
Draw the diagram of villi in the small intestine and label its parts.
Answer
573.9k+ views
Hint:The small intestine is that part of the GI tract responsible for maximum absorption of nutrients from our diet. It is particularly important for absorption of glucose, galactose, and fructose, as digestion of starch begins in the mouth, but stops in the stomach and continues in the intestine.
Complete answer:
About 90% of the digestion and absorption of our food occurs in the small intestines, the remaining taking place in the stomach and large intestine. Bile and pancreatic juices contain various enzymes that assist in this process, though the brush border cells of the villus also have enzymes on their surfaces to help in digestion and absorption. The villi are tiny hair-like projections of the intestinal surface into the lumen of the intestine. These structures increase the available surface area of the intestine enabling extremely efficient breakdown of foods and uptake of nutrients.
The villi are well supplied with blood vessels, lymphatic ducts, and have a very thin epithelium allowing easy absorption of nutrients. The blood vessels are where most of the glucose, amino acids and nucleotides are taken up, while the luteal (lymphatic vessel) is responsible for the absorption of fatty acids. There are about 10-40 villi for every square millimetre of intestinal surface.
The centre of each villus has an artery, vein, lacteal, muscle, and connective tissue for support. The surface is a mucosal membrane with columnar epithelium and goblet cells (which secrete mucus).
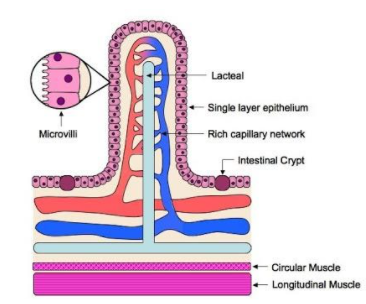
Note:Villi are found in other parts of our bodies as well including the placenta. Being thin walled, they are ideal for transfer of nutrients via diffusion. Each villus then also has several microvilli on the surface.
Complete answer:
About 90% of the digestion and absorption of our food occurs in the small intestines, the remaining taking place in the stomach and large intestine. Bile and pancreatic juices contain various enzymes that assist in this process, though the brush border cells of the villus also have enzymes on their surfaces to help in digestion and absorption. The villi are tiny hair-like projections of the intestinal surface into the lumen of the intestine. These structures increase the available surface area of the intestine enabling extremely efficient breakdown of foods and uptake of nutrients.
The villi are well supplied with blood vessels, lymphatic ducts, and have a very thin epithelium allowing easy absorption of nutrients. The blood vessels are where most of the glucose, amino acids and nucleotides are taken up, while the luteal (lymphatic vessel) is responsible for the absorption of fatty acids. There are about 10-40 villi for every square millimetre of intestinal surface.
The centre of each villus has an artery, vein, lacteal, muscle, and connective tissue for support. The surface is a mucosal membrane with columnar epithelium and goblet cells (which secrete mucus).

Note:Villi are found in other parts of our bodies as well including the placenta. Being thin walled, they are ideal for transfer of nutrients via diffusion. Each villus then also has several microvilli on the surface.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




