
Draw the diagram of the embryo sac.
Answer
578.4k+ views
Hint: Three cells are grouped together at the micropylar. It also contains egg apparatus. The filiform apparatus is present at the tip of the micropyle. Two polar nuclei are present at the center.
Complete step by step answer:
1. Ovule is attached to the placenta by a stalk called funicle.
2. Hilum is the region where the funicle fuses with the body of ovules.
3. Integuments are the protective layers that envelopes the ovule. They may be one or two in number.
4. Micropyle is the only part that is not enclosed by internment.
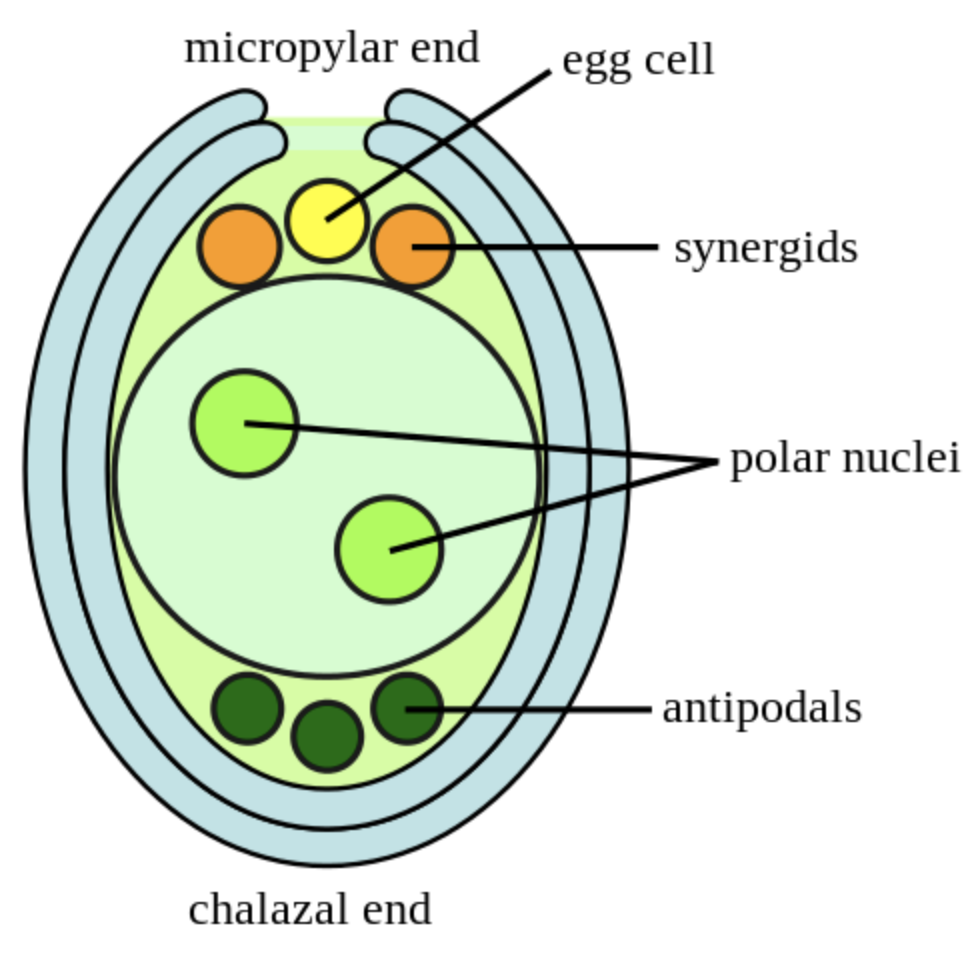
5. The basal part of the ovary called chalaza is present opposite to the micropylar end.
6. The mass of cells that are enclosed in the internment is called nacelles.
7. Embryo Sac or female gametophyte is located in the nucellus
8. The embryo sac is formed from megaspore through the reduction division. Each ovule contains a single embryo sac
9. Ovules are divided into 3 types namely orthotropous, anatropous, and campylotropous
10. Embryo Sac contains egg apparatus which consists of two synergids and one egg cell at the micropylar end where the filiform apparatus is also present. Antipodals are three cells present at the chalazal end.
11. Polygonum is an example of orthotropous ovule.sunflower and bean family members are the examples of anatropous and campylotropous ovules respectively.
Note:
- The ovule is not covered with integument in Loranthus and in helianthus and datura ovary is covered by a single integument. The ovary is covered with two integuments in monocot and polypetalous members.
- The nucellus is considered as a food source for ovules.
- 8-nucleate 7 celled embryo sac is present in a typical angiosperm.
Complete step by step answer:
1. Ovule is attached to the placenta by a stalk called funicle.
2. Hilum is the region where the funicle fuses with the body of ovules.
3. Integuments are the protective layers that envelopes the ovule. They may be one or two in number.
4. Micropyle is the only part that is not enclosed by internment.

5. The basal part of the ovary called chalaza is present opposite to the micropylar end.
6. The mass of cells that are enclosed in the internment is called nacelles.
7. Embryo Sac or female gametophyte is located in the nucellus
8. The embryo sac is formed from megaspore through the reduction division. Each ovule contains a single embryo sac
9. Ovules are divided into 3 types namely orthotropous, anatropous, and campylotropous
10. Embryo Sac contains egg apparatus which consists of two synergids and one egg cell at the micropylar end where the filiform apparatus is also present. Antipodals are three cells present at the chalazal end.
11. Polygonum is an example of orthotropous ovule.sunflower and bean family members are the examples of anatropous and campylotropous ovules respectively.
Note:
- The ovule is not covered with integument in Loranthus and in helianthus and datura ovary is covered by a single integument. The ovary is covered with two integuments in monocot and polypetalous members.
- The nucellus is considered as a food source for ovules.
- 8-nucleate 7 celled embryo sac is present in a typical angiosperm.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




