
Draw the electron dot structure of the ethane molecule $C_{2}H_{6}$
Answer
585.3k+ views
Hint: Electron dot structure, also known as lewis dot structure is used to indicate how the constituent atoms of a molecule are bonded. It is usually represented as the chemical symbol of a molecule surrounded by a number of dots which represent the valence electron of the atom.
Complete step by step answer: The rules that need to be followed while drawing the lewis dot structure are given below:
-Write the symbol for the atoms involved to show which atom is connected to which.
-Add the number of all valence electrons. If the molecule is neutral then it is just the sum of the valence electron of all the atoms present. In the case of negatively charged ions, add the number of charges in the number of valence electrons whereas in the case of positively charged ions subtract the number of charges from the number of valence electrons.
-Draw the single bond between each pair of the atom to be connected by bonding.
-Complete the octet of atoms attached to the central atom by adding electron pairs.
-Place the remaining electron on the central atom in pairs.
-If the central atom does not have an octet, form a double bond. If necessary, form a triple bond.
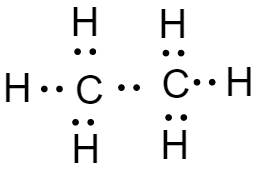
-In the case of ethane, each carbon atom makes three bonds with three hydrogen atoms and one bond with other carbon atoms to complete its octet.thus the lewis dot structure of ethane is:
Note: There are some limitations to the lewis dot structure.
-It fails to explain the cause of covalent bond formation.
-We cannot explain the nature of the attractive force between the constituent atom of a molecule using this structure.
-The geometry of molecules containing a covalent bond cannot be explained using this structure.
-No information about the energy released during covalent bond formation is available in this structure.
Complete step by step answer: The rules that need to be followed while drawing the lewis dot structure are given below:
-Write the symbol for the atoms involved to show which atom is connected to which.
-Add the number of all valence electrons. If the molecule is neutral then it is just the sum of the valence electron of all the atoms present. In the case of negatively charged ions, add the number of charges in the number of valence electrons whereas in the case of positively charged ions subtract the number of charges from the number of valence electrons.
-Draw the single bond between each pair of the atom to be connected by bonding.
-Complete the octet of atoms attached to the central atom by adding electron pairs.
-Place the remaining electron on the central atom in pairs.
-If the central atom does not have an octet, form a double bond. If necessary, form a triple bond.
-In the case of ethane, each carbon atom makes three bonds with three hydrogen atoms and one bond with other carbon atoms to complete its octet.thus the lewis dot structure of ethane is:

Note: There are some limitations to the lewis dot structure.
-It fails to explain the cause of covalent bond formation.
-We cannot explain the nature of the attractive force between the constituent atom of a molecule using this structure.
-The geometry of molecules containing a covalent bond cannot be explained using this structure.
-No information about the energy released during covalent bond formation is available in this structure.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




