
When (E)-3-bromo-3-hexene treated with ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{{\text{O}}^ - }$ in ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{OH}}$. The product formed is:
(A) 3-hexyne
(B) 2-hexyne
(C) 2,3-hexadiene
(D) 2,4-hexadiene
Answer
571.5k+ views
Hint: To solve this we can use the Saytzeff’s rule. Saytzeff’s rule is used in the analysis of elimination reactions. The elimination reactions of alcohols and halides produce alkenes. In elimination reactions, the major product is obtained by the Saytzeff’s rule.
Complete step by step solution: We are given (E)-3-bromo-3-hexene which is treated with ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{{\text{O}}^ - }$ in ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{OH}}$. The product of this reaction is obtained by Saytzeff's rule.
According to Saytzeff’s rule, the major alkene is formed by the removal of hydrogen from a ${{\beta }}$-carbon which has a low number of substituents.
When (E)-3-bromo-3-hexene is treated with ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{{\text{O}}^ - }$ in ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{OH}}$ it undergoes dehydrobromination reaction. in the dehydrobromination reaction, a hydrogen bromide molecule is eliminated.
The reaction of (E)-3-bromo-3-hexene with ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{{\text{O}}^ - }$ in ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{OH}}$ is as follows:
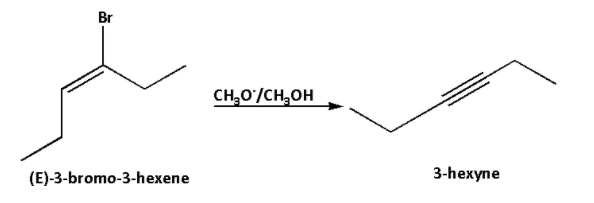
According to the Saytzeff’s rule, (E)-3-bromo-3-hexene undergoes dehydrobromination and hydrogen bromide gets eliminated fro (E)-3-bromo-3-hexene and 3-hexyne is formed as the major product.
Thus, when (E)-3-bromo-3-hexene is treated with ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{{\text{O}}^ - }$ in ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{OH}}$, the product formed is 3-hexyne.
Thus, the correct option is (A) 3-hexyne.
Note: We have solved the given reaction of (E)-3-bromo-3-hexene with ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{{\text{O}}^ - }$ in ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{OH}}$, with the help of Saytzeff’s rule. We know that Saytzeff’s rule favours the alkene with less number of hydrogen on double bonded carbon atoms. In the reaction dehydrobromination of (E)-3-bromo-3-hexene occurs. Thus, Saytzeff’s rule is applicable in this case. During an elimination reaction, a proton is removed from the carbon atom having less number of substituents. Thus when (E)-3-bromo-3-hexene is treated with ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{{\text{O}}^ - }$ in ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{OH}}$, we get 3-hexyne as a major product.
Complete step by step solution: We are given (E)-3-bromo-3-hexene which is treated with ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{{\text{O}}^ - }$ in ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{OH}}$. The product of this reaction is obtained by Saytzeff's rule.
According to Saytzeff’s rule, the major alkene is formed by the removal of hydrogen from a ${{\beta }}$-carbon which has a low number of substituents.
When (E)-3-bromo-3-hexene is treated with ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{{\text{O}}^ - }$ in ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{OH}}$ it undergoes dehydrobromination reaction. in the dehydrobromination reaction, a hydrogen bromide molecule is eliminated.
The reaction of (E)-3-bromo-3-hexene with ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{{\text{O}}^ - }$ in ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{OH}}$ is as follows:

According to the Saytzeff’s rule, (E)-3-bromo-3-hexene undergoes dehydrobromination and hydrogen bromide gets eliminated fro (E)-3-bromo-3-hexene and 3-hexyne is formed as the major product.
Thus, when (E)-3-bromo-3-hexene is treated with ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{{\text{O}}^ - }$ in ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{OH}}$, the product formed is 3-hexyne.
Thus, the correct option is (A) 3-hexyne.
Note: We have solved the given reaction of (E)-3-bromo-3-hexene with ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{{\text{O}}^ - }$ in ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{OH}}$, with the help of Saytzeff’s rule. We know that Saytzeff’s rule favours the alkene with less number of hydrogen on double bonded carbon atoms. In the reaction dehydrobromination of (E)-3-bromo-3-hexene occurs. Thus, Saytzeff’s rule is applicable in this case. During an elimination reaction, a proton is removed from the carbon atom having less number of substituents. Thus when (E)-3-bromo-3-hexene is treated with ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{{\text{O}}^ - }$ in ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{OH}}$, we get 3-hexyne as a major product.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




