
What is the electronic configuration of ${{O}^{2-}}$ ion?
Answer
593.4k+ views
Hint: Write the electronic configuration of oxygen atom in its neutral state. Then add two electrons to the outermost orbital of the configuration.
Complete answer:
For writing the electronic configuration of any element, we have to know its atomic number. The atomic number of an element is the number of protons present inside the nucleus of its atom or the number of electrons present inside a neutral atom of that element.
On the periodic table, the element oxygen occupies the position at the crossing of the second period and sixteenth group. The atomic number of oxygen is “$8$”. So, its electronic configuration is as below:
\[1{{s}^{2}}2{{s}^{2}}2{{p}^{4}}\]
The orbital arrangement of electrons for the above configuration is shown below:
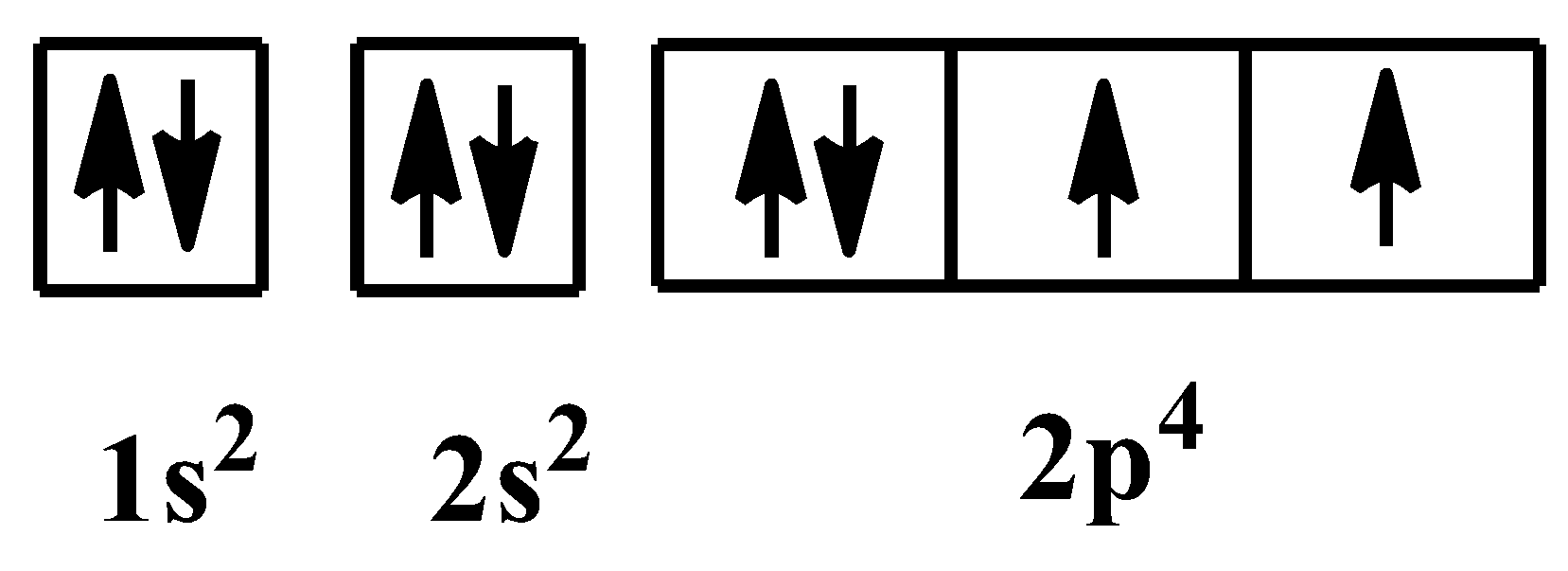
As you can see, there are two unpaired electrons in the valence subshell of the oxygen element. In${{O}^{2-}}$ion, there are two extra electrons which means, the unpaired electrons are paired now. So the electronic configuration becomes:
\[1{{s}^{2}}2{{s}^{2}}2{{p}^{6}}\]
This is the electronic configuration of neon, which is a noble gas. The orbital arrangement for the above configuration is as shown below:
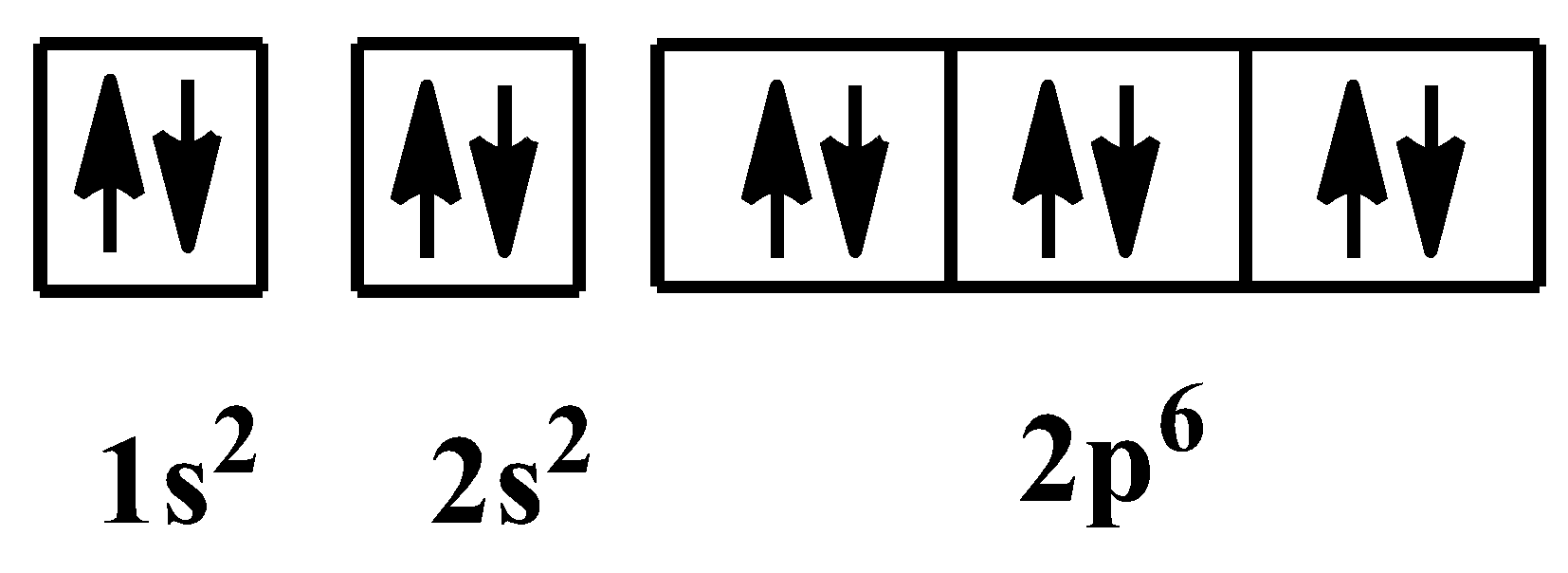
Additional Information:
- Oxygen is the second most electronegative element in the periodic table after fluorine.
- The oxygen element is relatively stable in its anionic state than other elements because of its higher electronegativity and small size.
- The small size of oxygen is due to its position in the periodic table. As you know, the size of an atom increases as we go down the group and across a period.
Note: Fluorine is more stable than oxygen in its anionic state because it is the most electronegative element in the whole periodic table.
Even if more electronegative elements are quite stable in their anionic forms, they cannot exist for much time if they are not supported by external agents. An example of such an external agent is water. The water molecules dissociate and surround these anions to stabilise the excess negative charge.
