
How do you draw the Lewis structure for $Se{{O}_{2}}$? What is the electron geometry around the central atom?
Answer
564.9k+ views
Hint:$Se{{O}_{2}}$ is a chemical compound known by the name selenium dioxide. It is colorless solid which is a one-dimensional polymer having the chain which consists of alternating selenium and oxygen atoms.
Complete answer:
Lewis structure basically tells us how the electrons are paired. In this every dot represents an electron and pair of dots between chemical symbols for atoms represents the bond. The main steps of draw a Lewis structure are as follows:
1. Central atom is that atom which is most electronegative in nature here central atom will be $Se$.
2. Calculate the valence electrons present in the molecule this can be calculated by adding the valency of individual atoms in the given molecule. In case of $Se{{O}_{2}}$ valence electrons are 18 given by $1Se+2O=1\times 6+2\times 6=18$
3. After that we have to calculate the formal charge present on the atom which describes that one oxygen atom contains negative charge of 1 and selenium contain positive charge of 1.
3. After that we have to find the bonding electrons which can be calculated by subtracting the octet electrons from valence electrons i.e. $18-10=8$
4. But we have to generate a structure with zero formal charge which can be possible if we move a lone pair from the single bonded oxygen to make a double bond with selenium.
By this we can draw the Lewis structure of $Se{{O}_{2}}$ which can be shown as follows:
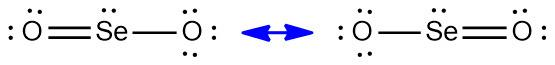
Electron geometry around the central atom will be triangular planar as there are three electron domains around the $Se$ atom.
Note:
If we know the molecular formula of any compound we can easily draw its Lewis dot structure which is also known by the name electron dot structure. These diagrams generally describe the chemical bonding between atoms in a molecule and also display the total number of lone pairs present in each of the atoms.
Complete answer:
Lewis structure basically tells us how the electrons are paired. In this every dot represents an electron and pair of dots between chemical symbols for atoms represents the bond. The main steps of draw a Lewis structure are as follows:
1. Central atom is that atom which is most electronegative in nature here central atom will be $Se$.
2. Calculate the valence electrons present in the molecule this can be calculated by adding the valency of individual atoms in the given molecule. In case of $Se{{O}_{2}}$ valence electrons are 18 given by $1Se+2O=1\times 6+2\times 6=18$
3. After that we have to calculate the formal charge present on the atom which describes that one oxygen atom contains negative charge of 1 and selenium contain positive charge of 1.
3. After that we have to find the bonding electrons which can be calculated by subtracting the octet electrons from valence electrons i.e. $18-10=8$
4. But we have to generate a structure with zero formal charge which can be possible if we move a lone pair from the single bonded oxygen to make a double bond with selenium.
By this we can draw the Lewis structure of $Se{{O}_{2}}$ which can be shown as follows:

Electron geometry around the central atom will be triangular planar as there are three electron domains around the $Se$ atom.
Note:
If we know the molecular formula of any compound we can easily draw its Lewis dot structure which is also known by the name electron dot structure. These diagrams generally describe the chemical bonding between atoms in a molecule and also display the total number of lone pairs present in each of the atoms.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




