
During electrolysis of ${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}$ molar ratio of ${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}$and ${{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ produced is:
(A)2:1
(B)1:2
(C)1:1
(D)1:4
Answer
578.4k+ views
Hint: Electrolysis of water is an electrochemical process in which electric current passed into water splits up water into its constituent elements. This process is called electrolysis.
Complete answer:
Let us know the experimental principle and then work on the chemical equations in order to find out the number of moles of products formed. So the principle of electrolysis of water is when a DC power supply is given to water from a power source through metal rods called electrodes, hydrogen and oxygen gases will be liberated from water at different electrodes.
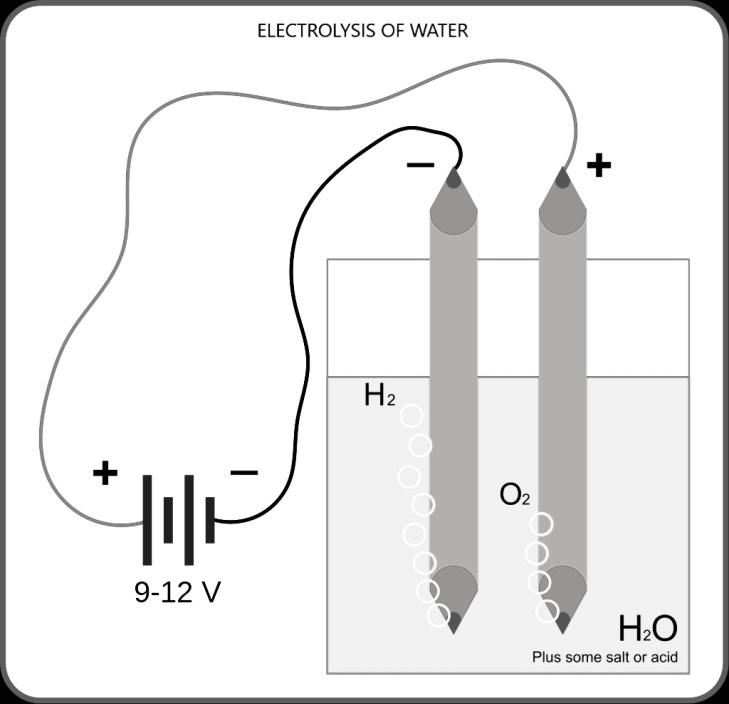
The experimental set up is, take a glass jar or a beaker with distilled water into which insert two inert metal rods, ideally platinum wires or graphite rods also can be used. Connect the rods to a battery and add some electrolyte into water such as sulphuric acid as acidic medium or an alkali for alkaline medium and note down the observations. It can be observed that bubbles of gases appear near both the electrodes. The oxygen gas separates from water and liberated at anode (+ve electrode) by oxidation reaction and hydrogen gas is liberated at cathode (-ve electrode) by reduction reaction.
The chemical reactions at both the electrodes and overall reaction is-
At anode: ${\text{2}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}} \to {{\text{O}}_2}{\text{ + 4}}{{\text{H}}^{\text{ + }}}{\text{ + 4}}{{\text{e}}^{\text{ - }}}{\kern 1pt} {\kern 1pt} {\kern 1pt} {{\text{E}}^{\text{o}}}{\text{ = + 1}}{\text{.23V}}$
At cathode: ${\text{2}}{{\text{H}}^{\text{ + }}}{\text{ + 2}}{{\text{e}}^{\text{ - }}} \to {{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\kern 1pt} {\kern 1pt} {\kern 1pt} {\kern 1pt} {{\text{E}}^{\text{o}}}{\text{ = 0}}{\text{.0V}}$
Overall reaction: ${\text{2}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\left( {\text{l}} \right)}} \to {{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}_{\left( {\text{g}} \right)}{\text{ + 2}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}_{\left( {\text{g}} \right)}{\kern 1pt} {\kern 1pt} {\kern 1pt} {\kern 1pt} {\kern 1pt} {\kern 1pt} {\kern 1pt} {\kern 1pt} {\kern 1pt} {\kern 1pt} {\kern 1pt} {\kern 1pt} {\kern 1pt} {\kern 1pt} {\kern 1pt} {\kern 1pt} {\kern 1pt} {\kern 1pt} {{\text{E}}^{\text{o}}}{\text{ = - 1}}{\text{.23V}}$
From the above equation, the number of moles of oxygen obtained from electrolysis of water is 1 and no. of moles of hydrogen is 2 respectively.
So the answer for the above question is option (A) 2:1.
Note:
The word electro denotes electric current and lysis means splitting or breakdown. This means during electrolysis of water it gets splitted up by using the energy from electricity to liberate hydrogen gas and oxygen gas.
Complete answer:
Let us know the experimental principle and then work on the chemical equations in order to find out the number of moles of products formed. So the principle of electrolysis of water is when a DC power supply is given to water from a power source through metal rods called electrodes, hydrogen and oxygen gases will be liberated from water at different electrodes.

The experimental set up is, take a glass jar or a beaker with distilled water into which insert two inert metal rods, ideally platinum wires or graphite rods also can be used. Connect the rods to a battery and add some electrolyte into water such as sulphuric acid as acidic medium or an alkali for alkaline medium and note down the observations. It can be observed that bubbles of gases appear near both the electrodes. The oxygen gas separates from water and liberated at anode (+ve electrode) by oxidation reaction and hydrogen gas is liberated at cathode (-ve electrode) by reduction reaction.
The chemical reactions at both the electrodes and overall reaction is-
At anode: ${\text{2}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}} \to {{\text{O}}_2}{\text{ + 4}}{{\text{H}}^{\text{ + }}}{\text{ + 4}}{{\text{e}}^{\text{ - }}}{\kern 1pt} {\kern 1pt} {\kern 1pt} {{\text{E}}^{\text{o}}}{\text{ = + 1}}{\text{.23V}}$
At cathode: ${\text{2}}{{\text{H}}^{\text{ + }}}{\text{ + 2}}{{\text{e}}^{\text{ - }}} \to {{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\kern 1pt} {\kern 1pt} {\kern 1pt} {\kern 1pt} {{\text{E}}^{\text{o}}}{\text{ = 0}}{\text{.0V}}$
Overall reaction: ${\text{2}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\left( {\text{l}} \right)}} \to {{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}_{\left( {\text{g}} \right)}{\text{ + 2}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}_{\left( {\text{g}} \right)}{\kern 1pt} {\kern 1pt} {\kern 1pt} {\kern 1pt} {\kern 1pt} {\kern 1pt} {\kern 1pt} {\kern 1pt} {\kern 1pt} {\kern 1pt} {\kern 1pt} {\kern 1pt} {\kern 1pt} {\kern 1pt} {\kern 1pt} {\kern 1pt} {\kern 1pt} {\kern 1pt} {{\text{E}}^{\text{o}}}{\text{ = - 1}}{\text{.23V}}$
From the above equation, the number of moles of oxygen obtained from electrolysis of water is 1 and no. of moles of hydrogen is 2 respectively.
So the answer for the above question is option (A) 2:1.
Note:
The word electro denotes electric current and lysis means splitting or breakdown. This means during electrolysis of water it gets splitted up by using the energy from electricity to liberate hydrogen gas and oxygen gas.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




