
Draw the diagram of a sarcomere of skeletal muscle showing different regions.
Answer
590.1k+ views
Hint: Sarcomere is the essential unit of striated tissue in the muscles. This means that it is the most important entity that makes up our skeletal muscle. It forms the unit which repeats between two Z lines. By contracting in unison, sarcomeres can initiate broad, sweeping movement. Its special structure enables these tiny units to coordinate the contractions of our muscles.
Complete answer:
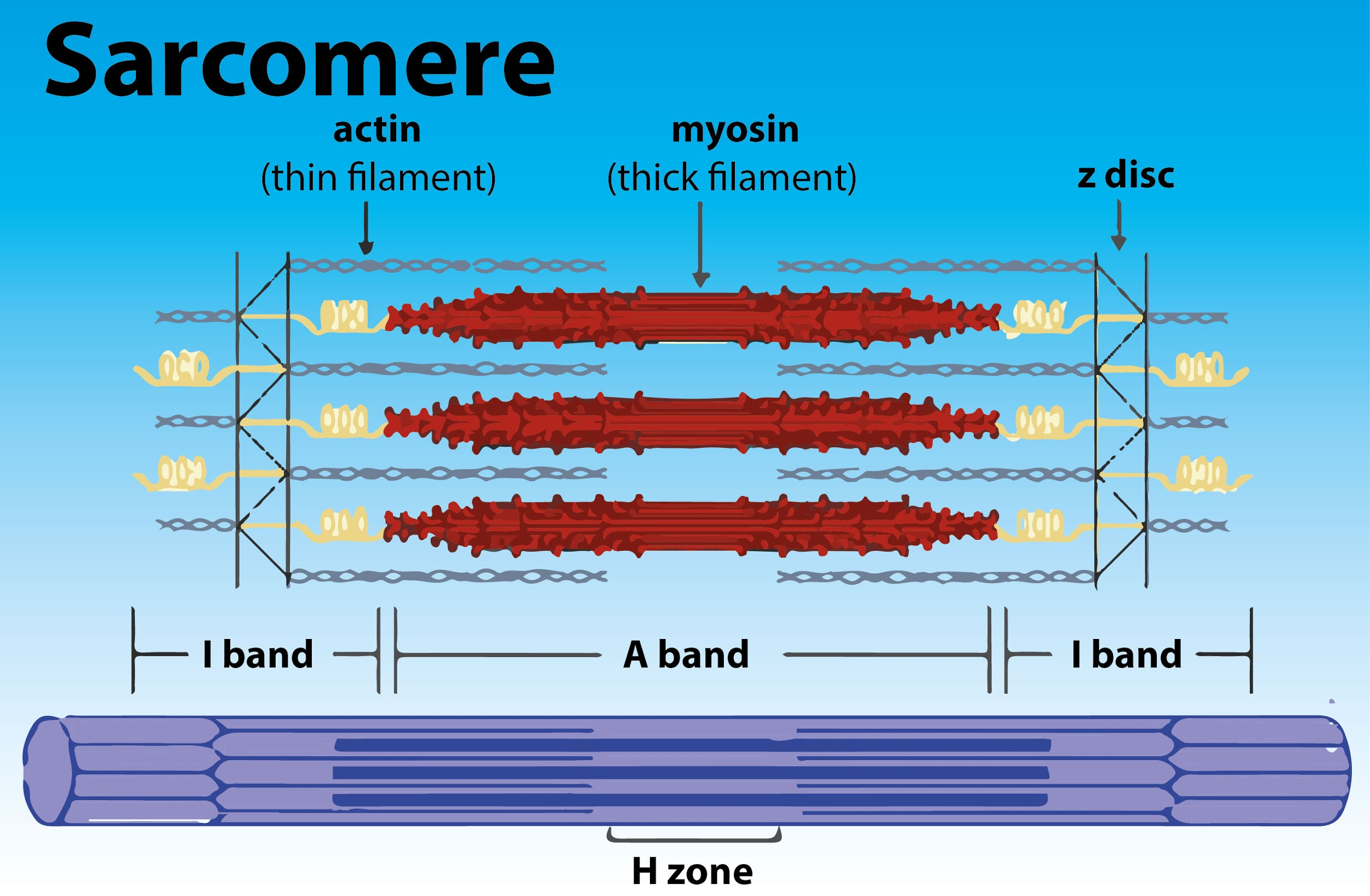
A sarcomere is defined as the myofibril area between two cytoskeletal structures called Z-discs (also known as Z-lines), and the striated appearance of skeletal muscle fibers is due to the arrangement of thick and thin myofilaments within each sarcomere. The dark striated band consists of thick filaments containing myosin, spanning the middle of the sarcomere toward the Z-disc. The thick filaments are anchored by a protein called myomesin at the center of the sarcomere (the M-line). The lighter I band regions contain thin actin filaments which a protein called α-actinin anchors at the Z-discs. The thin filaments extend into the M-line into the A band and overlap with thick filament regions. Owing to the thicker myosin filaments the A band is dark as well as contrast with the actin filaments. The H zone in the center of the A band is a little lighter in color, as the thin filaments do not reach into this area.
Note: Skeletal muscle is the type of muscle that starts all of our voluntary movement. Each skeletal muscle is an organ composed of different integrated tissues. These tissues include the muscle fibers of the body, blood vessels, nerve fibers, and connective tissue. Each skeletal muscle has three layers of connective tissue that enclose it, structure the muscle, and muscle fibers inside the muscle compartmentalize.
Complete answer:

A sarcomere is defined as the myofibril area between two cytoskeletal structures called Z-discs (also known as Z-lines), and the striated appearance of skeletal muscle fibers is due to the arrangement of thick and thin myofilaments within each sarcomere. The dark striated band consists of thick filaments containing myosin, spanning the middle of the sarcomere toward the Z-disc. The thick filaments are anchored by a protein called myomesin at the center of the sarcomere (the M-line). The lighter I band regions contain thin actin filaments which a protein called α-actinin anchors at the Z-discs. The thin filaments extend into the M-line into the A band and overlap with thick filament regions. Owing to the thicker myosin filaments the A band is dark as well as contrast with the actin filaments. The H zone in the center of the A band is a little lighter in color, as the thin filaments do not reach into this area.
Note: Skeletal muscle is the type of muscle that starts all of our voluntary movement. Each skeletal muscle is an organ composed of different integrated tissues. These tissues include the muscle fibers of the body, blood vessels, nerve fibers, and connective tissue. Each skeletal muscle has three layers of connective tissue that enclose it, structure the muscle, and muscle fibers inside the muscle compartmentalize.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




