
Earthworm, a friend of a farmer belongs to ………. phylum.
(a) Arthropoda
(b) Echinodermata
(c) Mollusca
(d) Annelids
Answer
585.6k+ views
Hint: The characteristic feature of the phylum that earthworm belongs to is that their body is divided into segments or metameres. Other members of this phylum include Nereis (aquatic member) and Hirudinaria (bloodsucking leech).
Complete Step by Step Answer:
Earthworms belong to the phylum Annelida. They show the organ-system level of body organization and bilateral symmetry. They are metamerically segmented, triploblastic, and coelomate. Reproduction is sexual and sexes are not separate (monoecious).
The common examples of Indian earthworms are Pheretima and Lumbricus.
Earthworms are known as ‘friends of farmers’ because they increase the fertility of the soil. Their fecal deposits known as worm castings have nitrogenous compounds that act as fertilizers for plants. They degrade organic matter into humus which is good for the quality of the soil. They live in burrows made by boring and swallowing the soil, thus making it aerated and porous. This helps in the respiration of the plant roots. This process by which earthworms increase the fertility of the soil is known as vermicomposting.
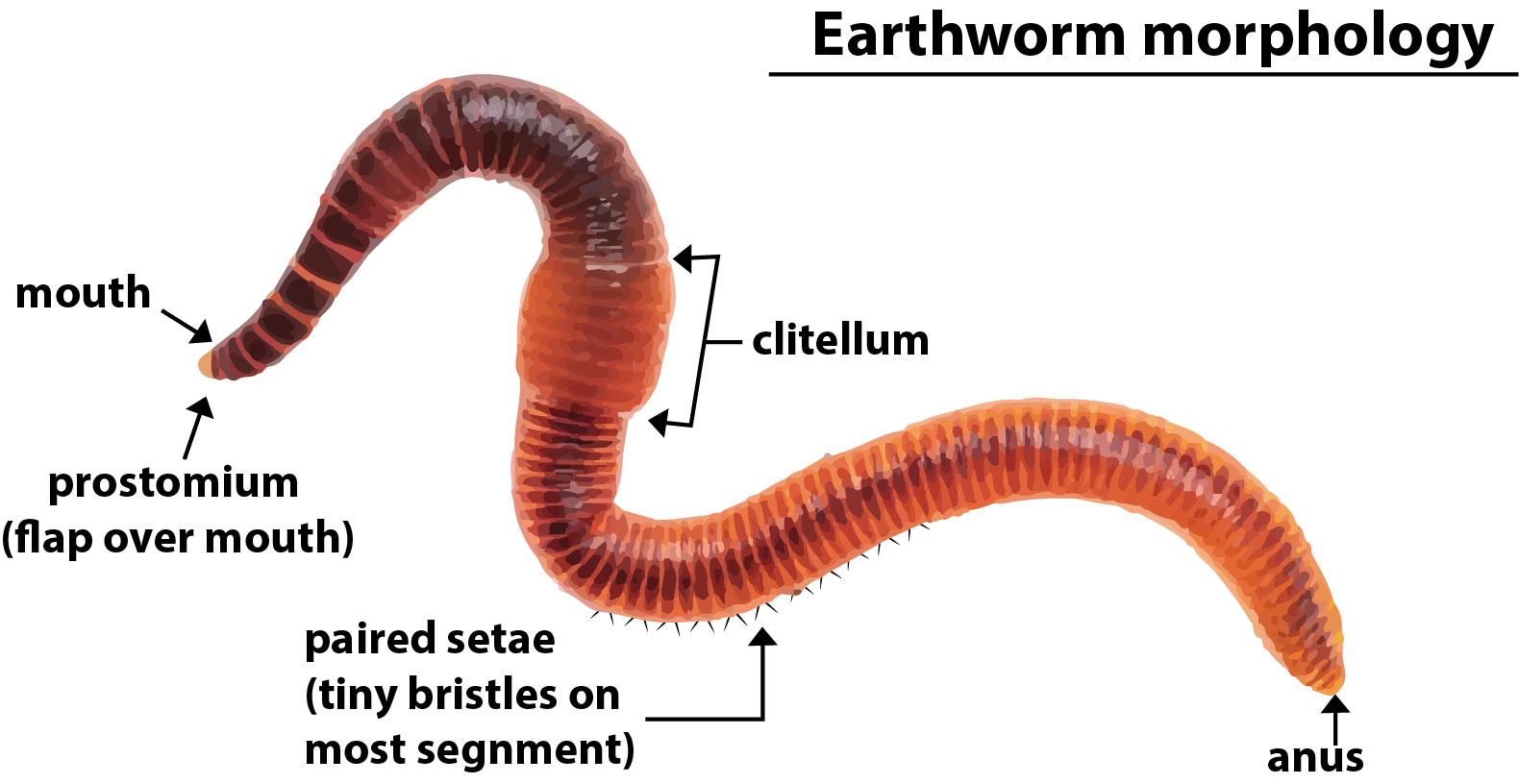
Additional information:
Let us study the other phyla mentioned in the options.
Arthropoda: It is the largest phylum of the animal kingdom and has two-thirds of all named species on Earth. They have jointed appendages hence the name Arthropoda because arthros means joint and poda means appendages.
Echinodermata: They have an endoskeleton of calcareous ossicles and hence the name Echinodermata which means spiny bodied. Their distinctive feature is the presence of a water canal system.
Mollusca: It is the second-largest animal phylum. The body of molluscs is divided into a distinct head, muscular foot, and visceral hump.
So, the correct answer is ‘Annelids’.
Note:
- In annelids, nephridia help carry out osmoregulation and excretion.
- Humus is a dark-colored amorphous substance that is highly resistant to microbial activity. Thus, it undergoes decomposition at an extremely slow rate. Due to it being colloidal in nature, it has many nutrients dissolved in it (reservoir).
- Humus is further broken down by microorganisms to release inorganic nutrients. This is known as mineralization.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
Earthworms belong to the phylum Annelida. They show the organ-system level of body organization and bilateral symmetry. They are metamerically segmented, triploblastic, and coelomate. Reproduction is sexual and sexes are not separate (monoecious).
The common examples of Indian earthworms are Pheretima and Lumbricus.
Earthworms are known as ‘friends of farmers’ because they increase the fertility of the soil. Their fecal deposits known as worm castings have nitrogenous compounds that act as fertilizers for plants. They degrade organic matter into humus which is good for the quality of the soil. They live in burrows made by boring and swallowing the soil, thus making it aerated and porous. This helps in the respiration of the plant roots. This process by which earthworms increase the fertility of the soil is known as vermicomposting.

Additional information:
Let us study the other phyla mentioned in the options.
Arthropoda: It is the largest phylum of the animal kingdom and has two-thirds of all named species on Earth. They have jointed appendages hence the name Arthropoda because arthros means joint and poda means appendages.
Echinodermata: They have an endoskeleton of calcareous ossicles and hence the name Echinodermata which means spiny bodied. Their distinctive feature is the presence of a water canal system.
Mollusca: It is the second-largest animal phylum. The body of molluscs is divided into a distinct head, muscular foot, and visceral hump.
So, the correct answer is ‘Annelids’.
Note:
- In annelids, nephridia help carry out osmoregulation and excretion.
- Humus is a dark-colored amorphous substance that is highly resistant to microbial activity. Thus, it undergoes decomposition at an extremely slow rate. Due to it being colloidal in nature, it has many nutrients dissolved in it (reservoir).
- Humus is further broken down by microorganisms to release inorganic nutrients. This is known as mineralization.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




