
Draw the nucleus and label its parts. What is the function of the nucleus in a cell?
Answer
574.8k+ views
Hint: The nucleus is known as the cell's director or controller. It is the location where the second process of central dogma takes place. The genetic material is in the nucleus. It also controls growth and cell metabolism.
Complete answer:
Structure of the nucleus:
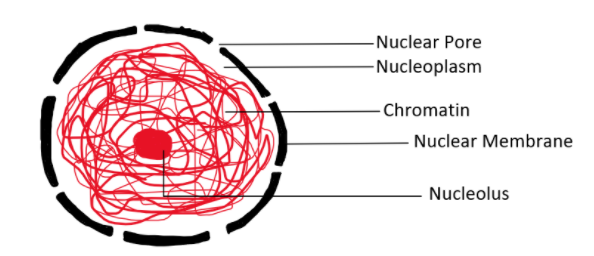
Functions of the nucleus in a cell are:
-The nucleus provides a genetic transcription site that is isolated from the translation site in the cytoplasm, enabling degrees of gene regulation not available to prokaryotes.
-During the cell cycle, the main purpose of the cell nucleus is to regulate gene expression and mediate DNA replication.
-It regulates an organism's genetic features.
-Protein synthesis, cell division, development, and differentiation are also the responsibility of the organelle.
Additional Information: -The genes in the form of long and thin DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) chains, referred to as chromatin, are stored as inherited material.
-Protein and RNA (ribonucleic acid) storage in the nucleolus takes place.
The nucleus is a transcription site where messenger RNA (mRNA) is produced for the synthesis of proteins.
-Chromatins are organized into chromosomes in the nucleus during cell division.
-Ribosome processing (protein factories) occurs in the nucleolus.
Note: The nucleus is an organelle that is double membrane-bound. Two membranes, an outer membrane, and an inner membrane form the nuclear envelope. The apertures known as nuclear pores perforate the nuclear membrane. Nuclear membranes surround the nucleus cytoplasm, known as the nucleoplasm. DNA is present in the form of chromatin in the nucleoplasm. The chromatin condenses and thickens into chromosomes as the cell prepares to divide. A spherical body known as a nucleolus is present inside the nucleus, and is closely associated with the nucleolar organizer area of two or more chromosomes of the collection.
Complete answer:
Structure of the nucleus:

Functions of the nucleus in a cell are:
-The nucleus provides a genetic transcription site that is isolated from the translation site in the cytoplasm, enabling degrees of gene regulation not available to prokaryotes.
-During the cell cycle, the main purpose of the cell nucleus is to regulate gene expression and mediate DNA replication.
-It regulates an organism's genetic features.
-Protein synthesis, cell division, development, and differentiation are also the responsibility of the organelle.
Additional Information: -The genes in the form of long and thin DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) chains, referred to as chromatin, are stored as inherited material.
-Protein and RNA (ribonucleic acid) storage in the nucleolus takes place.
The nucleus is a transcription site where messenger RNA (mRNA) is produced for the synthesis of proteins.
-Chromatins are organized into chromosomes in the nucleus during cell division.
-Ribosome processing (protein factories) occurs in the nucleolus.
Note: The nucleus is an organelle that is double membrane-bound. Two membranes, an outer membrane, and an inner membrane form the nuclear envelope. The apertures known as nuclear pores perforate the nuclear membrane. Nuclear membranes surround the nucleus cytoplasm, known as the nucleoplasm. DNA is present in the form of chromatin in the nucleoplasm. The chromatin condenses and thickens into chromosomes as the cell prepares to divide. A spherical body known as a nucleolus is present inside the nucleus, and is closely associated with the nucleolar organizer area of two or more chromosomes of the collection.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




