
Draw the structure of \[\text{BeC}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}\] in solid state and vapour state.
Answer
520.1k+ views
Hint: Solve this question by drawing its structure first. Keep in mind that all elements have the ultimate tendency to achieve stability by completing its octet.
Complete step by step answer:
\[\text{BeC}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}\] is the chemical formula of beryllium chloride, with molar mass around 7.72 g/mol. It is an inorganic compound which occurs as a colorless, hygroscopic solid, which is soluble in polar solvents. Its monomer occurs as:
Cl – Be – Cl
which is a sp hybridized molecule and therefore has a linear shape.
However, \[\text{BeC}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}\] exists in different forms in solid and vapour states.
The structure of \[\text{BeC}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}\] in vapour state is as given below –
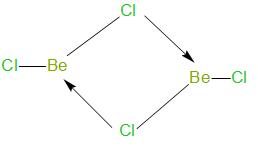 As we can see, in vapour state, it exists as a bridge dimer.
As we can see, in vapour state, it exists as a bridge dimer.
The structure of \[\text{BeC}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}\] in solid state is as given below –
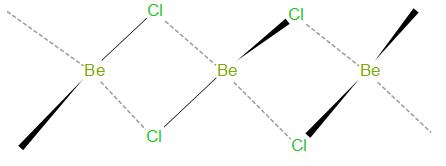 As we can see, in solid state it forms a bridge like structure.
As we can see, in solid state it forms a bridge like structure.
In solid state, Beryllium chloride forms a polymer structure. Beryllium has two empty orbitals after it forms covalent bonds with chlorine atoms. Therefore, it forms two coordinate bonds with neighboring chlorine atoms to complete its octet. This leads to formation of \[\text{B}{{\text{e}}_{\text{2}}}\text{C}{{\text{l}}_{\text{6}}}\], which has a tetrahedral geometry.
Note: Beryllium chloride is very stable in dry air, but it is hygroscopic (i.e. it absorbs moisture) and forms a tetrahydrate, \[\text{BeC}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}\text{.4}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{O}\].
It dissolves in water to undergo hydrolysis and evolve hydrochloric acid:
\[\text{BeC}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}+2{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{O} \to \text{Be(OH}{{\text{)}}_{\text{2}}}\text{+2HCl}\]
Complete step by step answer:
\[\text{BeC}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}\] is the chemical formula of beryllium chloride, with molar mass around 7.72 g/mol. It is an inorganic compound which occurs as a colorless, hygroscopic solid, which is soluble in polar solvents. Its monomer occurs as:
Cl – Be – Cl
which is a sp hybridized molecule and therefore has a linear shape.
However, \[\text{BeC}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}\] exists in different forms in solid and vapour states.
The structure of \[\text{BeC}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}\] in vapour state is as given below –

The structure of \[\text{BeC}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}\] in solid state is as given below –

In solid state, Beryllium chloride forms a polymer structure. Beryllium has two empty orbitals after it forms covalent bonds with chlorine atoms. Therefore, it forms two coordinate bonds with neighboring chlorine atoms to complete its octet. This leads to formation of \[\text{B}{{\text{e}}_{\text{2}}}\text{C}{{\text{l}}_{\text{6}}}\], which has a tetrahedral geometry.
Note: Beryllium chloride is very stable in dry air, but it is hygroscopic (i.e. it absorbs moisture) and forms a tetrahydrate, \[\text{BeC}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}\text{.4}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{O}\].
It dissolves in water to undergo hydrolysis and evolve hydrochloric acid:
\[\text{BeC}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}+2{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{O} \to \text{Be(OH}{{\text{)}}_{\text{2}}}\text{+2HCl}\]
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