Complete answer:
For writing the electronic configuration of any element, we have to know its atomic number. The atomic number of an element is the number of protons present inside the nucleus of its atom or the number of electrons present inside a neutral atom of that element.
On the periodic table, the element oxygen occupies the position at the crossing of the second period and sixteenth group. The atomic number of oxygen is “$8$”. So, its electronic configuration is as below:
\[1{{s}^{2}}2{{s}^{2}}2{{p}^{4}}\]
The orbital arrangement of electrons for the above configuration is shown below:

As you can see, there are two unpaired electrons in the valence subshell of the oxygen element. In${{O}^{2-}}$ion, there are two extra electrons which means, the unpaired electrons are paired now. So the electronic configuration becomes:
\[1{{s}^{2}}2{{s}^{2}}2{{p}^{6}}\]
This is the electronic configuration of neon, which is a noble gas. The orbital arrangement for the above configuration is as shown below:

Additional Information:
- Oxygen is the second most electronegative element in the periodic table after fluorine.
- The oxygen element is relatively stable in its anionic state than other elements because of its higher electronegativity and small size.
- The small size of oxygen is due to its position in the periodic table. As you know, the size of an atom increases as we go down the group and across a period.
Note: Fluorine is more stable than oxygen in its anionic state because it is the most electronegative element in the whole periodic table.
Even if more electronegative elements are quite stable in their anionic forms, they cannot exist for much time if they are not supported by external agents. An example of such an external agent is water. The water molecules dissociate and surround these anions to stabilise the excess negative charge.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




