
Draw the structure of Eukaryotic cell(Plant cell)
Answer
554.7k+ views
Hint: There are membrane-bound organelles such as a nucleus, mitochondria, and an endoplasmic reticulum in a eukaryotic cell. Eukaryotic cell related species include protozoa, fungi, plants, and animals. These species are classified into Eukaryota, the biological realm.
Complete answer:
The distinction between the eukaryotic cell and the prokaryotic cell is simple: the eukaryotic cells of the membrane-bound organelles. In a prokaryotic cell (such as a bacteria) the DNA actually floats around the cytoplasm. Although prokaryotic cells have one type of organelle (ribosomes), these organelles are not protected by a plasma membrane.
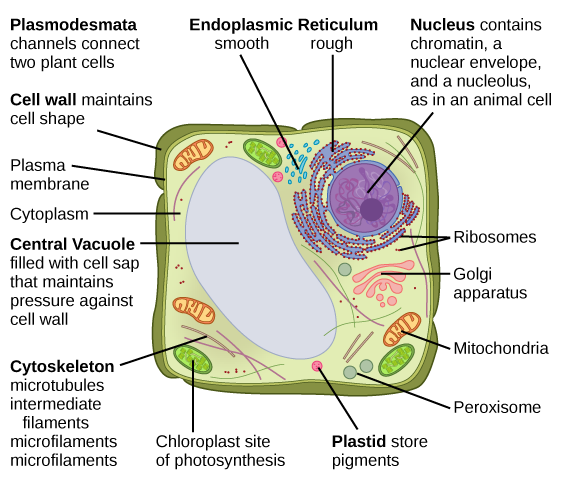
Plant cells are eukaryotic cells that differ in a number of fundamental factors from other eukaryotic organisms. Plant and animal cells, along with similar organelles, contain nucleus. One of the distinctive features of a plant cell is the presence of a cell wall outside the cell membrane.
The cell of a plant is rectangular and relatively bigger than the cell of an animal. Although plant and animal cells are eukaryotic and share a few cell organelles, plant cells are quite distinct when compared to animal cells because they have different functions. Some of these differences can be clearly understood when the cells are examined by an electron microscope.
Note: The cells of the matured and higher plant become specialised in performing certain vital functions that are essential for their survival. Few plant cells are involved in the transport of nutrients and water, while others are involved in food storage.
Specialized plant cells include parenchyma cells, sclerenchyma cells, collenchyma cells, xylem cells and phloem cells.
Complete answer:
The distinction between the eukaryotic cell and the prokaryotic cell is simple: the eukaryotic cells of the membrane-bound organelles. In a prokaryotic cell (such as a bacteria) the DNA actually floats around the cytoplasm. Although prokaryotic cells have one type of organelle (ribosomes), these organelles are not protected by a plasma membrane.
Plant cells are eukaryotic cells that differ in a number of fundamental factors from other eukaryotic organisms. Plant and animal cells, along with similar organelles, contain nucleus. One of the distinctive features of a plant cell is the presence of a cell wall outside the cell membrane.
The cell of a plant is rectangular and relatively bigger than the cell of an animal. Although plant and animal cells are eukaryotic and share a few cell organelles, plant cells are quite distinct when compared to animal cells because they have different functions. Some of these differences can be clearly understood when the cells are examined by an electron microscope.
| Structure | Function |
| Cell wall | The primary function of the cell wall is to protect and provide structural support for the cell wall. |
| Cell membrane | It plays an important role in regulating the entry and exit of specific substances into the cell. |
| Nucleus | The vital function of the nucleus is to store the DNA or hereditary information needed for cell division, metabolism and growth. |
| Plastids | Leucoplasts-For storage of proteins , lipids and starch.Chloroplasts- A green pigment Used for photosynthesis.Chromoplasts- have red, orange and yellow pigments that give colour to all ripe fruits and flowers. |
| Central vacuole | The important function of the central vacuole, in addition to storage, is to maintain turgor pressure against the cell wall. The central vacuole consists of a sap in the cell. It's a blend of salts, enzymes and other compounds. |
| Golgi apparatus | They are found in all eukaryotic cells that are involved in the distribution of synthesised macromolecules to different parts of the cell. |
| Ribosomes | They are the smallest membrane-bound organelles made up of RNA and protein. They are the sites for protein synthesis, which is why they are also referred to as cell protein factories. |
| Mitochondria | They are the double-membrane organelles found in the cytoplasm of all eukaryotic cells. They provide energy by breaking down carbohydrates and sugar molecules, which is why they are also referred to as the cell powerhouse. |
| Lysosomes | Lysosomes are called suicidal sacs because they hold digestive enzymes in the enclosed membrane. They perform the function of cell waste disposal by digesting worn-out organelles, food particles and foreign cells in the cell. |

Note: The cells of the matured and higher plant become specialised in performing certain vital functions that are essential for their survival. Few plant cells are involved in the transport of nutrients and water, while others are involved in food storage.
Specialized plant cells include parenchyma cells, sclerenchyma cells, collenchyma cells, xylem cells and phloem cells.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




