
Draw the diagram of the pyramid of energy. Explain ‘In the ecosystem, the energy flow is unidirectional’.
Answer
573.9k+ views
Hint: The pyramid of energy shows how energy flows from the first producer of food to the final consumer. There are various levels of consumers because we as humans cannot produce our own food like photosynthesis like algae or plants. The pyramid explains how every organism consumes food and provides itself to the upper consumer.
Complete answer:
- The pyramid of energy represents the amount of energy stored in the form of biomass at each trophic level in an ecosystem.
- Approximately $10\%$ of the energy is transferred from one trophic level to another to prevent a large number of trophic levels.
- The pyramid not only depicts the amount of total energy utilized by organisms at each trophic level of it but also the role of various organisms in the transfer of energy.
- For the ecosystem to sustain itself, there must be more energy at lower trophic levels than there is at higher trophic levels.
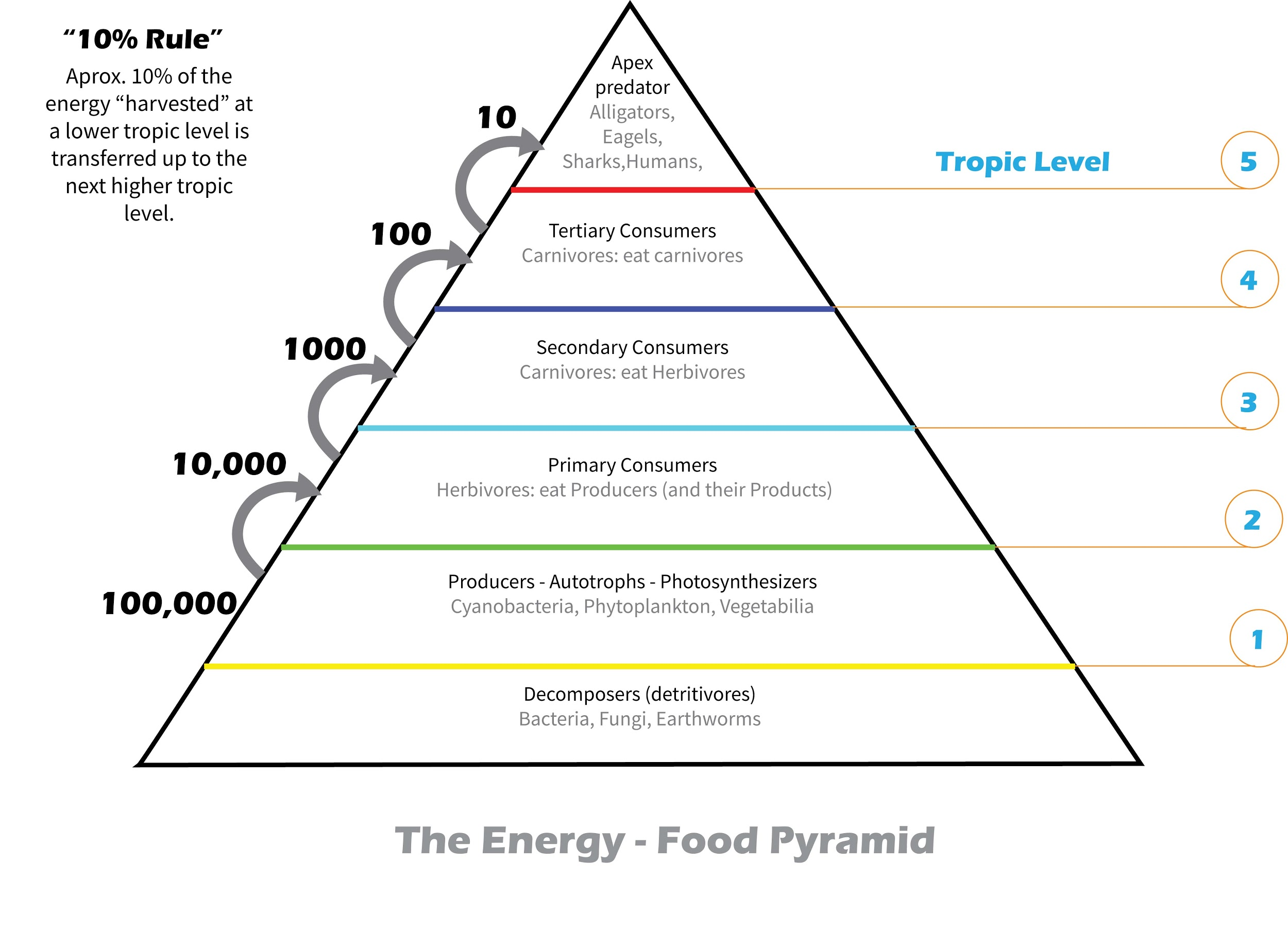
- The pyramid begins at the base with producers that are autotrophs and organisms that carry out photosynthesis, then proceeds to various trophic levels such as herbivores or primary producers, then to secondary consumers such as carnivores, to tertiary consumers like omnivores, and finally to the top of the food chain that consists of humans and apex predators.
