
Draw the labelled diagram of the electrolytic cell of alumina and write the chemical reactions taking place in it?
Answer
559.2k+ views
Hint: Before drawing the cell try to identify the solvent, and electrodes. After that, refer to the electrode potentials of the electrodes to know where oxidation will take place and where reduction will take place. Then write the respective chemical reactions taking place and then finally draw the electrolytic cell.
Complete step by step answer:
Alumina is the common name given to aluminum oxide ($A{{l}_{2}}{{O}_{3}}$). Alumina is produced from the ore bauxite, that is mined from topsoil in various tropical and subtropical regions.
- The Bayer process, discovered in 1887, is the primary process by which pure alumina can be extracted from bauxite. This process is used to separate alumina from its ore impurities like iron(III) oxide.
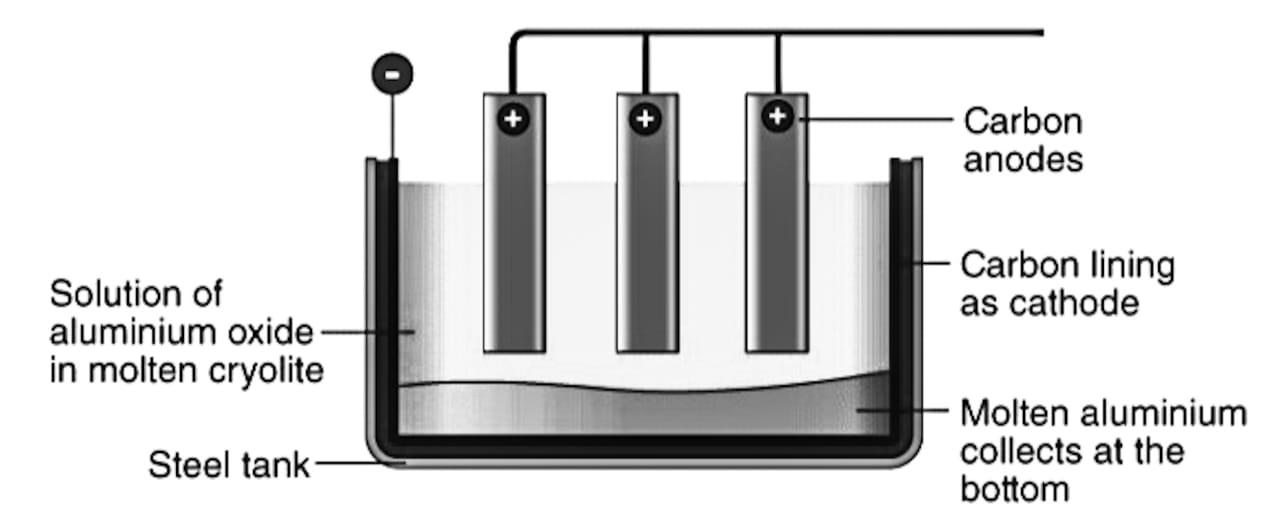
- The process through which alumina is purified is called the Hall-Heroult process. Electrolysis of alumina is done in an iron tank fitted with a carbon lining that acts a cathode. Graphite rod acts as an anode and a bulb is fitted in parallel combination as an indicator for alumina content.
- The electrolyte is a mixture of alumina and cryolite($N{{a}_{3}}Al{{F}_{6}}$). The melting point of alumina is very high ( about ${{2050}^{0}}C$). However, in addition to cryolite and fluorspar ($Ca{{F}_{2}}$), the mixture melts at ${{870}^{0}}C$.
- The below chemical reaction takes place:
$\text{N}{{\text{a}}_{\text{3}}}\text{Al}{{\text{F}}_{\text{6}}}\text{ }\to \text{ 3NaF + Al}{{\text{F}}_{3}}$
$\text{Al}{{\text{F}}_{3}}\text{ }\to \text{ A}{{\text{l}}^{+3}}\text{ + 3}{{\text{F}}^{-}}$
$3{{\text{F}}^{-}}\text{ }\to \text{ 3F + 3}{{\text{e}}^{-}}$ (oxidation at anode)
$\text{A}{{\text{l}}^{+3}}\text{ + 3}{{\text{e}}^{-}}\text{ }\to \text{ Al}$(reduction at cathode)
$2\text{A}{{\text{l}}_{2}}{{\text{O}}_{3}}\text{ + 12F }\to \text{ 4Al}{{\text{F}}_{3}}\text{ + 3}{{\text{O}}_{2}}\uparrow $
- The diagram of electrolytic cell of alumina is as follows:
Note: The electrolysis of alumina to obtain pure aluminium is called Hoopes process. The flux used in the Hall-Heroult process is used as electrolyte is Hoopes process. The flux is a mixture of cryolite and fluorspar. In the electrolysis process three layers are formed,
- impure Al at the bottom,
- cryolite in the middle,
- pure Al at the top.
Complete step by step answer:
Alumina is the common name given to aluminum oxide ($A{{l}_{2}}{{O}_{3}}$). Alumina is produced from the ore bauxite, that is mined from topsoil in various tropical and subtropical regions.
- The Bayer process, discovered in 1887, is the primary process by which pure alumina can be extracted from bauxite. This process is used to separate alumina from its ore impurities like iron(III) oxide.
- The process through which alumina is purified is called the Hall-Heroult process. Electrolysis of alumina is done in an iron tank fitted with a carbon lining that acts a cathode. Graphite rod acts as an anode and a bulb is fitted in parallel combination as an indicator for alumina content.
- The electrolyte is a mixture of alumina and cryolite($N{{a}_{3}}Al{{F}_{6}}$). The melting point of alumina is very high ( about ${{2050}^{0}}C$). However, in addition to cryolite and fluorspar ($Ca{{F}_{2}}$), the mixture melts at ${{870}^{0}}C$.
- The below chemical reaction takes place:
$\text{N}{{\text{a}}_{\text{3}}}\text{Al}{{\text{F}}_{\text{6}}}\text{ }\to \text{ 3NaF + Al}{{\text{F}}_{3}}$
$\text{Al}{{\text{F}}_{3}}\text{ }\to \text{ A}{{\text{l}}^{+3}}\text{ + 3}{{\text{F}}^{-}}$
$3{{\text{F}}^{-}}\text{ }\to \text{ 3F + 3}{{\text{e}}^{-}}$ (oxidation at anode)
$\text{A}{{\text{l}}^{+3}}\text{ + 3}{{\text{e}}^{-}}\text{ }\to \text{ Al}$(reduction at cathode)
$2\text{A}{{\text{l}}_{2}}{{\text{O}}_{3}}\text{ + 12F }\to \text{ 4Al}{{\text{F}}_{3}}\text{ + 3}{{\text{O}}_{2}}\uparrow $
- The diagram of electrolytic cell of alumina is as follows:

Note: The electrolysis of alumina to obtain pure aluminium is called Hoopes process. The flux used in the Hall-Heroult process is used as electrolyte is Hoopes process. The flux is a mixture of cryolite and fluorspar. In the electrolysis process three layers are formed,
- impure Al at the bottom,
- cryolite in the middle,
- pure Al at the top.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




