
Draw the graph of :
(i) Mass against K.E when velocity is constant
(ii) K.E against velocity when mass is constant
Answer
581.4k+ views
Hint:In order to draw the graph,we are going to use the relation of kinetic energy that contains mass and velocity quantity and after comparing it with the standard set of equations of the curve from mathematics we can arrive at the desired result.
Formula used:
kinetic energy in terms of mass and velocity
$KE = \dfrac{1}{2}m{v^2}$
Where
m $ = $ mass of body
v $ = $ velocity of body
Complete step by step answer:
We know that the kinetic energy is given is terms of mass and velocity as :
$KE = \dfrac{1}{2}m{v^2}$
(i) If velocity is constant them
$KE \propto m(mass)$
Here we can see, the above relation is similar to the equation of straight line. So, the graph will be following as :
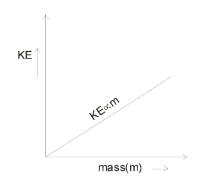
(ii) If mass is constant them
$KE. \propto {v^2}$
Here, we can see the above relation is similar to the equation of parabolic.
So, the graph will be following as :
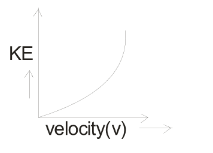
Note: Many times students may get confused between kinetic energy, potential energy and mechanical energy.
-Kinetic energy is the energy which his possesses due to its motion and given as :
$KE = \dfrac{1}{2}m{v^2}$
-Potential energy is the energy held by an object because of its position relative to other objects. It is also known as rest mass energy.
-Mechanical energy is the sum of KE and PE, also known as total energy.
Mechanical energy $ = KE + PE$
Formula used:
kinetic energy in terms of mass and velocity
$KE = \dfrac{1}{2}m{v^2}$
Where
m $ = $ mass of body
v $ = $ velocity of body
Complete step by step answer:
We know that the kinetic energy is given is terms of mass and velocity as :
$KE = \dfrac{1}{2}m{v^2}$
(i) If velocity is constant them
$KE \propto m(mass)$
Here we can see, the above relation is similar to the equation of straight line. So, the graph will be following as :

(ii) If mass is constant them
$KE. \propto {v^2}$
Here, we can see the above relation is similar to the equation of parabolic.
So, the graph will be following as :

Note: Many times students may get confused between kinetic energy, potential energy and mechanical energy.
-Kinetic energy is the energy which his possesses due to its motion and given as :
$KE = \dfrac{1}{2}m{v^2}$
-Potential energy is the energy held by an object because of its position relative to other objects. It is also known as rest mass energy.
-Mechanical energy is the sum of KE and PE, also known as total energy.
Mechanical energy $ = KE + PE$
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