- Only $10\%$ of the energy is converted to biomass which becomes stored energy. A portion of the energy is lost to the environment and the rest is used for metabolic processes.
- This pyramid is the only type of ecological pyramid that is upright because the flow of energy in the food chain is unidirectional. The energy taken from the sun is not given back by the producers, the primary consumers do not return the energy back to the producers, and so on. The unidirectional transfer of energy is proven from the collapse of the entire pyramid if the producers or the lowermost tier is eliminated.
- The energy at each level can be monitored here and solar energy is taken into consideration.
Additional information:
- The different types of ecological pyramids are - pyramid of numbers, the pyramid of biomass, and pyramid of energy.
- The disadvantage of having a pyramid of energy is the lack of understanding on which trophic level to assign the decomposers, saprophytes, and detritivores (detritus consumers).
- This pyramid also does not acknowledge food webs.
Note:
- The pyramid of biomass shows the relationship between the energy and trophic level by quantifying the total biomass per trophic level.
- The disadvantage of this pyramid is that the mass that is not consumed by the next energy level, like bones, is also considered while calculating energy.
- Biomass can be measured using a bomb calorimeter.
Complete answer:
- The pyramid of energy represents the amount of energy stored in the form of biomass at each trophic level in an ecosystem.
- Approximately $10\%$ of the energy is transferred from one trophic level to another to prevent a large number of trophic levels.
- The pyramid not only depicts the amount of total energy utilized by organisms at each trophic level of it but also the role of various organisms in the transfer of energy.
- For the ecosystem to sustain itself, there must be more energy at lower trophic levels than there is at higher trophic levels.

- The pyramid begins at the base with producers that are autotrophs and organisms that carry out photosynthesis, then proceeds to various trophic levels such as herbivores or primary producers, then to secondary consumers such as carnivores, to tertiary consumers like omnivores, and finally to the top of the food chain that consists of humans and apex predators.
- Only $10\%$ of the energy is converted to biomass which becomes stored energy. A portion of the energy is lost to the environment and the rest is used for metabolic processes.
- This pyramid is the only type of ecological pyramid that is upright because the flow of energy in the food chain is unidirectional. The energy taken from the sun is not given back by the producers, the primary consumers do not return the energy back to the producers, and so on. The unidirectional transfer of energy is proven from the collapse of the entire pyramid if the producers or the lowermost tier is eliminated.
- The energy at each level can be monitored here and solar energy is taken into consideration.
Additional information:
- The different types of ecological pyramids are - pyramid of numbers, the pyramid of biomass, and pyramid of energy.
- The disadvantage of having a pyramid of energy is the lack of understanding on which trophic level to assign the decomposers, saprophytes, and detritivores (detritus consumers).
- This pyramid also does not acknowledge food webs.
Note:
- The pyramid of biomass shows the relationship between the energy and trophic level by quantifying the total biomass per trophic level.
- The disadvantage of this pyramid is that the mass that is not consumed by the next energy level, like bones, is also considered while calculating energy.
- Biomass can be measured using a bomb calorimeter.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




