
Draw the structures of all isomeric alcohols of molecular formula ${{\text{C}}_{\text{5}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{12}}}\text{O}$ and give their IUPAC names.
Answer
601.5k+ views
Hint: There are few rules which are required to be followed in order to write the isomeric alcohols. The very first step involves the recognizing of the isomers of the compound that is mentioned in the question. Identifying the organic compounds which contain the substituents is a significant part of the process. In the answer below the rules are mentioned and at the same time the isomers of the given compound is also mentioned.
Complete step by step answer:
To determine structures of all isomeric alcohols we must need to understand how we can recognize isomers of a given compound. We know that organic compounds which contain substituents from Group C are named following the sequence of steps mentioned below:
- We must first find the longest continuous carbon chain and determine the root name for the parents in that chain. In the case of cyclic compounds, usually, the ring is considered as the parent chain unless it is attached to a chain of carbons which is longer. And hence we can get the process of ‘cyclo’ before the root name.
- We must number the chain in a direction such that the position number of the first carbon subsequent is the smallest number if the substituents in the beginning from either and have the same number then we need two numbers such that the second substituent has the smaller number
- We must determine the name and the position number of each substituent.
- We can indicate the number of identical groups by prefixes such as di, tri, tetra, etc.
- We can also place position numbers and names of the substituent groups in alphabetical order prior to the root name. Before writing in alphabetical order, we must ignore prefixes such as sec-, tert-, di-, tri-, etc. But we should include prefixes like iso and cyclo, and we must always include position number for each substituent regardless of any redundancies.
A total of 8 isomeric alcohols are possible, they are:
- $\text{pentan}-1-\text{ol}(1{}^\circ )$
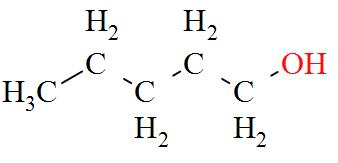
- $2-\text{Methylbutanol}(2{}^\circ )$
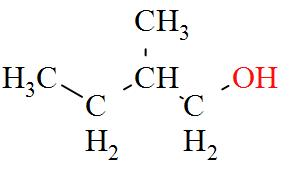
- $3-\text{methylbutan}-1-\text{ol}(1{}^\circ )$
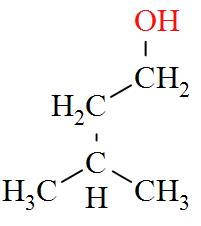
- $2,2-\text{Dimethylpropan}-1-\text{ol}(1{}^\circ )$
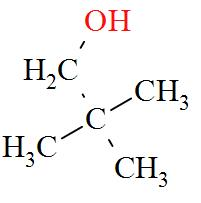
- $\text{pentan}-2-\text{ol(}1{}^\circ )$
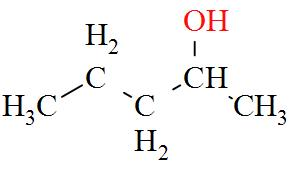
- $3-\text{methylbutan}-2-\text{ol}(2{}^\circ )$
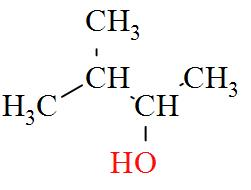
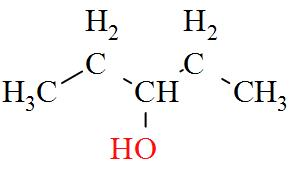
- $\text{pentan}-3-\text{ol}(3{}^\circ )$
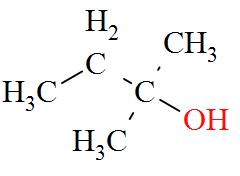
- $2-\text{methylbutan}-2-\text{ol}(3{}^\circ )$
Note: We should know that alcohols which consist of three or more carbon atoms can exhibit position isomerism. In other words for carbon atoms to which the - OH group is attached is different.
Talking about isomerism we should know that it is the phenomena in which more than one compound has the same chemical formula but different chemical structure. Chemical compounds that have identical chemical formula but different properties and arrangement of atoms in the molecule are called isomers.
Complete step by step answer:
To determine structures of all isomeric alcohols we must need to understand how we can recognize isomers of a given compound. We know that organic compounds which contain substituents from Group C are named following the sequence of steps mentioned below:
- We must first find the longest continuous carbon chain and determine the root name for the parents in that chain. In the case of cyclic compounds, usually, the ring is considered as the parent chain unless it is attached to a chain of carbons which is longer. And hence we can get the process of ‘cyclo’ before the root name.
- We must number the chain in a direction such that the position number of the first carbon subsequent is the smallest number if the substituents in the beginning from either and have the same number then we need two numbers such that the second substituent has the smaller number
- We must determine the name and the position number of each substituent.
- We can indicate the number of identical groups by prefixes such as di, tri, tetra, etc.
- We can also place position numbers and names of the substituent groups in alphabetical order prior to the root name. Before writing in alphabetical order, we must ignore prefixes such as sec-, tert-, di-, tri-, etc. But we should include prefixes like iso and cyclo, and we must always include position number for each substituent regardless of any redundancies.
A total of 8 isomeric alcohols are possible, they are:
- $\text{pentan}-1-\text{ol}(1{}^\circ )$
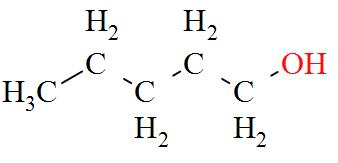
- $2-\text{Methylbutanol}(2{}^\circ )$

- $3-\text{methylbutan}-1-\text{ol}(1{}^\circ )$

- $2,2-\text{Dimethylpropan}-1-\text{ol}(1{}^\circ )$

- $\text{pentan}-2-\text{ol(}1{}^\circ )$

- $3-\text{methylbutan}-2-\text{ol}(2{}^\circ )$

- $\text{pentan}-3-\text{ol}(3{}^\circ )$

- $2-\text{methylbutan}-2-\text{ol}(3{}^\circ )$

Note: We should know that alcohols which consist of three or more carbon atoms can exhibit position isomerism. In other words for carbon atoms to which the - OH group is attached is different.
Talking about isomerism we should know that it is the phenomena in which more than one compound has the same chemical formula but different chemical structure. Chemical compounds that have identical chemical formula but different properties and arrangement of atoms in the molecule are called isomers.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




