
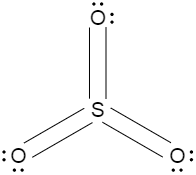
Draw the resonance hybrid of $S{{O}_{3}}$
Answer
569.4k+ views
Hint: The concept of resonance was formerly introduced in order to deal with the kind of difficulty experienced in the depiction of accurate structures of molecules.
The phenomena of resonance is represented by a double headed arrow. Each structure of resonance has an equal contribution to the resonance hybrid structure and no individual structure is totally responsible for the final structure.
Complete step by step answer:
According to the concept of resonance, whenever a single Lewis structure cannot describe a molecule accurately, a number of structures with similar energy, positions of nuclei, bonding as well as non-bonding pairs of the involved electrons are taken as the resonating structures of the hybrid which describes the molecule accurately.
In the given structures, we can see that the double bond characteristics of the sulphur and oxygen is not present at any one oxygen, it keeps on delocalisation, or in other words, the pi electron cloud present in the double bond, keeps on delocalisation and shifting between the three oxygen atoms which are attached to the sulphur.
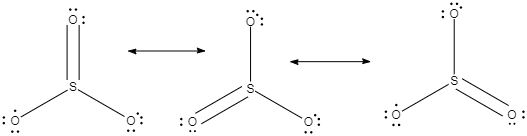
We can see that the Lewis structure, in each of them the sulphur has a formal charge of $+2$ and two of the oxygen atoms have $-1$ charge.
Now, in each of the three structures which are present in the middle, we can see that the $S$ has a formal charge of $+1$ and one of $O$ atoms has a formal charge of $-1$.
Now if we consider each of the structures present at the bottom, the formal charge is zero.
Note: The phenomena of resonance results in stabilisation of a molecule, as the electron clouds are more delocalised throughout the whole molecule, and no electron cloud is localised in just one atom.
Due to which the energy of the resonance hybrid is much less as compared to the energy of any single resonating structure.
The phenomena of resonance is represented by a double headed arrow. Each structure of resonance has an equal contribution to the resonance hybrid structure and no individual structure is totally responsible for the final structure.
Complete step by step answer:
According to the concept of resonance, whenever a single Lewis structure cannot describe a molecule accurately, a number of structures with similar energy, positions of nuclei, bonding as well as non-bonding pairs of the involved electrons are taken as the resonating structures of the hybrid which describes the molecule accurately.
In the given structures, we can see that the double bond characteristics of the sulphur and oxygen is not present at any one oxygen, it keeps on delocalisation, or in other words, the pi electron cloud present in the double bond, keeps on delocalisation and shifting between the three oxygen atoms which are attached to the sulphur.



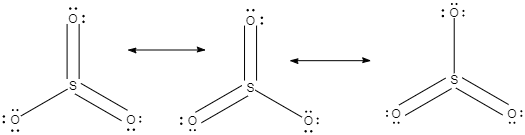
We can see that the Lewis structure, in each of them the sulphur has a formal charge of $+2$ and two of the oxygen atoms have $-1$ charge.
Now, in each of the three structures which are present in the middle, we can see that the $S$ has a formal charge of $+1$ and one of $O$ atoms has a formal charge of $-1$.
Now if we consider each of the structures present at the bottom, the formal charge is zero.
Note: The phenomena of resonance results in stabilisation of a molecule, as the electron clouds are more delocalised throughout the whole molecule, and no electron cloud is localised in just one atom.
Due to which the energy of the resonance hybrid is much less as compared to the energy of any single resonating structure.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




