. The genes encode cellular proteins that further assists cell functioning. Also, genes are the units that get transferred from parent to offspring. All eukaryotic cells consist of a membrane-bound nucleus. On the other hand, prokaryotes do not contain a nucleus, the genetic material lies freely in the cytoplasm. The region in a prokaryotic cell where the chromosomes are present is called the nucleoid. Important cellular processes like replication and transcription occur inside the nucleus. Thus, the nucleus directly regulates cellular functions. Replication is a process of the formation of DNA from existing DNA molecules. This process occurs during cell division. The nucleus is the last to divide into the newly formed daughter cells.

Note: Almost all cells of the body contain a nucleus. The nucleus assists in gene regulation. Gene regulation means switching on and off of the genes for their expressions. Cells specialized to perform beating of the heart have their genes off for thinking function as in brain cells. The RBCs are the cells that lack a nucleus and hence they die in a short period of life.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




