
Due to its sextet (having six electrons) the carbonium ions are:
(A) Unstable
(B) Very stable
(C) Negatively charged
(D) All of these
Answer
563.1k+ views
Hint: Carbocation which is also called carbonium or carbenium ion is a positively charged molecule having a planar geometry. It is a short-lived intermediate formed during the chemical reactions. It has a vacant p- orbital.
Complete step by step answer:
Carbocation has two types of ions based on their valence shell electrons.
Carbenium:
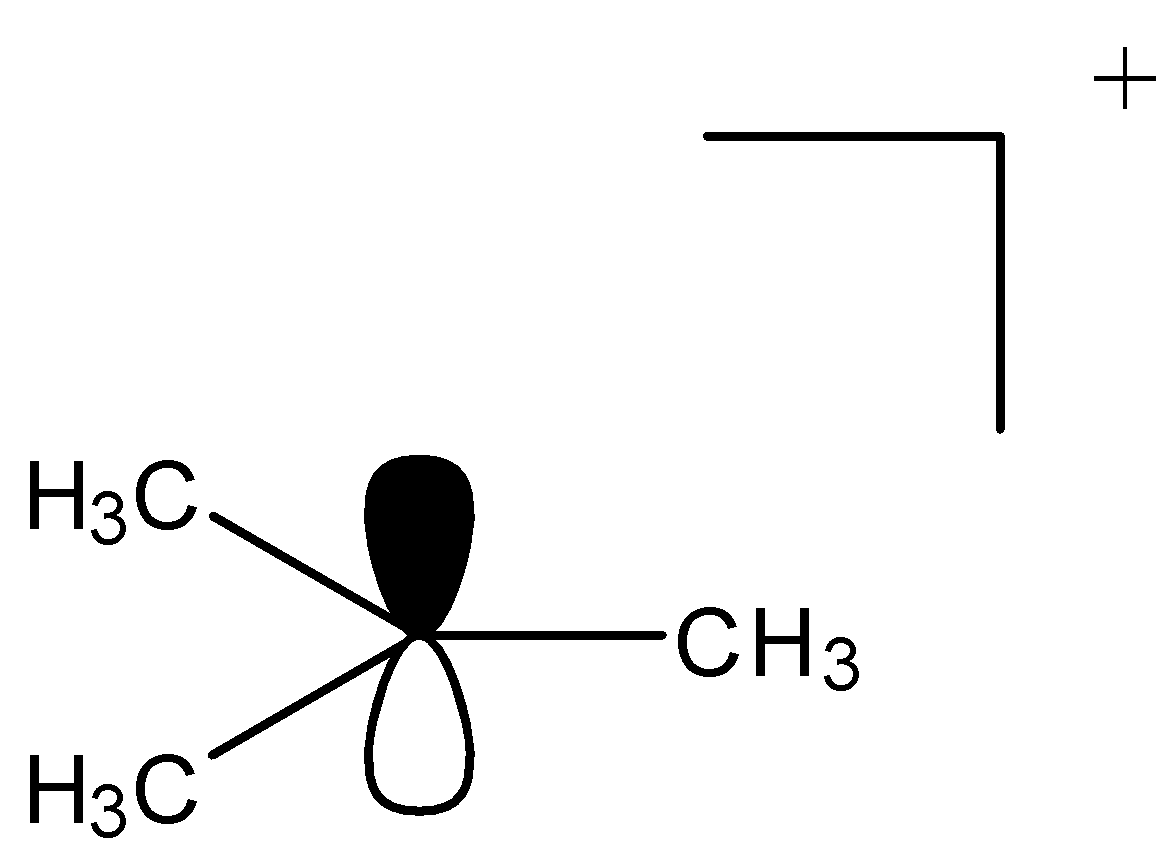
1.It contains ${\text{6}}$ electrons i.e sextet moiety.
2.Carbenium is a positively charged species.
3.It contains a ${\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{2}}}$ hybridized central carbon.
4.It contains vacant p-orbital on the central atom.
5.Carbenium ions have trivalent central carbon.
6.This is unstable structure and stability depends on substituent groups attached.
7.It has ${\text{2c - 2}}{{\text{e}}^{\text{ - }}}$ bonds for every carbon.
Carbonium:
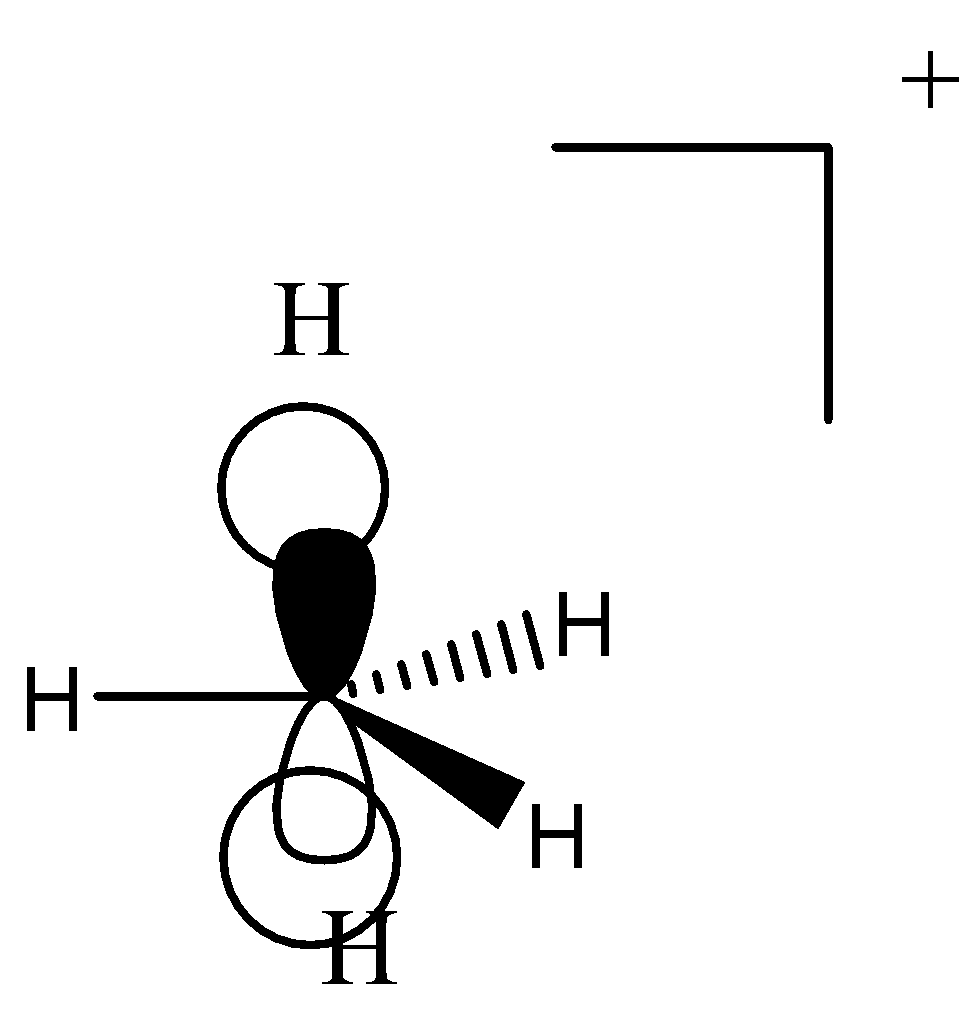

