
Due to the back bonding in metal carbonyls:
(A) Strength of metal-carbon bond decreases
(B) Strength of carbon-oxygen bond increases
(C) Strength of all bonds is unaffected
(D) Strength of carbon-oxygen bond decreases
Answer
570.6k+ views
Hint: Back bounding is a type of bonding that occurs between atoms in a compound in which one atom has a lone pair of electrons and the other has a vacant orbital placed adjacent to each other.
Complete step by step answer:
Synergic bonding interactions are present in metal carbonyls. The sigma bond is formed when a lone pair of electrons of carbonyl carbon is donated to a vacant orbital of metal. To form a pi bond, an electron pair is donated from filled metal d-orbital to vacant anti-bonding pi-orbitals of $CO$. This involves lateral overlap of orbitals. Due to this the electron density in the bonding pi-orbitals of $CO$ decreases and anti-bonding pi-orbitals increases. This decreases the bond order. Hence, the strength of carbon oxygen bond decreases. The strength of metal carbon bonds increases.
So, the correct answer is Option D .
Additional information:
A compound with back bonding has pi-bonding character since it results after formation of sigma bond.
Back bonding allows the molecule to stabilize as it completes its octet. Back bonding results in decrease in bond length and increase in bond order.
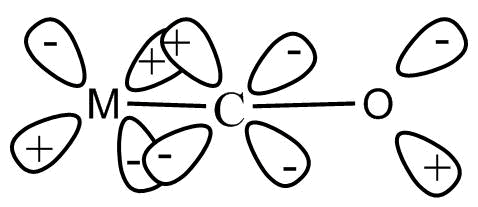
Note: Condition for back bonding is that both the atoms bonded in back bonding must be present in $2nd - 2nd$ or $2nd - 3rd$ period. One of the atoms has lone pairs and another has vacant orbital and direction of back bonding depends upon vacant orbital. The vacant orbital must have a localized donatable electron pair.
Complete step by step answer:
Synergic bonding interactions are present in metal carbonyls. The sigma bond is formed when a lone pair of electrons of carbonyl carbon is donated to a vacant orbital of metal. To form a pi bond, an electron pair is donated from filled metal d-orbital to vacant anti-bonding pi-orbitals of $CO$. This involves lateral overlap of orbitals. Due to this the electron density in the bonding pi-orbitals of $CO$ decreases and anti-bonding pi-orbitals increases. This decreases the bond order. Hence, the strength of carbon oxygen bond decreases. The strength of metal carbon bonds increases.
So, the correct answer is Option D .
Additional information:
A compound with back bonding has pi-bonding character since it results after formation of sigma bond.
Back bonding allows the molecule to stabilize as it completes its octet. Back bonding results in decrease in bond length and increase in bond order.

Note: Condition for back bonding is that both the atoms bonded in back bonding must be present in $2nd - 2nd$ or $2nd - 3rd$ period. One of the atoms has lone pairs and another has vacant orbital and direction of back bonding depends upon vacant orbital. The vacant orbital must have a localized donatable electron pair.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




