
Draw the tetrahedral dimer structure of $AlC{{l}_{3}}$
Answer
492.6k+ views
Hint: Compounds having the formula$AlC{{l}_{3}}{{({{H}_{2}}O)}_{n}}$ (n = 0 or 6) are known as aluminium chlorides. They are made up of aluminum and chlorine atoms in a 1:3 ratio, with one form containing six hydration fluids. Both are white solids, although samples frequently contain iron(III) chloride, which gives them a yellow hue.
Complete answer:
Aluminium chloride is a chlorine-aluminum compound. The solid is covalently linked and has a low melting and boiling point. At 178 degrees Celsius, it reaches its pinnacle. Unlike more ionic halides like sodium chloride, molten$AlC{{l}_{3}}$conducts electricity weakly. It has a six-coordinate layer lattice in the solid state. The structure of$AlC{{l}_{3}}$is "$YC{{l}_{3}}$," with$A{{l}^{3+}}$ cubic tightly packed layered structure. When$AlC{{l}_{3}}$is melted, it forms the dimer\[A{{l}_{2}}C{{l}_{6}}\], which may be vaporized. This\[A{{l}_{2}}C{{l}_{6}}\]dimer dissociates into trigonal planar$AlC{{l}_{3}}$at higher temperatures.
$AlC{{l}_{3}}$ can form a dimer,\[A{{l}_{2}}C{{l}_{6}}\], because aluminium possesses empty d-orbitals that can accommodate an electron from the chlorine atom.$AlC{{l}_{3}}$ is an electron deficient (octet incomplete) combination in $A{{l}^{3+}}$, thus it acts as a Lewis acid, and Al completes it by taking an electron pair from the $C{{l}^{-}}$ atom, as indicated in the picture.
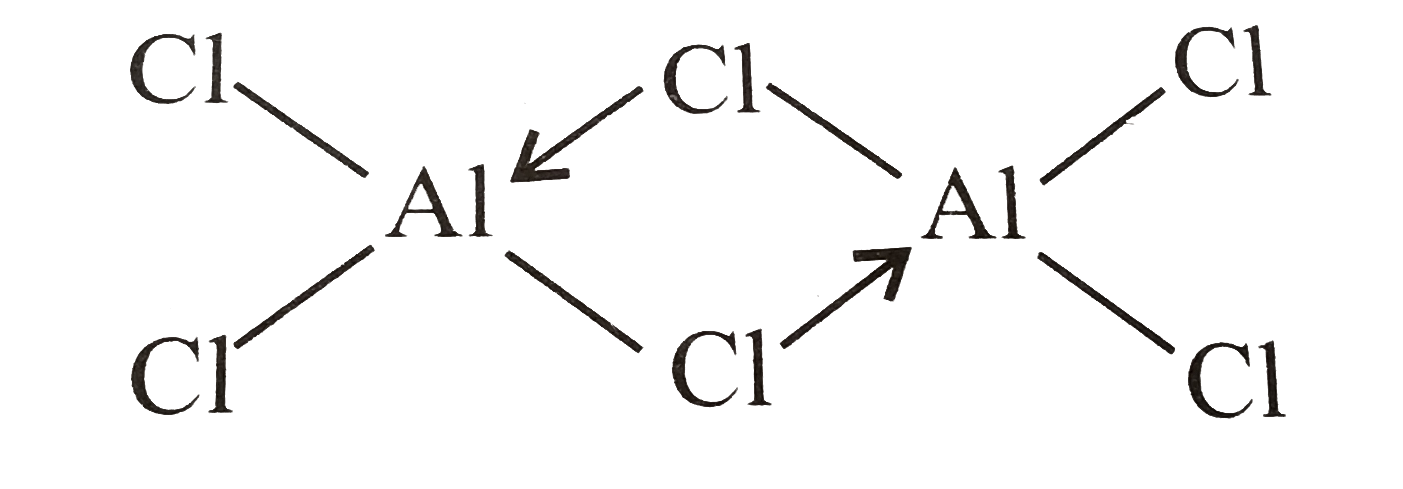
A dimer is an oligomer made up of two monomers linked by covalent or intermolecular interactions that might be strong or weak. When the two molecules are identical (e.g. A–A), the word homodimer is used, and when they are not (e.g. A–B), the term heterodimer is used. Dissociation is the polar opposite of dimerisation. Bjerrum pairs are named after Niels Bjerrum, who discovered that two oppositely charged ions may form dimers.
Note:
Aldehyde groups can be brought in or attached to aromatic series or rings using aluminum chloride. Consider the Gatterman-Koch reaction, in which the Lewis acid (aluminum chloride) is employed to extract a chloride ion from a species. It's also utilized in light molecular weight hydrocarbon polymerization and isomerization processes. Ethylbenzene synthesis and dodecylbenzene production for detergents are two common examples. Bis(arene) metal complexes can be made by mixing aluminum chloride with aluminum and arene.
Complete answer:
Aluminium chloride is a chlorine-aluminum compound. The solid is covalently linked and has a low melting and boiling point. At 178 degrees Celsius, it reaches its pinnacle. Unlike more ionic halides like sodium chloride, molten$AlC{{l}_{3}}$conducts electricity weakly. It has a six-coordinate layer lattice in the solid state. The structure of$AlC{{l}_{3}}$is "$YC{{l}_{3}}$," with$A{{l}^{3+}}$ cubic tightly packed layered structure. When$AlC{{l}_{3}}$is melted, it forms the dimer\[A{{l}_{2}}C{{l}_{6}}\], which may be vaporized. This\[A{{l}_{2}}C{{l}_{6}}\]dimer dissociates into trigonal planar$AlC{{l}_{3}}$at higher temperatures.
$AlC{{l}_{3}}$ can form a dimer,\[A{{l}_{2}}C{{l}_{6}}\], because aluminium possesses empty d-orbitals that can accommodate an electron from the chlorine atom.$AlC{{l}_{3}}$ is an electron deficient (octet incomplete) combination in $A{{l}^{3+}}$, thus it acts as a Lewis acid, and Al completes it by taking an electron pair from the $C{{l}^{-}}$ atom, as indicated in the picture.

A dimer is an oligomer made up of two monomers linked by covalent or intermolecular interactions that might be strong or weak. When the two molecules are identical (e.g. A–A), the word homodimer is used, and when they are not (e.g. A–B), the term heterodimer is used. Dissociation is the polar opposite of dimerisation. Bjerrum pairs are named after Niels Bjerrum, who discovered that two oppositely charged ions may form dimers.
Note:
Aldehyde groups can be brought in or attached to aromatic series or rings using aluminum chloride. Consider the Gatterman-Koch reaction, in which the Lewis acid (aluminum chloride) is employed to extract a chloride ion from a species. It's also utilized in light molecular weight hydrocarbon polymerization and isomerization processes. Ethylbenzene synthesis and dodecylbenzene production for detergents are two common examples. Bis(arene) metal complexes can be made by mixing aluminum chloride with aluminum and arene.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