1.It contains ${\text{8}}$ electrons in this chemical moiety.
2.It is also a positively charged species.
3.It does not contain a vacant p-orbital as it is occupied by two hydrogen atoms.
4.Carbonium ions have a pentavalent central carbon.
5.It has ${\text{1 3c - 2}}{{\text{e}}^{\text{ - }}}$ bond in it.
6.It is also an unstable moiety.
Carbocations in themselves are very unstable that’s why they are the reaction intermediate for most the reaction mechanism because they will react fast and try to become stable.
Still we can increase the stability of carbocation by changing the adjacent groups to which it is attached. A tertiary carbocation having three alkyl groups around are comparably stabler than primary or secondary carbocation.
If carbonium ions have a sextet of electrons it will be very unstable.
So, the correct answer is Option A.
Additional information:
Carbocations due to being unstable are intermediate for many reactions like ${\text{S}}{{\text{N}}^{\text{1}}}$ reactions take place only when carbocation is formed. The migration of carbocation happens very frequently to attain stability like primary carbocation migrates its charge to form secondary stable carbocation.
Note: Phenyl carbocation having three phenyl rings attached to it is the most stable of carbocation present. The stability of carbocation can be altered this way by changing the nature of substituent. Electron releasing groups will increase the stability of the carbocation while electron withdrawing groups will decrease the stability of carbocation.
Complete step by step answer:
Carbocation has two types of ions based on their valence shell electrons.
Carbenium:

1.It contains ${\text{6}}$ electrons i.e sextet moiety.
2.Carbenium is a positively charged species.
3.It contains a ${\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{2}}}$ hybridized central carbon.
4.It contains vacant p-orbital on the central atom.
5.Carbenium ions have trivalent central carbon.
6.This is unstable structure and stability depends on substituent groups attached.
7.It has ${\text{2c - 2}}{{\text{e}}^{\text{ - }}}$ bonds for every carbon.
Carbonium:

1.It contains ${\text{8}}$ electrons in this chemical moiety.
2.It is also a positively charged species.
3.It does not contain a vacant p-orbital as it is occupied by two hydrogen atoms.
4.Carbonium ions have a pentavalent central carbon.
5.It has ${\text{1 3c - 2}}{{\text{e}}^{\text{ - }}}$ bond in it.
6.It is also an unstable moiety.
Carbocations in themselves are very unstable that’s why they are the reaction intermediate for most the reaction mechanism because they will react fast and try to become stable.
Still we can increase the stability of carbocation by changing the adjacent groups to which it is attached. A tertiary carbocation having three alkyl groups around are comparably stabler than primary or secondary carbocation.
If carbonium ions have a sextet of electrons it will be very unstable.
So, the correct answer is Option A.
Additional information:
Carbocations due to being unstable are intermediate for many reactions like ${\text{S}}{{\text{N}}^{\text{1}}}$ reactions take place only when carbocation is formed. The migration of carbocation happens very frequently to attain stability like primary carbocation migrates its charge to form secondary stable carbocation.
Note: Phenyl carbocation having three phenyl rings attached to it is the most stable of carbocation present. The stability of carbocation can be altered this way by changing the nature of substituent. Electron releasing groups will increase the stability of the carbocation while electron withdrawing groups will decrease the stability of carbocation.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




