
Draw the flow charts for singular circulation and double circulation.
Answer
550.8k+ views
Hint: The circulatory system is responsible for transporting the body and metabolic waste products away from the body, nutrients and gases such as oxygen. In circulating and purifying blood throughout the body, the heart and the lungs play an important role.
Complete answer:
Two types of circulatory systems exist in animals: an open circulatory system and a closed circulatory system. A double circulatory system is used by the majority of mammals, including humans. Based on the number of times blood circulation takes place through the heart, the closed circulatory system is further classified into two types:
1. Singular Circulation
2. Double circulation
Single Circulation:
The blood will pass through the heart to the gills in a single circulatory system, and then blood will be distributed to different parts of the body after purification. It completes only one cardiac cycle, hence the name single circulation. Single circulation, for example, is mainly seen in birds, fish, reptiles, etc.
Double Circulation:
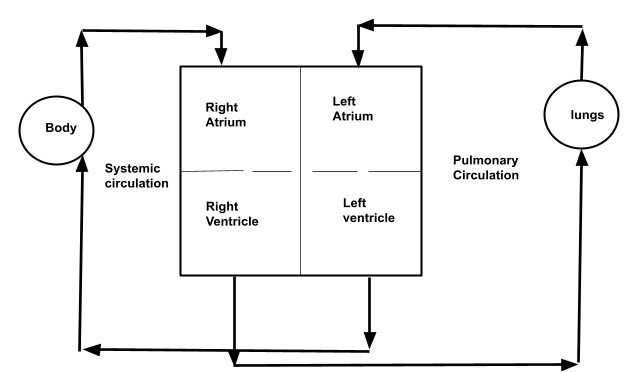
The heart is the key organ for blood circulation, and as it provides an efficient way of circulation, double circulation is an effective method of circulation. The primary difference is that two routes are followed by the blood, one for oxygenated blood and the other for deoxygenated blood. Hence the name "double circulation." A double circulatory system is used by most mammals, including humans.
The human heart is divided into four chambers:
1) Left Atria
2) Right Atria
3) Left Ventricles
4) Right Ventricles
Further, through the pulmonary artery and vein, the heart is connected to the lungs. There are two pathways in dual circulation in which the blood flows. They are:
systemic Circulation
Oxygenated blood from the left ventricles is transported to the tissue capillaries by systemic circulation.
In order to circulate to different areas of the body, oxygen-rich blood is transported to the aorta.
Later, from different parts of the body, the veins and venules absorb the deoxygenated blood, which is rich in carbon dioxide.
Through the superior vena cava and then to the right atrium, the deoxygenated blood is pumped out.
Once, the right atrium carries blood to the right ventricle for pulmonary circulation after receiving the deoxygenated blood.
Pulmonary Circulation
Blood circulation begins in the pulmonary circulation, from the right atrium to the left atrium. Along this path:
The pulmonary artery gathers blood from the right ventricle for oxygenation and transfers it to the lungs.
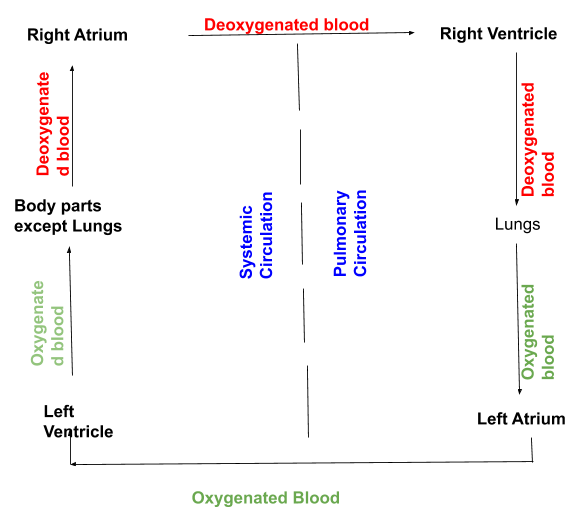
Once, the oxygenated blood is pumped back to the left atrium via the pulmonary vein that is brought to the left ventricles during the purification process.
For systemic circulation, the left ventricles pump oxygenated blood to the aorta.
Note: A strict distinction of both oxygenated and deoxygenated blood is facilitated by double circulation. This circulation thus ensures that the body still has a dedicated oxygen supply and thus increases body quality. This is also one of the reasons why their body temperatures can be preserved by mammals. A third portal system, in addition to double circulation, also exists to increase circulation quality.
Complete answer:
Two types of circulatory systems exist in animals: an open circulatory system and a closed circulatory system. A double circulatory system is used by the majority of mammals, including humans. Based on the number of times blood circulation takes place through the heart, the closed circulatory system is further classified into two types:
1. Singular Circulation
2. Double circulation
Single Circulation:
The blood will pass through the heart to the gills in a single circulatory system, and then blood will be distributed to different parts of the body after purification. It completes only one cardiac cycle, hence the name single circulation. Single circulation, for example, is mainly seen in birds, fish, reptiles, etc.

Double Circulation:
The heart is the key organ for blood circulation, and as it provides an efficient way of circulation, double circulation is an effective method of circulation. The primary difference is that two routes are followed by the blood, one for oxygenated blood and the other for deoxygenated blood. Hence the name "double circulation." A double circulatory system is used by most mammals, including humans.
The human heart is divided into four chambers:
1) Left Atria
2) Right Atria
3) Left Ventricles
4) Right Ventricles
Further, through the pulmonary artery and vein, the heart is connected to the lungs. There are two pathways in dual circulation in which the blood flows. They are:
systemic Circulation
Oxygenated blood from the left ventricles is transported to the tissue capillaries by systemic circulation.
In order to circulate to different areas of the body, oxygen-rich blood is transported to the aorta.
Later, from different parts of the body, the veins and venules absorb the deoxygenated blood, which is rich in carbon dioxide.
Through the superior vena cava and then to the right atrium, the deoxygenated blood is pumped out.
Once, the right atrium carries blood to the right ventricle for pulmonary circulation after receiving the deoxygenated blood.
Pulmonary Circulation
Blood circulation begins in the pulmonary circulation, from the right atrium to the left atrium. Along this path:
The pulmonary artery gathers blood from the right ventricle for oxygenation and transfers it to the lungs.

Once, the oxygenated blood is pumped back to the left atrium via the pulmonary vein that is brought to the left ventricles during the purification process.
For systemic circulation, the left ventricles pump oxygenated blood to the aorta.
Note: A strict distinction of both oxygenated and deoxygenated blood is facilitated by double circulation. This circulation thus ensures that the body still has a dedicated oxygen supply and thus increases body quality. This is also one of the reasons why their body temperatures can be preserved by mammals. A third portal system, in addition to double circulation, also exists to increase circulation quality.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




