
Draw the structure of S-cis and S-trans form of 1, 3-butadiene.
Answer
584.1k+ views
Hint:To solve this question, it is required to have knowledge about cis and trans isomers. 1, 3-butadiene consists of two double bonds on alternating positions. So, instead of determining cis and trans with respect to the double bonded carbons, its structure is determined by the position of the double bonds with respect to the central single bond.
Complete step by step answer:
1, 3-butadiene falls under the category of conjugated dienes, the double bonds are in conjugation with each other which increases the stability of the compound. Normally it is represented as:
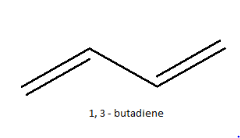
This is just the normal representation without any geometrical isomerisation. Normally, in case of double bonds, isomerism is determined by the atoms or groups attached to either end of the double bond, classifying it as either as cis or trans isomers or as E or Z isomers. If similar groups are on the same side of the double bond, it is cis isomer. If similar groups are attached on the opposite side of the double bond, it is trans isomer.In the case of 1, 3-butadiene, the presence of two double bonds makes the case complicated. So, instead of classifying both their double bonds only the single bond in between is considered and the isomers are named as S-cis or S-trans, where S stands for single. So, when both the double bonds are on the same side, it is names as S-cis and when they are on the opposite side, it is named S-trans. Their structures are:
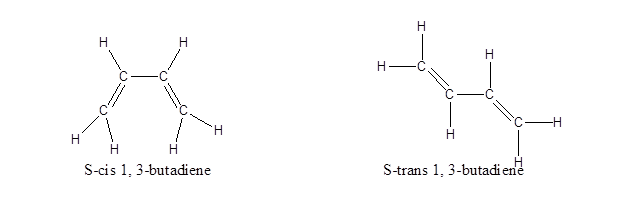
Note:
Conjugated dienes are more stable as both the double bonds are in hyper conjugation with each other which stabilises the structure, forming partial double bond character on all the three C-C bonds.
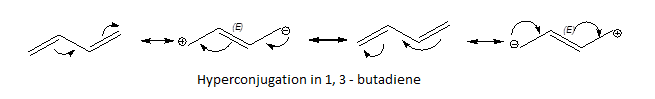

Complete step by step answer:
1, 3-butadiene falls under the category of conjugated dienes, the double bonds are in conjugation with each other which increases the stability of the compound. Normally it is represented as:

This is just the normal representation without any geometrical isomerisation. Normally, in case of double bonds, isomerism is determined by the atoms or groups attached to either end of the double bond, classifying it as either as cis or trans isomers or as E or Z isomers. If similar groups are on the same side of the double bond, it is cis isomer. If similar groups are attached on the opposite side of the double bond, it is trans isomer.In the case of 1, 3-butadiene, the presence of two double bonds makes the case complicated. So, instead of classifying both their double bonds only the single bond in between is considered and the isomers are named as S-cis or S-trans, where S stands for single. So, when both the double bonds are on the same side, it is names as S-cis and when they are on the opposite side, it is named S-trans. Their structures are:
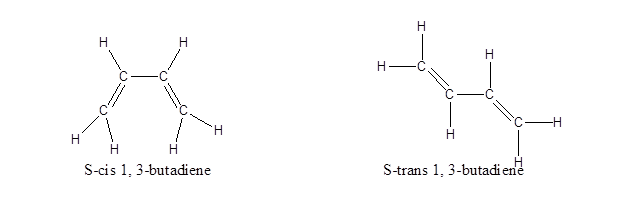
Note:
Conjugated dienes are more stable as both the double bonds are in hyper conjugation with each other which stabilises the structure, forming partial double bond character on all the three C-C bonds.


Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




